Difference Between Saytzeff and Hofmann Rule | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Saytzeff Rule? |

|
| What is Hofmann Rule? |

|
| What is the Difference Between Saytzeff and Hofmann Rule? |

|
| Bulky Bases in Elimination Reactions |

|
Introduction
- The key difference between Saytzeff and Hofmann rule is that Saytzeff rule indicates that the most substituted product is the most stable product, whereas Hofmann rule indicates that the least substituted product is the most stable product.
- Saytzeff rule and Hofmann rule are very important in predicting the end product of an organic elimination reaction. These rules can indicate the nature of the final product of a particular organic chemical reaction, based on the substitution of the final product, e.g. most substituted or least substituted product.
What is Saytzeff Rule?
- Saytzeff rule is an empirical rule that determines the final product of a particular reaction as the most substituted product. It is named mostly as Zaitsev’s rule. This rule is important in predicting the substitution of the final alkene product obtained from an elimination reaction. According to the carbon atom where the double bond forms in the final alkene product, we can define Saytzeff rule as “the alkene that forms via elimination of hydrogen from the beta-carbon having the least hydrogen substituents”. Therefore, the most substituted final product is the major product of the chemical reaction, which also turns out to be the most stable product.
- For example, 2-iodobutane contains an iodide group at the second carbon of the carbon chain. When this compound is treated with a strong acid such as potassium hydroxide, we can get 2-butene as the major product and the minor product is 1-butene. Here, the carbon atom that has the fewest hydrogen substituents is the third carbon atom; therefore, the elimination of a hydrogen atom occurs from this carbon which gives 2-butene. The first carbon atom has the most hydrogen substituents; thus, elimination of hydrogen from the first carbon atom forms the minor product 1-butene. The reaction is as follows:

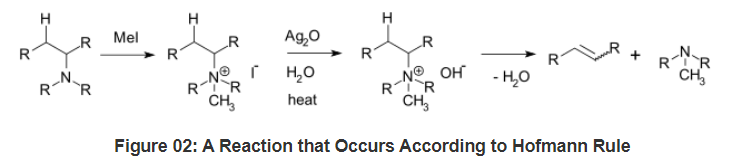
What is Hofmann Rule?
- Hofmann rule is an empirical rule that determines the final product of a particular reaction as the least substituted product. That means; a chemical reaction takes place according to this rule if the majority of the final product is the least substituted olefin (alkene product). According to the carbon atom where the double bond forms in the final alkene product, we can define Hofmann rule as “the alkene that forms via elimination of hydrogen from the alpha-carbon having the most hydrogen substituents”.
- Let’s look at an example:

- During the creation of quaternary ammonium and alkene via the reaction between a tertiary amine and excess methyl iodide, the least substituted product of alkene forms as the major product.
What is the Difference Between Saytzeff and Hofmann Rule?
The key difference between Saytzeff and Hofmann rule is that Saytzeff rule indicates that the most substituted product is the most stable product, whereas Hofmann rule indicates that the least substituted product is the most stable product. According to Saytzeff rule, the majority is the most substituted product, while according to Hofmann rule, the majority is the least substituted product.
Summary – Saytzeff vs Hofmann Rule
Saytzeff rule and Hofmann rule are very important in predicting the end product of an organic elimination reaction. The key difference between Saytzeff and Hofmann rule is that Saytzeff rule indicates that the most substituted product is the most stable product, whereas Hofmann rule indicates that the least substituted product is the most stable product.
Bulky Bases in Elimination Reactions
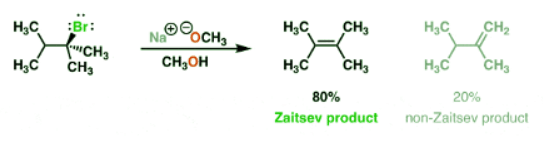
1. “Normal” E2 Reactions Follow Zaitsev’s Rule, Giving The “More Substituted” Alkene
- Most elimination reactions follow Zaitsev’s rule : you should expect that the “more substituted” alkene will be formed if at all possible. Like in the elimination reaction below, for instance, we get 80% of the tetrasubstituted alkene [“Zaitsev” – more substituted because there are 4 carbons attached to the alkene] and 20% of the disubstituted “non-Zaitsev” product.

- The Zaitsev product generally forms because the more substituted alkene is generally more stable.
- However, today we’ll talk about one interesting exception to this “rule” and how under certain conditions we actually end up with the “non-Zaitsev” alkene product instead.
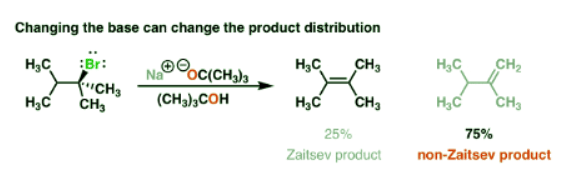
2. “Bulky Bases” Tend To Give A Higher Proportion Of “Non-Zaitsev” Products
- For instance, instead of using sodium methoxide, (NaOCH3) if you use the base NaOC(CH3)3 [or KOC(CH3)3, changing sodium for potassium doesn’t really matter here] you end up with an interesting reversal of products!

- So what’s going on here? Why might we get less of the Zaitsev product here and more of the “non-Zaitsev” product?
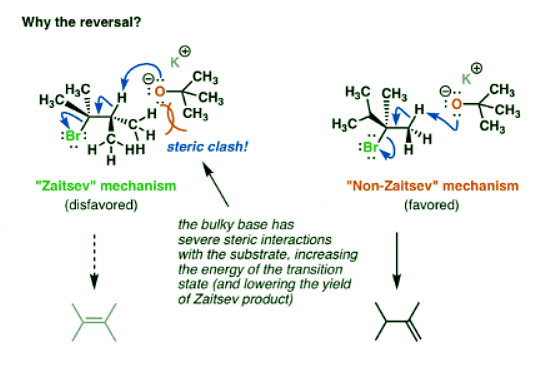
3. Bulky Bases Give More “Non-Zaitsev” Products Due To Steric Interactions With The Alkyl Halide
- Well, if we draw out what the structure of the reactants might look like in their transition state, we can start to see why. [Note: this is not technically a transition state since we’re not drawing partial bonds, but you can at least see how the reactants are assembled].
- The base in this instance – potassium t-butoxide – is an extremely bulky base, and the proton we remove to form the Zaitsev product is on a tertiary carbon. As the oxygen from the base draws nearer to this proton, a steric clash occurs.
- In essence the electron clouds around the methyl groups are interacting with each other, and the repulsion between these clouds will raise the energy of the transition state [remember – opposite charges attract, like charges repel]. This will slow down the reaction.

- Looking at the reactant assembly that produces the non-Zaitsev product, the bulky base is removing a proton from a primary carbon. Steric clash is considerably reduced in comparison to that for the Zaitsev product. Elimination is faster, and we therefore end up with the less substituted alkene as our major product.
- This is one example of a reaction where the more thermodynamically stable product is not formed. [recall that alkene stability increases with the number of carbons directly attached to the alkene].
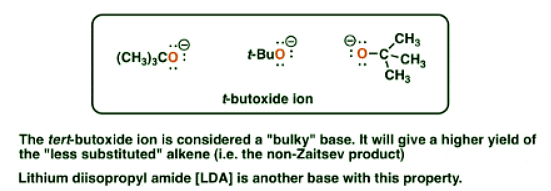
4. Two Common Bulky Bases Are The t-Butoxide Ion And Lithium Di-Isopropyl Amide (LDA)
- So the bottom line for this post is that when performing an E2 reaction, using a bulky base will produce a greater proportion of non-Zaitsev alkene products relative to a less bulky base.
- As far as we’ll see, the most common “bulky base” we need to consider is the t-butoxide ion, which can be drawn in many forms [see diagram]; occasionally you might see lithium di-isopropyl amide (LDA) used as well. For our purposes this completes the roster of bulky bases.

FAQs on Difference Between Saytzeff and Hofmann Rule - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is Saytzeff Rule? |  |
| 2. What is Hofmann Rule? |  |
| 3. What is the Difference Between Saytzeff and Hofmann Rule? |  |
| 4. How do bulky bases affect elimination reactions? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of elimination reactions that follow the Saytzeff and Hofmann rules? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|