National AIDS Control Programme | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The National AIDS Control Programme was initiated in India in 1987.
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare established the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) as a dedicated wing to implement and closely monitor various aspects of the program.
Objective: The primary objective of the program is to prevent further transmission of HIV, reduce morbidity and mortality associated with HIV infection, and minimize the socio-economic impact resulting from HIV infection.
Milestones:
- 1986: First case of HIV detected; AIDS Task Force established by the JCMR; National AIDS Committee formed under the Ministry of Health.
- 1990: Medium Term Plan launched for four states and the four metros.
- 1992: NACP-1 launched to slow down the spread of HIV infection; National AIDS Control Board constituted; NACO established.
- 1999: NACP-II begins, focusing on behavior change, increased decentralization, and NGO involvement; State AIDS Control Societies established.
- 2002: Adoption of National AIDS Control Policy and National Blood Policy.
- 2004: Initiation of anti-retroviral treatment.
- 2006: Constitution of the National Council on AIDS under the chairmanship of the Prime Minister; Formulation of the National Policy on Paediatric ART.
- 2007: Launch of NACP-III for a five-year period (2007-2012).
- 2014: Launch of NACP-IV for five years (2012-2017).
- 2017: Formulation of the National Strategic Plan for HIV/AIDS and STIs (2017-2024); Enactment of the HIV and AIDS ACT 2017.
National Strategic Plan for HIV/AIDS and STIs 2017-24 (Forging a Path Towards an Aids-Free India)
Key Highlights:
- India is dedicated to eradicating the AIDS epidemic as a public health threat by 2030, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
- Embrace of the 'Fast-Track' targets, including achieving the 90-90-90 targets by 2020.
- Implementation of the 'test and treat' policy, extending treatment to all individuals testing positive for HIV, regardless of their CD4 count.
- Emphasis on eliminating mother-to-child transmission of HIV and Syphilis by 2020. The Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan facilitates a nationwide initiative, encompassing both public and private sectors, to provide comprehensive antenatal care, including HIV testing, to all pregnant women.
- Enactment of the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Bill, 2017, establishing the legal framework for the Government's commitments, including the elimination of stigma and discrimination against individuals affected by HIV.

Fast-Track Targets
By 2020, the primary focus of the national program will be to accomplish the following fast-track targets:
- Achieve a 75% reduction in new HIV infections.
- Attain the 90-90-90 goals: Ensure that 90% of individuals who are HIV positive in the country are aware of their status, 90% of those aware are on treatment, and 90% of those on treatment achieve effective viral load suppression.
- Eliminate mother-to-child transmission of HIV and Syphilis.
- Eradicate stigma and discrimination.
By 2024, the envisioned further achievements include:
- Attain an 80% reduction in new HIV infections.
- Ensure that 95% of individuals who are HIV positive in the country are aware of their status, with 95% of those aware on treatment and 95% of those on treatment achieving effective viral load suppression.
National AIDS Control Programme
Interventions Planned for Achievement of 90-90-90 by 2020




The broad strategies for prevention, testing and treatment are summarised in the figure below.

The HIV and AIDS ACT 2017
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017
"Legislation aimed at preventing and controlling the spread of Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome, safeguarding the human rights of individuals affected by the virus and syndrome, and addressing related matters or issues."
Key Highlights
- Prevention of discrimination - Chapter II, clause c: Prohibition of denial or discontinuation of, and unfair treatment in, healthcare services. Chapter II, clause L: Prohibition of HIV testing as a prerequisite for obtaining employment, accessing healthcare services, education, or for the continuation of the same, or accessing or using any other service or facility.
- Implementation of medically recommended safeguards and precautions to minimize the risk of infection shall not be considered as discrimination.
Significant risk and Significant risk body substances
"Significant-risk" is defined as:
(a) the presence of body substances associated with significant risk,
(b) a circumstance that poses a significant risk of transmitting or contracting HIV infection, or
(c) the presence of an infectious source and an uninfected person.
"Significant-risk body substances" include blood, blood products, semen, vaginal secretions, breast milk, tissue, and specific body fluids such as cerebrospinal, amniotic, peritoneal, synovial, pericardial, and pleural fluids.

Prohibition of Act
HIV testing cannot be a prerequisite for employment, accessing healthcare services, education, or for the continuation of the same, or for accessing or using any other service or facility.
Informed Consent
No HIV test shall be conducted on any person or a protected person subjected to medical treatment, medical interventions, or research, except with the informed consent of the individual or their representative, as specified in the guidelines. Informed consent for the disclosure of HIV-related information is not required in cases where the disclosure is made by:
(a) a healthcare provider to another healthcare provider involved in the care, treatment, or counseling of the person, when necessary for providing care or treatment; or
(b) by an order of a court that deems the disclosure necessary in the interest of justice for determining issues before it.
Confidentiality
Every establishment maintaining records of HIV-related information for protected persons must adopt data protection measures following guidelines to ensure that such information is safeguarded from disclosure.
Right of Residency
Every protected person has the right to reside in the shared household, the right not to be excluded from the shared household or any part of it, and the right to enjoy and use the facilities of such shared household in a non-discriminatory manner.
Penalties
- Penalty for breach of confidentiality - punishable with a fine that may extend to one lakh rupees.
- Penalty for contravention - imprisonment for a term not less than three months but may extend to two years, and a fine that may extend to one lakh rupees, or both.
Key features of this Act include:
- Prohibition of HIV testing as a prerequisite for employment or accessing healthcare.
- Affirmation of the right of every HIV-infected or affected person below 18 to reside in a shared household and enjoy household facilities.
- Provision for the appointment of an ombudsman by State/UT Governments to address grievances and ensure compliance with the Act, with penalties for non-compliance.
- Creation of an environment to enhance access to healthcare services, ensuring informed consent and confidentiality for HIV-related testing, treatment, and clinical research. The Act stipulates penal action against any healthcare provider, excluding physicians or counselors, who discloses the HIV-positive status of a person to their partner.
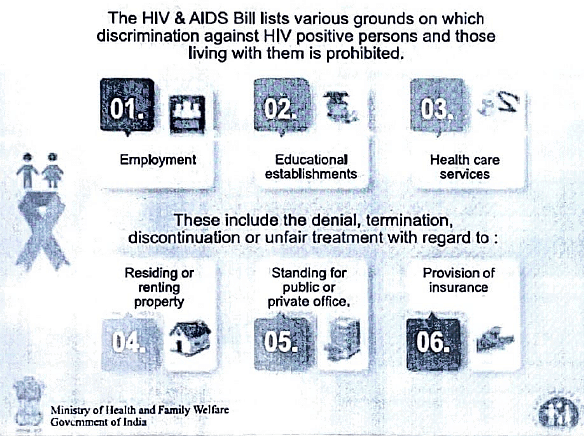
- Identification of specific grounds on which discrimination against people living with HIV is prohibited, including employment, educational establishments, healthcare services, residence or property rental, standing for public or private office, and provision of insurance.
ICTC (Integrated counselling and Testing centers)
Note: Under the NACP-III, VCTC and PPTCT were consolidated into a single entity known as ICTC in 2006.
An Integrated Counselling and Testing Center (ICTC) is a facility where individuals voluntarily undergo counseling and testing for HIV, either on their own accord or as recommended by a healthcare professional. The primary functions of an ICTC include:
- Administering HIV diagnostic tests.
- Offering essential information on HIV transmission modes and advocating behavioral changes to minimize vulnerability.
- Connecting individuals with additional HIV prevention, care, and treatment services.
As of August 31, 2016, India had 20,756 ICTCs, predominantly situated in government hospitals.
It is not within the scope of an ICTC to counsel and test the entire general population. Instead, the focus is on specific subpopulations exhibiting greater vulnerability, engaging in high-risk behavior, or having elevated HIV prevalence rates.
High-Risk Groups:
- Sex workers and their clients
- Men who have sex with men (MSM)
- Transgender individuals
- Injecting drug users (IDUs)
- Truckers
- Migrant workers
- Spouses and children of individuals engaging in risky behavior
Two distinct types of ICTCs exist: Fixed types (standalone and facility-integrated) and mobile types. Individuals seeking counseling and testing services can access accurate information about HIV prevention and care while undergoing an HIV test in a supportive and confidential environment. Those testing negative receive information and counseling to mitigate risks and maintain HIV-negative status, while those testing positive are provided with psychosocial support and connected to treatment and care.
The fundamental components of PPTCT services in India include the following:
Regularly offering HIV counseling and testing to all pregnant women enrolled in antenatal care, with an 'opt-out' choice.
Ensuring the participation of spouses and other family members, transitioning from an "ANC-Centric" to a "Family-Centric" approach.
Providing lifelong ART (TDF+3TC+EFV) to all pregnant and breastfeeding HIV-infected women, irrespective of CD4 count and clinical HIV progression stage.
Advocating for institutional deliveries for all HIV-infected pregnant women.
Offering care for associated conditions (STI/RTI, TB, and other opportunistic infections).
Providing nutrition, counseling, and psychosocial support for HIV-infected pregnant women.
Offering counseling and support for initiating exclusive breastfeeding within an hour of delivery as the preferred option, continuing for 6 months.
Providing ARV prophylaxis to infants from birth up to a minimum of 6 months.
Integrating follow-up for HIV-exposed infants into routine healthcare services, including immunization.
Ensuring the initiation of Co-trimoxazole Prophylactic Therapy (CPT) and Early Infant Diagnosis (EID) using HIV-DNA PCR at 6 weeks of age onwards, following EID guidelines.
Reinforcing community follow-up and outreach through local community networks to assist HIV-positive pregnant women and their families.

- PITC (Provider-Initiated HIV Testing and Counseling)
- DR-TB (Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis)
- PLHIV (People Living with HIV)
- ICF (Intensified TB Case Finding) activities
- ART (Anti-Retroviral Therapy)
- LAC (Link ART Centers)
- TI (Targeted Interventions)
STD Control programme
STI vs RTI
- Sexually transmitted and reproductive tract infections encompass interconnected categories.
- Sexually transmitted denotes the mode of transmission, while reproductive tract pertains to the site of infection.
- Not all sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are reproductive tract infections (RTIs), and vice versa.
- HIV is classified as an STI, but its impact is not confined solely to the reproductive tract.
Controlling STDs is interconnected with HIV/AIDS control since the behaviors leading to the transmission of both STDs and HIV are similar. HIV transmission is more facilitated when there is a concurrent presence of another STD.
The following approach is adopted for the STD control:
(a) The syndromic approach is employed in the management of STDs, involving the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases based on specific symptoms and signs without reliance on laboratory investigations.
(b) Despite being highly prevalent among women, STDs are often concealed due to the social stigma associated with the disease. Therefore, a decision has been made to integrate services for treating reproductive tract infections (RTIs) and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) at all levels of healthcare.
(c) Strengthening STDs clinics in district hospitals, medical colleges, and other centers will involve providing technical support, equipment, reagents, and drugs.
(d) An extensive orientation and training program will be implemented to educate all medical and paramedical workers involved in delivering STDs/RTIs services through a syndromic approach.
(e) STDs clinics will not only offer treatment but also provide counseling services and distribute high-quality condoms to STD patients.
NACO has branded the STI/RTI services as "Suraksha Clinic" and has developed a communication strategy to generate demand for these services.
Pre-Packed STI/RTI Colour Coded KITS
Pre-packaged, color-coded STI/RTI kits are distributed free of charge to all designated STI/RTI clinics. These kits are centrally procured and supplied to all State AIDS Control Societies, each assigned a specific color code:
- Kit 1 - Grey: Designed for urethral discharge, anorectal discharge, and cervicitis.
- Kit 2 - Green: Intended for vaginitis.
- Kit 3 - White: Allocated for the treatment of genital ulcers.
- Kit 4 - Blue: Specifically designated for genital ulcers.
- Kit 5 - Red: Allocated for the management of genital ulcers.
- Kit 6 - Yellow: Designed for addressing lower abdominal pain.
- Kit 7 - Black: Intended for the treatment of scrotal swelling.


IEC (Information, Education and Communication)
Effective communication plays a crucial role in raising awareness about prevention and encouraging access to testing, treatment, care, and support. The communication efforts are aimed at:
- Enhancing knowledge among the general population, with a particular focus on youth and women, regarding safe sexual behavior.
- Maintaining behavior change in high-risk groups and bridge populations.
- Creating a demand for care, support, and treatment services.
- Facilitating adjustments to societal norms that promote positive attitudes, beliefs, and practices, ultimately reducing stigma and discrimination.
Adolescence Education Programme: Implemented in secondary and senior secondary schools, this initiative aims to enhance the life skills of adolescents, enabling them to navigate the physical and psychological changes associated with adolescence. The program schedules 16-hour sessions during the academic terms of classes IX and XI.
Red Ribbon Clubs: Formed in colleges, Red Ribbon Clubs aim to facilitate peer-to-peer messaging on HIV prevention and provide a secure environment for young people to address their questions and dispel myths related to HIV/AIDS. Additionally, these clubs actively promote voluntary blood donation among the youth.
Out of School Youth (OSY): Targeting youth who have either discontinued their education or have never attended school, the OSY program collaborates nationally with the NIOS to reach adolescents who are not enrolled in formal education.
Advocacy Communication and Social Mobilization (ACSM) is the updated term used in the national strategic plan for HIV/AIDS and HIV 2017-2024, replacing the previous designation of Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) programs.
Health programs-Repeats
STDs/HIV-AIDS
- Describe the functions of VCTC and PPTCT programme (2004).
- Discuss the role of Information, Education and Communication (IEC) systems in the management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs). (2013)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on National AIDS Control Programme - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the National AIDS Control Programme? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the HIV and AIDS ACT 2017? |  |
| 3. What are ICTCs and their role in HIV/AIDS control? |  |
| 4. What is the STD Control Programme and how does it relate to HIV/AIDS? |  |
| 5. What is IEC in the context of the National AIDS Control Programme? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















