Metal π-Complexes and Metal Clusters | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| General methods of preparation of metal cluster compounds |

|
| Reactions of metal cluster compounds |

|
| Summary |

|
Introduction
Metal-metal bond is a bond between two metal centers, particularly between two transition metal atoms, which ranges from a single to a quadruple bond. The existence of metal-metal bond in transition metals is mainly due to the of presence of (n+1)s, (n+1)p and nd orbitals as valence shell electronic configuration. The transition metals can form three general types of bonds such as covalent bonds, dative bonds and weak metal-metal symmetry interactions where covalent bonds being the strongest and symmetry interactions are the weakest.
The compounds containing a large number of metal-metal bonds forming triangular and larger structures are called cluster compounds, however these also include linear M-M bonds. The metal clusters can also be defined as any entity that contains a metal-metal bond. The journey started with the identification of the Hg-Hg in the Hg22+ ion (Hg2Cl2) which was the first d-block metal-metal bonded species. Most of these cluster compounds are homo-metallic; however there are few exceptions with hetero-metallic cluster complexes. The molecular complexes containing metal-metal bonds that form triangular or larger structures are called as metal clusters, however the linear metal-metal bonds also come under the category of metal clusters. Therefore, any metal complex having a bond between two metal ions is called a metal cluster. Some examples are shown as i to vi below: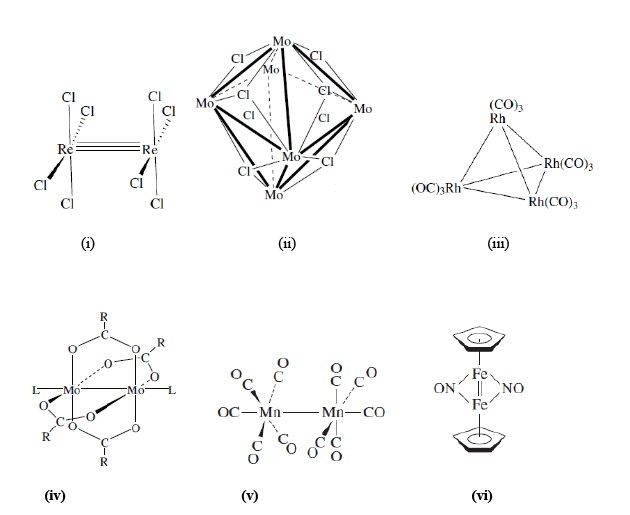
General methods of preparation of metal cluster compounds
Initially, metal complex clusters were either obtained as side products in other reactions or by unplanned routes. Eventually, the efficient synthetic methodologies were developed to prepare a variety of cluster complexes containing various types of bonds. Later on, specific methods were also developed for the synthesis of hetero-metallic metal-metal bonds and to build up cluster complexes. Now, well-defined and highly efficient methods are known for synthesis of desirable metal-metal bond for specific application.
Some of the methods are given below:
- By pyrolysis of metal carbonyl complexes: This method is mainly applied to metal carbonyls where the lower carbonyl complexes are heated to expel few but not all carbon monoxide molecules. The unsaturated fragments thus formed can rearrange and react to form higher metal carbonyl complexes containing metal-metal bonds.
 In some cases, these reactions can also be done by photolysis of lower metal carbonyls.
In some cases, these reactions can also be done by photolysis of lower metal carbonyls.
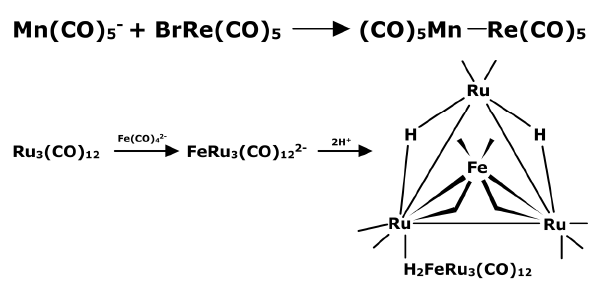
- By nucleophilic attack of a metal carbonyl anion: A metal carbonyl anion such as pentacarbonylmanganese(I) anion can show a nucleophilic substitution reaction with bromopentacarbonylrhenium(I) which possesses a replaceable bromide. The reaction results in the formation of a Mn-Re covalent bond.

- Binuclear reductive elimination: Reductive elimination takes place at metal centers with higher oxidation states where the oxidation state of the metal ion undergoing reaction is reduced by two units in the product. The reductive elimination is the reverse of oxidative addition and decreases both the oxidation state and the coordination number by two.
 By addition of a coordinatively saturated cluster to an unsaturated cluster via a bridging group. In this method, hydride is used to link the coordinatively saturated species to the unsaturated cluster.
By addition of a coordinatively saturated cluster to an unsaturated cluster via a bridging group. In this method, hydride is used to link the coordinatively saturated species to the unsaturated cluster.
- By the addition of a M-C multiple bond to a metal complex. This method was developed on the basis of isolobal analogy. The M=C double bond which is metal carbine, is isolobal with the C=C double bond, hence those metals that are able to form alkene complexes can also be expected to form complexes with metal carbenes.

- By the addition of metal to a metal-metal multiple bond. This method was developed by Green and coworkers and was based on the isolobal analogy between the M=M multiple bond and an alkene. Like the addition reactions shown by alkenes, metal-metal multiple bond (M=M) can also display addition reaction with other metal precursors.

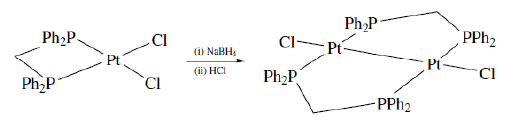
- By using bridging ligand. Few chelating ligands such as common diphosphines (Ph2PCH2PPh2) has the ability to either act as a chelating ligand to bind one metal ion or to act as bidentate ligand to coordinate with two metal ions. This is due to the geometric factors of the ligand which allows different chelate ring sizes in the two cases. A large number of other chelating ligands display the ability to behave both as chelating ligand and bidentate ligands.

- Main group elements have also been utilized for metal cluster formation or
expansion.

Reactions of metal cluster compounds
Reaction of metal clusters
Metal cluster display a large variety of chemical reactions and hence exhibit rich and unusual organometallic chemistry. It is however, difficult to predict the outcome of the reactions and to rationalize a reaction pathway. Reaction on the metal clusters containing multiple metal-metal bonds often takes place at the multiple bonds.
The metal clusters containing M-M single bonds display variety of reactions which are discussed below:
- Reactions with electrophiles: The proton (H+) can be considered as the simplest electrophile because it is a zeroelectron species and smallest in size. Therefore, it can undergo addition reactions with a variety of compounds with great ease. The binding of proton to a metal cluster is expected to take place without much change in the cluster geometry. It can be easily inferred that the anionic clusters are preferentially easier to protonate and these often result in hydride complexes where a hydride is bridging two or more metal ions. For example, the Re-carbonyl trinuclear cluster can undergo sequential protonation to form a tri-hydride cluster where the parent structure of the tri-nuclear cluster remained largely unchanged and the rhenium ion are bridged by three hydride bridges connecting two rhenium ions each.
 Bulkier electrophiles, on the other, are hesitant to act as bridging species and often display reactions at carbonyl ligands in a reaction with metal carbonyl cluster. For example, the reaction of Ru3(CO)12 with alkylaluminium compounds (AlR3) resulted in the conversion of Ru3(CO)12 from a normal CO-unbridged structure to a bridged Ru3(μ-COAlR3)CO)10.
Bulkier electrophiles, on the other, are hesitant to act as bridging species and often display reactions at carbonyl ligands in a reaction with metal carbonyl cluster. For example, the reaction of Ru3(CO)12 with alkylaluminium compounds (AlR3) resulted in the conversion of Ru3(CO)12 from a normal CO-unbridged structure to a bridged Ru3(μ-COAlR3)CO)10.

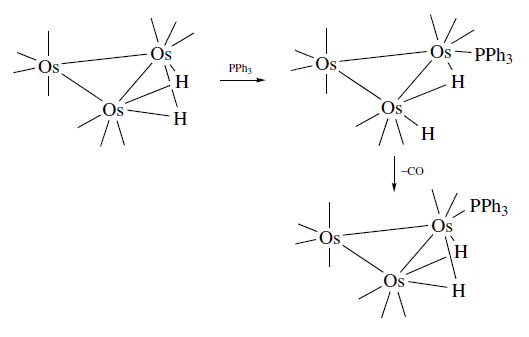
- Reactions with nucleophiles: Addition of nucleophiles adds two electrons to the metal cluster. Addition of two electrons to the metal cluster must either rearrange or loose a two electron ligand. On addition of a nucleophile, the unsaturated cluster (μ2-H)2Os3(CO)10 does not lose a ligand and one of the M-H-M bridges opens up and generates a vacant site. For example, CO and PPh3 adds to give a product (μ2-H)HOs3(CO)11 where one of the two M-H-M bridges opened up and the hydride became terminal. The Os=Os turned into a Os-Os maintaining the applicability of the EAN rule on the metal complex. There is always a possibility of cluster fragmentation into various substituents. For example, Ru3(CO)12 gives a variety of products such as Ru3(CO)9L3, Ru (CO)3L2 and Ru (CO)4L as substitution products on reaction with PPh3.
 Nucleophiles can also attack the coordinated ligands. A metala-amide is formed on reaction of amines with Os3(CO)12. It can labilize the coordinated COs in the metal complex by bridging.
Nucleophiles can also attack the coordinated ligands. A metala-amide is formed on reaction of amines with Os3(CO)12. It can labilize the coordinated COs in the metal complex by bridging.
- Oxidative addition: Oxidative addition is the reaction that adds two electrons to the cluster on reaction. In carbonyl clusters, the loss of one carbonyl is required to keep the cluster structure intact. Oxidative addition reactions take place with different mechanisms with different ligands. For example, the addition of Cl2 to the Os3(CO)12 cluster does not require prior dissociation of any of the carbonyls. The Cl2 oxidizes the cluster by taking two electrons from one of the metal-metal bonds which causes the breaking of cyclic metal-metal ring and leads to a linear cluster with only two M‒M bonds.

- Reactions on metal-metal multiple bond: Like carbon-carbon multiple bonds, metal-metal multiple bonds are centers of reaction. However, metal-metal multiple bonds display variety of chemical and unexpected products as compared with carbon-carbon multiple bonds. For example, HI can add to the Mo-Mo multiple bond where both H and I are bridging the metal atoms. Such type of a product formation with a carbon-carbon multiple bond is most unlikely.
 Large and hetero-metallic metal cluster can also be formed by similar reactions on metalmeal multiple bonds with appropriate metal precursor complexes. For example, the Pt(PPh3)4 can add to the Mo-Mo triple bonds with the loss of two triphenylphosphine units, resulting in a three metal cluster.
Large and hetero-metallic metal cluster can also be formed by similar reactions on metalmeal multiple bonds with appropriate metal precursor complexes. For example, the Pt(PPh3)4 can add to the Mo-Mo triple bonds with the loss of two triphenylphosphine units, resulting in a three metal cluster. Cluster compounds can also show catalytic activity with a variety of molecules. For example, one of the major objectives of cluster carbonyl chemistry is to activate the carbon monoxide and to facilitate its addition to various alkane or alkene.
Cluster compounds can also show catalytic activity with a variety of molecules. For example, one of the major objectives of cluster carbonyl chemistry is to activate the carbon monoxide and to facilitate its addition to various alkane or alkene.
Summary
- Cluster compounds contain metal-metal single or multiple bonds and form rings or linear chains. Apart from containing σ and π bonds, cluster complexes also display δ bonds.
- Cluster compounds are formed by almost all the metal atoms, metal clusters consisting of transition metals are known in large numbers. These metal-metal bonds containing complexes can be homo-nuclear, i.e. consisting of one type of metal atoms, and hetero-nuclear which consist of two or more types of metal atoms.
- Cluster complexes can be synthesized by various methods such as pyrolysis of carbonyl clusters, nucleophilic attack on clusters, reductive elimination and attack of metal precursors on multiple bond containing clusters.
- Cluster compounds display a variety of reactions. The products of these reactions are sometimes unexpected.
- The types of reactions that cluster complexes undergo are reactions with electrophiles and nucleophiles, oxidative addition reactions and reactions on the metal-metal multiple bonds.
FAQs on Metal π-Complexes and Metal Clusters - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are metal cluster compounds? |  |
| 2. What are the general methods used to prepare metal cluster compounds? |  |
| 3. What are some common reactions of metal cluster compounds? |  |
| 4. What are metal π-complexes? |  |
| 5. How are metal clusters and metal π-complexes different? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
 In some cases, these reactions can also be done by photolysis of lower metal carbonyls.
In some cases, these reactions can also be done by photolysis of lower metal carbonyls.
 By addition of a coordinatively saturated cluster to an unsaturated cluster via a bridging group. In this method, hydride is used to link the coordinatively saturated species to the unsaturated cluster.
By addition of a coordinatively saturated cluster to an unsaturated cluster via a bridging group. In this method, hydride is used to link the coordinatively saturated species to the unsaturated cluster.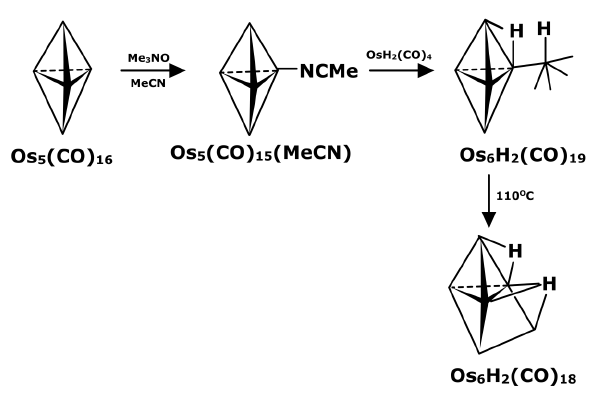


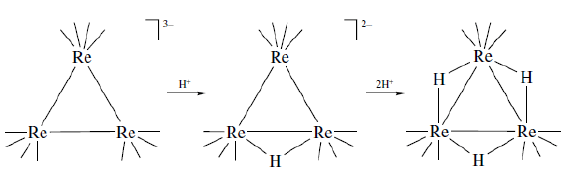 Bulkier electrophiles, on the other, are hesitant to act as bridging species and often display reactions at carbonyl ligands in a reaction with metal carbonyl cluster. For example, the reaction of Ru3(CO)12 with alkylaluminium compounds (AlR3) resulted in the conversion of Ru3(CO)12 from a normal CO-unbridged structure to a bridged Ru3(μ-COAlR3)CO)10.
Bulkier electrophiles, on the other, are hesitant to act as bridging species and often display reactions at carbonyl ligands in a reaction with metal carbonyl cluster. For example, the reaction of Ru3(CO)12 with alkylaluminium compounds (AlR3) resulted in the conversion of Ru3(CO)12 from a normal CO-unbridged structure to a bridged Ru3(μ-COAlR3)CO)10.

 Nucleophiles can also attack the coordinated ligands. A metala-amide is formed on reaction of amines with Os3(CO)12. It can labilize the coordinated COs in the metal complex by bridging.
Nucleophiles can also attack the coordinated ligands. A metala-amide is formed on reaction of amines with Os3(CO)12. It can labilize the coordinated COs in the metal complex by bridging.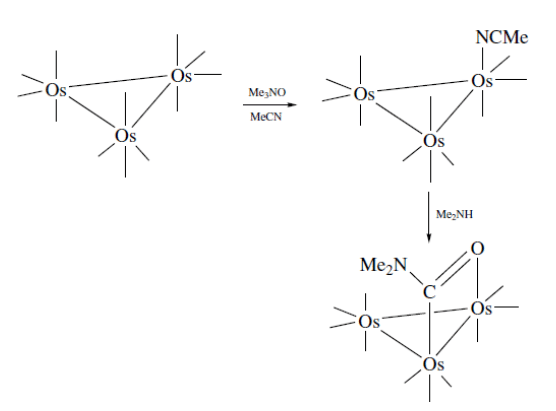

 Large and hetero-metallic metal cluster can also be formed by similar reactions on metalmeal multiple bonds with appropriate metal precursor complexes. For example, the Pt(PPh3)4 can add to the Mo-Mo triple bonds with the loss of two triphenylphosphine units, resulting in a three metal cluster.
Large and hetero-metallic metal cluster can also be formed by similar reactions on metalmeal multiple bonds with appropriate metal precursor complexes. For example, the Pt(PPh3)4 can add to the Mo-Mo triple bonds with the loss of two triphenylphosphine units, resulting in a three metal cluster. Cluster compounds can also show catalytic activity with a variety of molecules. For example, one of the major objectives of cluster carbonyl chemistry is to activate the carbon monoxide and to facilitate its addition to various alkane or alkene.
Cluster compounds can also show catalytic activity with a variety of molecules. For example, one of the major objectives of cluster carbonyl chemistry is to activate the carbon monoxide and to facilitate its addition to various alkane or alkene.















