Peptide Sequencing- The Edman Degradation | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Peptide Sequencing- The Edman Degradation
With the identities and relative amounts of amino acids known, a peptide can then be sequenced to find out in what order the amino acids are linked. Much peptide sequencing is now done by mass spectrometry, using either electrospray ionization (ESI) or matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) linked to a time-of-flight (TOF) mass analyzer, as described in Section 12.4. Also in common use is a chemical method of peptide sequencing called the Edman degradation.
The general idea of peptide sequencing by Edman degradation is to cleave one amino acid at a time from an end of the peptide chain. That terminal amino acid is then separated and identified, and the cleavage reactions are repeated on the chain-shortened peptide until the entire peptide sequence is known. Automated protein sequencers are available that allow as many as 50 repetitive sequencing cycles to be carried out before a buildup of unwanted by-products interferes with the results. So efficient are these instruments that sequence information can be obtained from as little as 1 to 5 picomoles of sample—less than 0.1 μg.
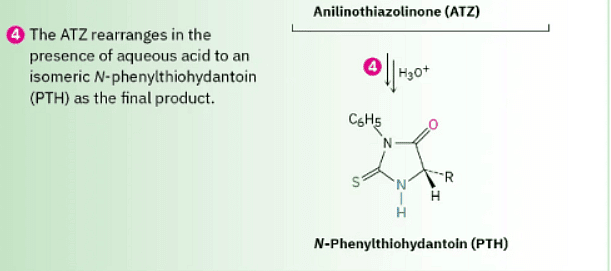
As shown in Figure 26.5, Edman degradation involves treatment of a peptide with phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC), C6H5–N═C═, followed by reaction with trifluoroacetic acid. The first step attaches the PITC to the –NH2 group of the N-terminal amino acid, and the second step splits the N-terminal residue from the peptide chain, yielding an anilinothiazolinone (ATZ) derivative plus the chain-shortened peptide. Further acid-catalyzed rearrangement of the ATZ derivative with aqueous acid converts it into a phenylthiohydantoin (PTH), which is identified by comparison of its elution time with the known elution times of PTH derivatives of the 20 common amino acids. The chain-shortened peptide is then automatically resubmitted for another round of Edman degradation.
Figure 26.5 MECHANISM Mechanism of the Edman degradation for N-terminal analysis of peptides.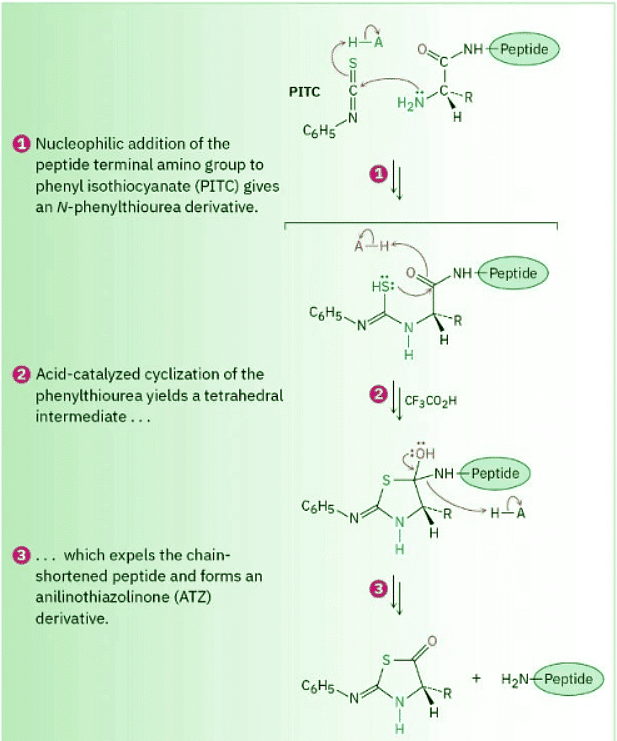
Complete sequencing of large proteins by Edman degradation is impractical because of the buildup of unwanted by-products. To get around this problem, a large peptide chain is first cleaved by partial hydrolysis into a number of smaller fragments, the sequence of each fragment is determined, and the individual fragments are fitted together by matching their overlapping ends. In this way, protein chains with more than 400 amino acids have been sequenced.
Partial hydrolysis of a peptide can be carried out either chemically with aqueous acid or enzymatically. Acid hydrolysis is unselective and gives a more-or-less random mixture of small fragments, but enzymatic hydrolysis is quite specific. The enzyme trypsin, for instance, catalyzes hydrolysis of peptides only at the carboxyl side of the basic amino acids arginine and lysine; chymotrypsin cleaves only at the carboxyl side of the aryl-substituted amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan.
FAQs on Peptide Sequencing- The Edman Degradation - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is peptide sequencing? |  |
| 2. What is the Edman degradation method? |  |
| 3. How does the Edman degradation work? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of the Edman degradation method? |  |
| 5. Are there alternative methods for peptide sequencing? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















