Orientation of Electrophilic Additions - Markovnikov's Rule | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Orientation of Electrophilic Additions - Markovnikov's Rule
Look carefully at the electrophilic addition reactions shown in the previous section. In each case, an unsymmetrically substituted alkene has given a single addition product rather than the mixture that might be expected. For example, 2-methylpropene might react with HCl to give both 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane, but it doesn’t. It gives only 2-chloro-2-methylpropane as the sole product. Similarly, it’s invariably the case in biological alkene addition reactions that only a single product is formed. We say that such reactions are regiospecific (ree-jee-oh-specific) when only one of two possible orientations of an addition occurs.
After looking at the results of many such reactions, the Russian chemist Vladimir Markovnikov proposed in 1869 what has become known as:
Markovnikov’s rule
In the addition of HX to an alkene, the H attaches to the carbon with fewer alkyl substituents and the X attaches to the carbon with more alkyl substituents.
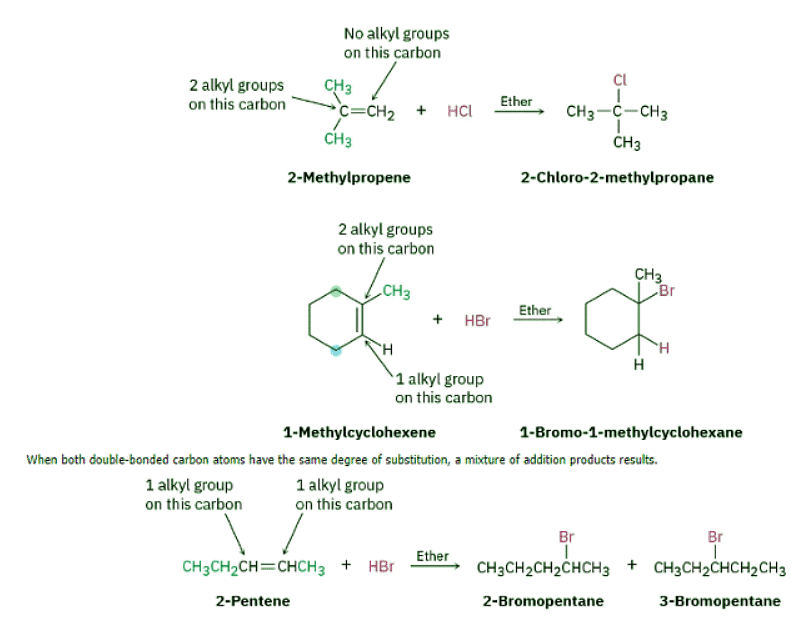
When both double-bonded carbon atoms have the same degree of substitution, a mixture of addition products results.
Because carbocations are involved as intermediates in these electrophilic addition reactions, Markovnikov’s rule can be restated in the following way:
Markovnikov’s rule restated
In the addition of HX to an alkene, the more highly substituted carbocation is formed as the intermediate rather than the less highly substituted one.
For example, addition of H+ to 2-methylpropene yields the intermediate tertiary carbocation rather than the alternative primary carbocation, and addition to 1-methylcyclohexene yields a tertiary cation rather than a secondary one. Why should this be?
Solved Examples
Example 1: Predicting the Product of an Electrophilic Addition Reaction
What product would you expect from reaction of HCl with 1-ethylcyclopentene?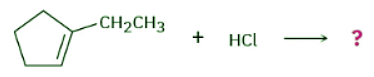
Ans: Strategy: When solving a problem that asks you to predict a reaction product, begin by looking at the functional group(s) in the reactants and deciding what kind of reaction is likely to occur. In the present instance, the reactant is an alkene that will probably undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with HCl. Next, recall what you know about electrophilic addition reactions to predict the product. You know that electrophilic addition reactions follow Markovnikov’s rule, so H+ will add to the double-bond carbon that has one alkyl group (C2 on the ring) and the Cl will add to the double-bond carbon that has two alkyl groups (C1 on the ring).
Solution: The expected product is 1-chloro-1-ethylcyclopentane.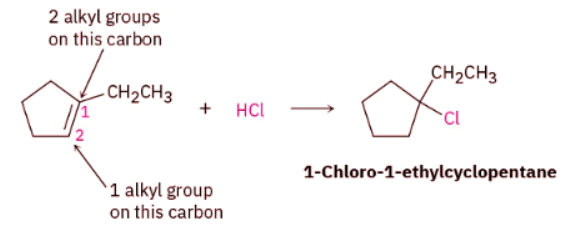
Example 2: Predicting the Product of an Electrophilic Addition Reaction
What product would you expect from reaction of HCl with 1-ethylcyclopentene? Ans: Strategy: When solving a problem that asks you to predict a reaction product, begin by looking at the functional group(s) in the reactants and deciding what kind of reaction is likely to occur. In the present instance, the reactant is an alkene that will probably undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with HCl. Next, recall what you know about electrophilic addition reactions to predict the product. You know that electrophilic addition reactions follow Markovnikov’s rule, so H+ will add to the double-bond carbon that has one alkyl group (C2 on the ring) and the Cl will add to the double-bond carbon that has two alkyl groups (C1 on the ring).
Ans: Strategy: When solving a problem that asks you to predict a reaction product, begin by looking at the functional group(s) in the reactants and deciding what kind of reaction is likely to occur. In the present instance, the reactant is an alkene that will probably undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with HCl. Next, recall what you know about electrophilic addition reactions to predict the product. You know that electrophilic addition reactions follow Markovnikov’s rule, so H+ will add to the double-bond carbon that has one alkyl group (C2 on the ring) and the Cl will add to the double-bond carbon that has two alkyl groups (C1 on the ring).
Solution: The expected product is 1-chloro-1-ethylcyclopentane.
Example 3: Synthesizing a Specific Compound
What alkene would you start with to prepare the following alkyl halide? There may be more than one possibility. Ans: Strategy: When solving a problem that asks how to prepare a given product, always work backward. Look at the product, identify the functional group(s) it contains, and ask yourself, “How can I prepare that functional group?” In the present instance, the product is a tertiary alkyl chloride, which can be prepared by reaction of an alkene with HCl. The carbon atom bearing the −Cl atom in the product must be one of the double-bond carbons in the reactant. Draw and evaluate all possibilities.
Ans: Strategy: When solving a problem that asks how to prepare a given product, always work backward. Look at the product, identify the functional group(s) it contains, and ask yourself, “How can I prepare that functional group?” In the present instance, the product is a tertiary alkyl chloride, which can be prepared by reaction of an alkene with HCl. The carbon atom bearing the −Cl atom in the product must be one of the double-bond carbons in the reactant. Draw and evaluate all possibilities.
Solution: There are three possibilities, all of which could give the desired product according to Markovnikov’s rule.
FAQs on Orientation of Electrophilic Additions - Markovnikov's Rule - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is Markovnikov's rule? |  |
| 2. How does Markovnikov's rule affect electrophilic additions? |  |
| 3. Why is Markovnikov's rule important in organic chemistry? |  |
| 4. Can Markovnikov's rule be violated? |  |
| 5. Are there any exceptions to Markovnikov's rule? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















