UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Preparation and Properties of Indole
Preparation and Properties of Indole | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Preparation Methods |

|
| Physical Properties of Indole |

|
| Chemical Properties of Indole |

|
| Medicinal Importance of indole |

|
Introduction
- Indole consists of a benzene ring fused to the Alpha and Beta positions of a pyrrole ring.
- Indole occurs in coal-tar and in the oils of jasmine and orange blossoms. It is also found as a part of the total structure of a number of alkaloids and amino acids e.g., serotonin, reserpine, and tryptophan

Preparation Methods
Indole may be obtained;.
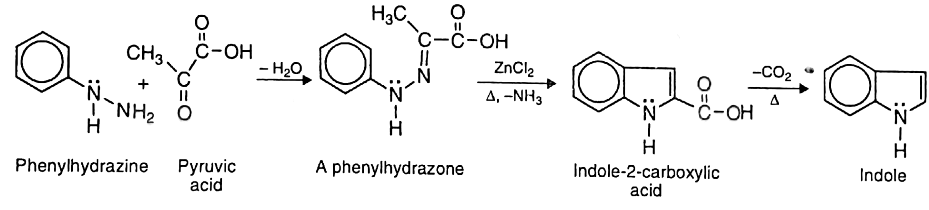
- By Fischer-indole synthesis: In this method, pyruvic acid is first treated with phenylhydrazine to form the corresponding phenylhydrazone. The hydrazone is heated with anhydrous zinc chloride to give indole-2-carboxylic acid which on decarboxylation yields indole.
- By the Reissert Synthesis. In this method o-nitrotoluene is condensed with diethyl oxalate in the presence of a base to form a 2-keto-ester. This is then reduced with zinc and glacial acetic acid to give indole-2-carboxylic acid which on decarboxylation gives indole.

- From o-Toluidine: This involves treatment of o-toluidine with formic acid to form N-formyl-o-toluidine. This undergoes dehydration on heating with potassium t-butoxide to yield indole.

- By the Lip Synthesis. In this method o-amino-w-chlorostyrene is heated with sodium ethoxide at l60-170°C

- From o-Nitrophenylacetaldehyde: This involves reduction of onitrophenylacetaldehyde with iron powder and sodium bisulphite to give o-aminophenylacetaldehyde which cyclises spontaneously to yield indole.

Physical Properties of Indole
- Indole is a colorless, volatile solid,
- Melting point 52C
- It is sparingly soluble in cold water, but dissolves in hot water and most organic solvents.
- Indole has a powerful odour which is pleasant and flowery in low concentrations. It is, in fact, used commercially as a perfume base. In contrast, indole and its 3-methyl derivative (Skatole) are responsible for the strong offensive odour of faeces.
Chemical Properties of Indole
- Basic and Acidic Character: Like pyrrole, indole is a weak base and also a weak acid. It is polymerized by strong acids and reacts with potassium hydroxide and Grignard reagents.
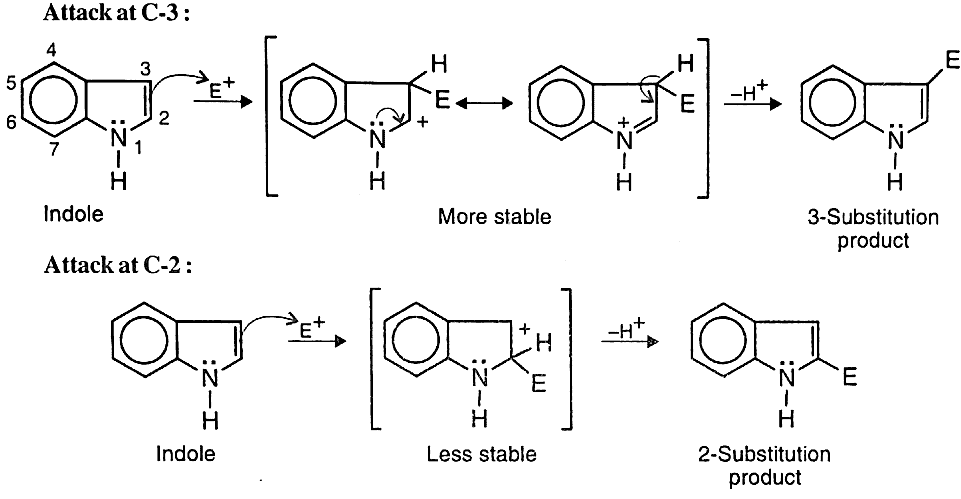
- Electrophilic Substitutions: Unlike pyrrole, indole undergoes electrophilic substitution at C-3. This is because two resonance forms can be written for intermediate cation obtained from attack at C-3 (without disturbing the benzene ring), whereas only one such form is possible for substitution at C-2

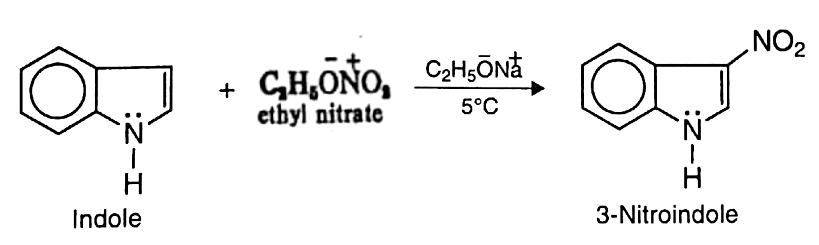
- a. Nitration: Indole may be nitrated at low temperature with ethyl nitrate in the presence of sodium ethoxide to yield 3-nitroindole
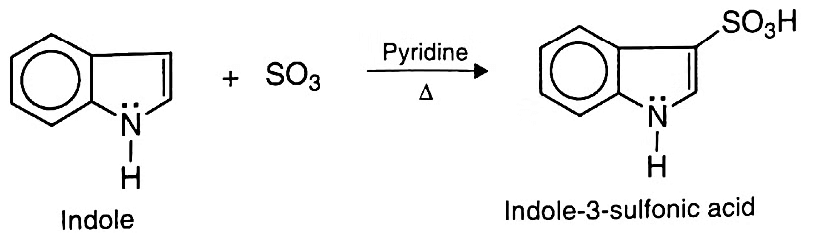
 (b) Sulphonation: Indole undergoes sulphonation with sulphur trioxide in pyridine at 110°C to give indole-3-sulphonic acid.
(b) Sulphonation: Indole undergoes sulphonation with sulphur trioxide in pyridine at 110°C to give indole-3-sulphonic acid.
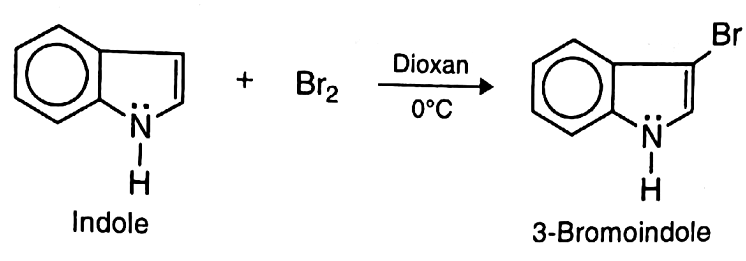
- C. Bromination: When treated with sodium methoxide and Methylene iodide, pyrrole undergoes ring expansion forming pyridine.

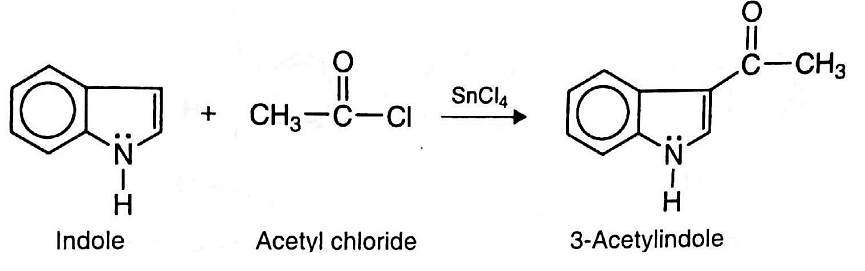
- d. Friedel-Craft Acylation: Indole may be acetylated with acetyl chloride in the presence of SnCl4 (Tin tetrachloride) to yield 3-acetylindole.

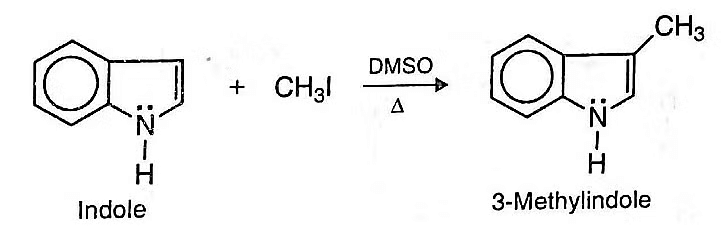
- e. Alkylation: Indole reacts with methyl iodide in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) at about 80°C to give 3-methylindole (skatole).

- Reimer-Tiemann Formylation: Indole reacts with chloroform in the presence of alkali to yield indole-3- aldehyde (3-formylindole) and 3-chloroquinoline

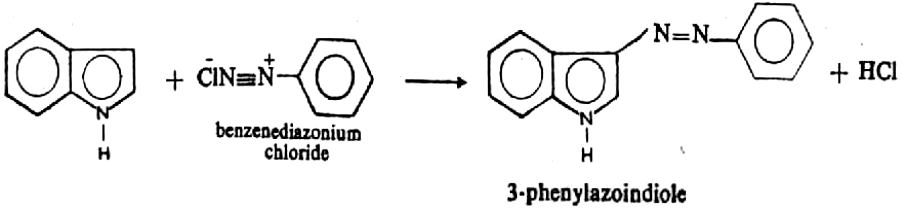
- Diazo Coupling: Indole couples with benzenediazonium chloride in a weakly acidic solution to yield 3-phenylazoindole.

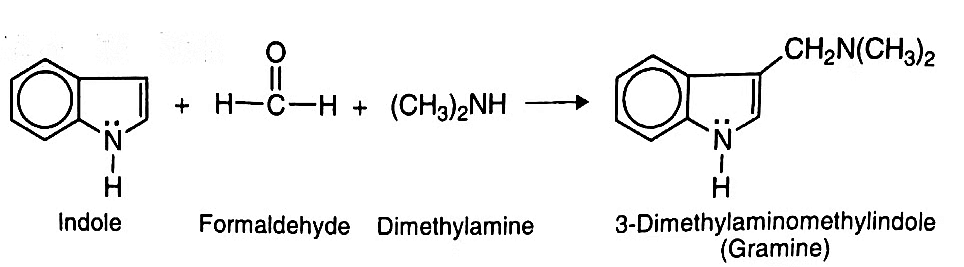
- Mannich Reaction: Indole undergoes Mannich reaction with formaldehyde and dimethylamine to give 3-dimethylaminomethylindole (Gramine).

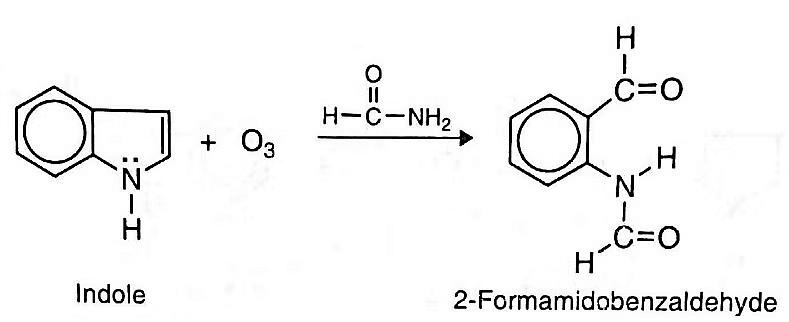
- Oxidation: Indole may be oxidized by ozone in formamide to give 2-formamido-benzaldehyde.

- Reduction: Mild reduction of indole with zinc (or tin) and hydrochloric acid yields 2,3 dihydroindole (Indoline). Catalytic reduction hydrogenates both rings and produces ocatahydroindole.

Medicinal Importance of indole

The document Preparation and Properties of Indole | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Preparation and Properties of Indole - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. How is indole prepared? |  |
Ans. Indole can be prepared through several methods, including:
- Fischer indole synthesis: It involves the reaction of an aryl hydrazine with a ketone or aldehyde in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- Leimgruber-Batcho indole synthesis: It involves the condensation of a nitroaryl with diethyl oxalate, followed by reduction and decarboxylation.
- Madelung synthesis: It involves the reaction of an aryl halide with an alkali metal salt of a carboxylic acid, followed by cyclization.
| 2. What are the physical properties of indole? |  |
Ans. Indole is a solid compound with a molecular formula C8H7N. It has a melting point of 52-54°C and a boiling point of 254-256°C. It is slightly soluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. Indole has a characteristic odor and is often described as having a fecal or floral smell.
| 3. What are the chemical properties of indole? |  |
Ans. Indole exhibits a variety of chemical properties, including:
- It can undergo electrophilic substitution reactions, where the nitrogen atom or the aromatic ring is attacked by electrophiles.
- It can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, where the nitrogen atom or the aromatic ring is attacked by nucleophiles.
- It can undergo oxidation reactions, where the indole ring is oxidized to form indole derivatives.
- It can undergo reduction reactions, where the indole ring is reduced to form indoline derivatives.
- It can form various derivatives through functional group modifications.
| 4. What is the medicinal importance of indole? |  |
Ans. Indole and its derivatives have significant medicinal importance. Some of its applications in medicine include:
- Indole derivatives are used as anti-inflammatory agents, as they inhibit the production of certain chemicals involved in inflammation.
- Indole alkaloids, such as reserpine, have been used as antihypertensive drugs to lower blood pressure.
- Indole compounds have antimicrobial properties and are used in the development of antibiotics.
- Indole alkaloids have shown potential anticancer activity and are being studied for their use in cancer treatment.
- Indole derivatives have been investigated for their role in neurological disorders and as potential antidepressant and antipsychotic agents.
| 5. How is indole used in the fragrance industry? |  |
Ans. Indole plays a crucial role in the fragrance industry. It is a natural component of many floral scents, providing a rich and complex aroma. Its unique odor, often described as fecal or animalic, adds depth and character to perfumes. Indole is often used in fragrances that aim to mimic the scent of flowers such as jasmine, orange blossom, and tuberose. Its presence in perfumes can evoke a sense of sensuality and allure.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches




 (b) Sulphonation: Indole undergoes sulphonation with sulphur trioxide in pyridine at 110°C to give indole-3-sulphonic acid.
(b) Sulphonation: Indole undergoes sulphonation with sulphur trioxide in pyridine at 110°C to give indole-3-sulphonic acid.