UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2020: Geography | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Q1: Consider the following minerals:
- Bentonite
- Chromite
- Kyanite
- Sillimanite
In India, which of the above is/are officially designated as major minerals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
According to the National Account Statistics (2007), minerals are broadly classified into major and minor minerals.
Major Minerals include the following:
- Fuel Minerals: Coal, Lignite, Natural Gas, Petroleum (Crude).
- Metallic Minerals: Bauxite, Chromite, Copper Ore, Gold, Iron Ore, Lead (Concentrates), Zinc (Concentrates), Manganese Ore, Silver, Tin (Concentrates), Tungsten (Concentrates).
- Non-Metallic Minerals: Agate, Andalusite, Apatite, Asbestos, Ball Clay, Barytes, Calcite, Chalk, Clay, Corundum, Calcarious sand, Diamond, Diaspore, Dolomite, Kyanite, Laterite, Limestone, Limestone Kankar, Lime Shell, Magnesite, Mica (crude), Ochre, Pyrites, Pyrophyllite, Phosphorite, Quartz, impure quartz, Quartzite, Fuchsite Quartzite, Silica Sand, Salt (Rock), Salt (Evaporated), Shale, Slate, Steatite, Sillimanite, Vermiculite, Wollastonite.
- Minor Minerals include Bentonite, Boulder, Brick Earth, Building Stones, Chalcedony or Corundum, Fuller’s Earth, Gravel, Lime Stone, Dunite, Felspar, Fire Clay, Felsite, Flourite (Graded), Flourite (Concentrates), Gypsum, Garnet (Abrasives), Garnet (Gem), Graphite run-on-mines, Jasper, Kaolin, Marble, Murram, Ordinary Clay, Ordinary Sand, Ordinary Earth, Pebbles or Kankar, Quartzite and Sand stone, Road Metal, Salt Petre, Shale, Shingle, Slate.
- Chromite, Kyanite and Sillimanite are major minerals, whereas Bentonite is a minor mineral.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2: With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct?
- OMT is measured up to a depth of 26ºC isotherm which is 129 meters in the south- western Indian Ocean during January-March.
- OMT collected during January-March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in monsoon will be less or more than a certain long-term mean.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Scientists from Pune’s Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) have found that OMT has better ability to predict Indian summer monsoon than the Sea Surface Temperature (SST).
- The SST is restricted to a few millimetres of the top ocean layer and is largely influenced by strong winds, evaporation, or thick clouds. In contrast, OMT, which is measured up to a depth of 26ºC isotherm, is more stable and consistent, and the spatial spread is also less.
- The 26°C isotherm is seen at depths varying from 50-100 metres. During January- March, the mean 26ºC isotherm depth in the Southwestern Indian Ocean is 59 metres. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- With OMT, in addition to better predictive success, the information on whether the amount of monsoon rainfall will be more or less than the long-term mean will be available by beginning of April, two months before the southwest monsoon can set in. This is because OMT is analysed by measuring the ocean thermal energy during the period from January to March. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q3: With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements:
- At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.
- Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.
- Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Government of India subsidizes fertilizers to ensure that fertilizers are easily available to farmers and the country remains self-sufficient in agriculture production. The same has been achieved largely by controlling the price of fertilizer and the amount of production. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Ammonia (NH3) has been synthesized from natural gas. In this process, natural gas molecules are reduced to carbon and hydrogen. The hydrogen is then purified and reacted with nitrogen to produce ammonia. This synthetic ammonia is used as fertilizer, either directly as ammonia or indirectly after synthesis as urea, ammonium nitrate, and monoammonium or diammonium phosphates. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Sulfur is a major by-product of oil refining and gas processing. Most crude oil grades contain some sulfur, most of which must be removed during the refining process to meet strict sulfur content limits in refined products. This is typically done through hydrotreating and results in production of H2S gas, which is converted into elemental sulfur. Sulfur can also be mined from underground, naturally-occurring deposits, but this is more costly than sourcing from oil and gas and has largely been discontinued. Sulfuric acid is used in the production of both Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) and Diammonium Phosphate (DAP). Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
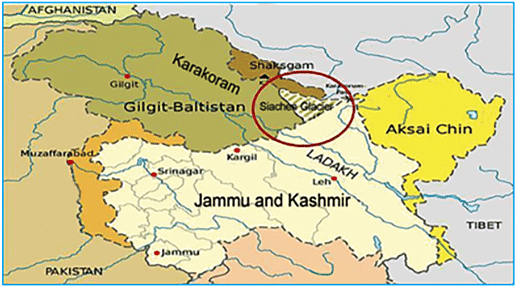
Q4: Siachen Glacier is situated to the
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley Explanation:
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. It has the distinction of being the largest glacier outside the polar and subpolar regions. It lies to the west of Aksai Chin, north of Nubra valley and almost east of Gilgit. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q5: Consider the following statements:
- Jet streams occur in the Northern Hemisphere only.
- Only some cyclones develop an eye.
- The temperature inside the eye of a cyclone is nearly 10ºC lesser than that of the surroundings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Jet Stream is a geostrophic wind blowing horizontally through the upper layers of the troposphere, generally from west to east, at an altitude of 20,000 - 50,000 feet. Jet Streams develop where air masses of different temperatures meet. So, usually surface temperatures determine where the Jet Stream will form. Greater the difference in temperature, faster is the wind velocity inside the jet stream. Jet Streams extend from 20° latitude to the poles in both hemispheres. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Cyclones are of two types, tropical cyclone and temperate cyclone. The center of a tropical cyclone is known as the ‘eye’, where the wind is calm at the center with no rainfall. However, in a temperate cyclone, there is not a single place where winds and rains are inactive, so the eye is not found. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The warmest temperatures are found in the eye itself, not in the eyewall clouds where the latent heat occurs. The air is saturated only where convective vertical motions pass through flight level. Inside the eye, the temperature is greater than 28°C and the dewpoint is less than 0°C. These warm and dry conditions are typical of the eyes of extremely intense tropical cyclones. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q6: What is/are the advantage/advantages of zero tillage in agriculture?
- Sowing of wheat without burning the residue of previous crop.
- Without the need for nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Zero Tillage, also called no-till farming, is a cultivation technique in which the soil is disturbed only along the slit or in the hole into which the seeds are planted, the reserved detritus from previous crops covers and protects the seedbed.
- As per a study, it has been found that farmers in north India can not only help reduce air pollution but also improve the productivity of their soil and earn more profits if they stop burning their crop residue and instead adopt the concept of no-till farming.
- Under zero tillage, the direct seeding of wheat into unploughed soil and with rice residues left behind has proved very beneficial. It saved on water, labour and use of agro-chemicals, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved soil health and crop yield and thus benefitted both farmers and the society at large. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) is a viable option to reduce the unproductive water flows. DSR refers to the process of establishing a rice crop from seeds sown in the field rather than by transplanting seedlings from the nursery. Conventional rice establishment system requires a substantial amount of water. It has been reported that water up to 5000 litres is used to produce 1 kg of rough rice. However, with increasing shortage of water, dry-DSR with minimum or zero tillage further enhances the benefits of this technology by saving labour. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- No tilled soils tend to be cooler than others, partly because a surface layer of plant residues is present. Carbon is sequestered in the soil enhancing its quality, reducing the threat of global warming. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q7: According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels?
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The National Policy on Biofuels, 2018, allows production of ethanol from damaged food grains like wheat, broken rice, etc., which are unfit for human consumption.
- The Policy also allows conversion of surplus quantities of food grains to ethanol, based on the approval of the National Biofuel Coordination Committee.
- The Policy expands the scope of raw material for ethanol production by allowing use of
- sugarcane juice, sugar containing materials like sugar beet, sweet sorghum, starch containing materials like corn, cassava, damaged food grains like wheat, broken rice, rotten potatoes, unfit for human consumption for ethanol production.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q8: With reference to pulse production in India, consider the following statements:
- Black gram can be cultivated as both kharif and rabi crop.
- Green-gram alone accounts for nearly half of pulse production.
- In the last three decades, while the production of kharif pulses has increased, the production of rabi pulses has decreased.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- In India, the important pulse crops grown in winter (rabi) are chickpea, lentil, lathyrus, field pea and kidney bean. However, green gram, black gram and cowpea are grown in both spring and rainy season.
- Black gram is a warm weather crop and comes up in areas receiving an annual rainfall ranging from 600 to 1000 mm. It is mainly cultivated in a cereal-pulse cropping system primarily to conserve soil nutrients and utilize the left over soil moisture particularly, after rice cultivation. Hence, although it can be grown in all the seasons, the majority of black gram cultivation falls in either rabi or late rabi seasons particularly in peninsular India. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- According to the Directorate of Economics and Statistics (DES), the share of pulse production in 2018- 19 was comprised of Tur (15.34%), Gram (43.29%), Moong (green gram,10.04%), Urad (black gram, 13.93%), Lentil (6.67%), and Other Pulses (10%). Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- In the last three decades, both, the production of kharif pulses and the production of rabi pulses have increased. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q9: “The crop is subtropical in nature. A hard frost is injurious to it. It requires at least 210 frost-free days and 50 to 100 centimeters of rainfall for its growth. A light well- drained soil capable of retaining moisture is ideally suited for the cultivation of the crop.” Which one of the following is that crop?
(a) Cotton
(b) Jute
(c) Sugarcane
(d) Tea
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Cotton:
- Temperature: Between 21-30°C, 210 frost free days.
- Rainfall: Around 50-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Well-drained black cotton soil of Deccan Plateau.
Jute:
- Temperature: Between 15-34°C
- Rainfall: Around 100-250 cm.
- Soil Type: Jute can be raised on all kinds of soils from clay to sandy loam, but loamy alluvial are best suited.
Sugarcane:
- Temperature: Between 28-32°C
- Rainfall: Around 75-120 cm.
- Soil Type: Sugarcane can grow in a variety of soils including black cotton soils, loams, brown or reddish loams, clayey loams and even laterites.
Tea:
- Temperature: Between 20-30°C.
- Rainfall: Around 150-300 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q10: With reference to the current trends in the cultivation of sugarcane in India, consider the following statements:
- A substantial saving in seed material is made when ‘bud chip settlings’ are raised in a nurse, and transplanted in the main field.
- When direct planting of setts is done, the germination percentage is better with single- budded setts as compared to setts with many buds.
- If bad weather conditions prevail when setts are directly planted, single-budded setts have better survival as compared to large setts.
- Sugarcane can be cultivated using settlings prepared from tissue culture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Tissue culture technology:
- Tissue culture is a technique in which fragments of plants are cultured and grown in a laboratory.
- It provides a new way to rapidly produce and supply disease-free seed cane of
- existing commercial varieties.
- It uses meristem to clone the mother plant. It also preserves genetic identity.
- The tissue culture technique, owing to its cumbersome outfit and physical limitation, is turning out to be uneconomical.
Bud chip technology:
- As a viable alternative of tissue culture, it reduces the mass and enables quick multiplication of seeds.
- This method has proved to be more economical and convenient than the traditional method of planting two to three bud setts.
- The returns are relatively better, with substantial savings on the seed material used for planting. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The researchers have found that the setts having two buds are giving germination about 65 to 70% with better yield. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Large setts have better survival under bad weather but single budded setts also give 70% germination if protected with chemical treatment. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q11: In the context of India, which of the following is/are considered to be practice(s) of eco-friendly agriculture?
- Crop diversification
- Legume intensification
- Tensiometer use
- Vertical farming
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Crop diversification: It refers to the addition of new crops or cropping systems to agricultural production on a particular farm taking into account the different returns from value added crops with complementary marketing opportunities. Introducing a greater range of varieties also leads to diversification of agricultural production which can increase natural biodiversity. Further, the diversification of agriculture is an alternate way for the regeneration and conservation of land and water. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Legume intensification: A leguminous plant (legume) is a group of plants that have vegetables or as foods grown from the ground knobs that enhance the ability of nitrogen- rich material. Examples include acacia, peas, clover, beans etc. Legumes improve soil health, especially compared to fallow, by adding nitrogen and organic matter and reducing potential erosion and leaching loss. Legumes may reduce the energy footprint of cropping systems by reducing the need for nitrogen fertilizer, and improve the stability and health of agro-ecosystems. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Tensiometer: It literally means tension measurement. In order to absorb water from soil, the plant has to overcome the suction tension of the soil. This tension is measured by the tensiometer, thus giving indication of the soil moisture at the depth in which it was placed. Tensiometer helps farmers and other irrigation managers to determine when to water the soil. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Vertical farming: It is the practice of growing crops in vertically stacked layers and often incorporates controlled-environment agriculture, which aims to optimize plant growth, and soilless farming techniques. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q12: Consider the following pairs

Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4 only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Mekong River, originating in the icy headwaters of the Tibetan highlands, flows through the steep canyons of China, known as the upper basin, through lower basin countries Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, and Cambodia, before fanning an expansive delta in Vietnam and emptying into the South China Sea. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly matched.
- River Thames, the longest river in England, flows 215 miles from the Cotswolds to the North Sea. The main tributaries of Thames are Buscot, Reading, and Kingston. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- The Volga River, the longest river in Europe, runs through Russia with its delta flowing into the Caspian Sea just south of the Kazakhstan border. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- The Zambezi is the fourth-largest river after the Congo/Zaire, Nile and Niger in Africa. It rises in the Kalene hills in north-western Zambia and flows eastwards for about 3000 km to the Indian Ocean. Hence, pair 4 is correctly matched.
Therefore, the option (c) is the correct answer.
Q13: Steel slag can be the material for which of the following?
- Construction of base road
- Improvement of agricultural soil
- Production of cement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- Steel slag is a by-product of the steel making process. It is produced during the separation of the molten steel from impurities in steel-making furnaces. The slag occurs as a molten liquid and is a complex solution of silicates and oxides that solidifies upon cooling.
- Steel slag is used as a base course material, the material under the surface layer of an asphalt road, track or surface. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Steel slag can be used in the agricultural sector due to its ability to correct soil acidity, as it contains some nutrients for the plants and also as silicate fertilizer that is capable of providing silicon to the plants. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Steel-slag can be used to produce cement. Further, slag cement is most widely used in concrete, either as a separate cementitious component or as part of a blended cement. It works synergistically with portland cement to increase strength, reduce permeability, improve resistance to chemical attack and inhibit rebar corrosion. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2020: Geography - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key topics covered in the Geography section of the UPSC Prelims 2020? |  |
| 2. How can candidates effectively prepare for the Geography section of the UPSC Prelims? |  |
| 3. What type of questions were asked in the Geography section of the UPSC Prelims 2020? |  |
| 4. Why is Geography important for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. What resources are recommended for studying Geography for the UPSC exam? |  |
















