Short Notes: Reaching The Age of Adolescence | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Entering adolescence is like crossing a bridge between being a kid and becoming a grown-up. It's a time when you start learning more about yourself and experience big changes, both in how you feel and how you grow.
Adolescence and Puberty
Adolescence brings about significant changes in the human body, signifying the onset of puberty, with the most crucial change being the capability for reproduction. Puberty concludes when an adolescent reaches reproductive maturity.
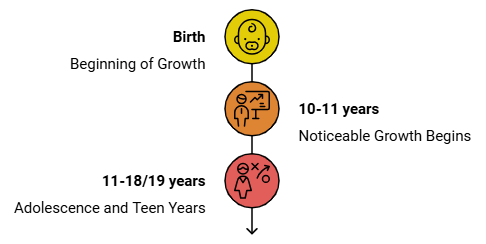
- Growth begins at birth and becomes noticeable around 10 or 11 years.
- Adolescence, occurring from 11 to 18 or 19 years, is marked by physical changes, making individuals 'teenagers.'
- Girls may enter adolescence earlier than boys, and the duration varies among individuals.
 Adult Male and Female
Adult Male and Female
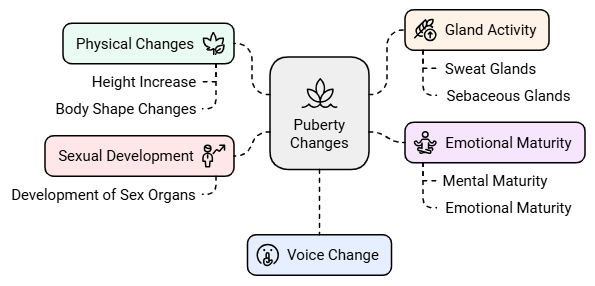
Changes at Puberty
Changes in Height
- During puberty, the most noticeable change is a sudden increase in height.
- Long bones, such as those in the arms and legs, elongate, making a person taller.
- Girls initially grow faster than boys, but by around 18 years, both genders reach their maximum height.
- The rate of height growth varies among individuals, with some experiencing sudden spurts and others growing gradually.
- Despite initial disproportions, all body parts eventually catch up, resulting in a proportionate body.
- Height is influenced by genetic factors inherited from parents.
- Proper nutrition during growth years is crucial for the nourishment of bones, muscles, and other body parts.
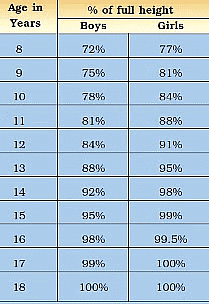 Height Chart
Height Chart
Changes in Body Shape
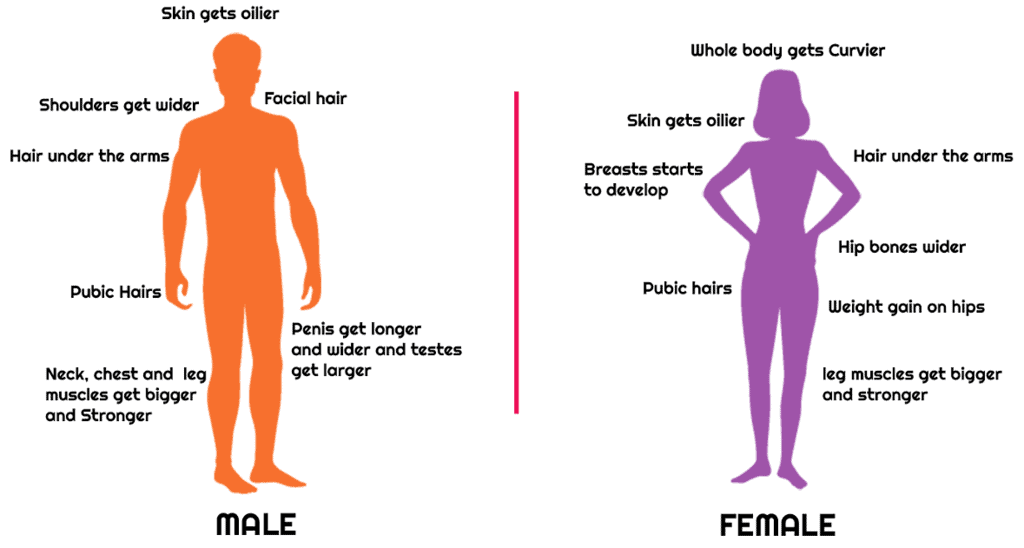
- Adolescent boys experience broader shoulders and wider chests due to puberty-related growth.
- Girls witness a widening of the region below the waist during this phase.
- Muscle development is more prominent in boys than in girls, leading to different physical changes.
Voice Change
- During puberty, the voice box or larynx grows, leading to changes in voice pitch.
- Boys develop a larger voice box, sometimes visible as Adam’s apple, resulting in a deeper voice.
- Girls generally have a high-pitched voice, while boys may experience temporary hoarseness during voice box growth.
Sweat and Sebaceous Glands Activity
- Puberty triggers increased secretion of sweat and oil glands, causing acne and pimples on the skin.
Development of Sex Organs
- Male sex organs like the testes and penis develop fully, with the testes producing sperm.
- In girls, ovaries enlarge, eggs mature, and the ovaries start releasing mature eggs.
Mental, Intellectual, and Emotional Maturity
- Adolescence marks a period of change in thinking, with increased independence and self-consciousness.
- Intellectual development occurs, and adolescents spend more time thinking, with the brain having its greatest capacity for learning.
- Feelings of insecurity may arise, but it's crucial for adolescent learners to understand that these changes are natural and part of growing up.
Secondary Sexual Characters
Testes and ovaries, identified as reproductive organs, produce gametes—sperms and ova, respectively.
- Girls experience breast development, while boys grow facial hair (moustaches and beard) and chest hair during puberty.
- These features, distinguishing males from females, are termed secondary sexual characters.
- Hair growth also occurs under the arms and in the pubic region for both boys and girls.
Role of Hormones
- Adolescent changes are regulated by hormones, which are chemical substances.
- Testosterone, the male hormone, is released by the testes during puberty, leading to changes in boys, such as facial hair growth.
- Estrogen, the female hormone, is produced by ovaries after puberty, contributing to breast development in girls.
- Mammary glands, responsible for milk secretion, develop inside the breasts under the influence of estrogen.
- The secretion of these hormones is controlled by another hormone from the pituitary gland.
Role of Pituitary Gland
- The pituitary gland controls the production of sex hormones by the testes and ovaries.
- Sex hormones, responsible for secondary sexual characters, are influenced by hormones from the pituitary gland.
- The pituitary gland secretes various hormones, including those that make ova mature in the ovaries and sperm form in the testes.
 Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function
- Testes and ovaries are responsible for secreting sex hormones.
- These sex hormones play a crucial role in the development of male and female secondary sexual characters.
- The pituitary gland regulates sex hormones, influencing their production and functioning.
- Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream, targeting specific body parts known as the target site.
- The target site responds to the hormone released by the endocrine glands.
- There are numerous endocrine glands, also known as ductless glands,in the body.
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
- Adolescents gain the capability for reproduction when their testes and ovaries start producing gametes.
- The capacity for maturation and gamete production lasts longer in males than in females.
- In females, the reproductive phase begins at puberty (10 to 12 years) and generally lasts until approximately 45 to 50 years of age.
- Ova starts maturing at the onset of puberty, with one ovum released every 28 to 30 days.
- During this period, the uterus wall thickens to receive the egg for potential development in case of fertilization, leading to pregnancy.
- If fertilization doesn't occur, the released egg, along with the thickened uterine lining and blood vessels, is shed off, causing menstruation.
- Menstruation, occurring every 28 to 30 days, begins at puberty and is termed menarche.
- Menstrual cycles cease at 45 to 50 years, marking menopause.
- Initially, menstrual cycles may be irregular and take time to become regular.
Menstrual Cycle and Hormonal Control
- The menstrual cycle, controlled by hormones, involves egg maturation, release, uterine wall thickening, and breakdown if pregnancy doesn't occur.
- If the egg is fertilized, it divides and embeds in the uterus for further development.
How is the Sex of the Baby Determined?
- The instructions for determining the sex of a baby are present in the fertilized egg or zygote.
- Chromosomes, thread-like structures in the fertilized egg's nucleus, carry these instructions.
- All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with two being the sex chromosomes, X and Y.
- Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome.
- Gametes (egg and sperm) have only one set of chromosomes, with unfertilized eggs always carrying one X chromosome.
- Sperms come in two types, one with an X chromosome and the other with a Y chromosome.
- If a sperm with an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote develops into a female child. If a sperm with a Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the zygote develops into a male child.
- Sex chromosomes from the father determine the unborn baby's sex.
- The belief that the mother is responsible for the baby's sex is incorrect and unjustified.
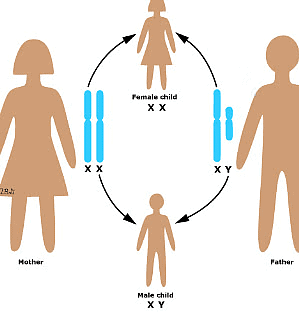 Sex Determination
Sex Determination
Hormones other than Sex Hormones
- Chromosomes carry instructions for determining the baby's sex in the zygote.
- There are various endocrine glands in the body, including the pituitary, testes, ovaries, thyroid, pancreas, and adrenals.
- The pituitary, testes, and ovaries produce sex hormones influencing reproductive functions.
- Other endocrine glands like the thyroid, pancreas, and adrenals produce hormones like thyroxine, insulin, and adrenalin, respectively.
- Thyroxine is necessary for normal growth, insulin regulates blood sugar, and adrenalin helps the body adjust to stress.
- Thyroid and adrenals secrete hormones upon receiving orders from the pituitary gland.
- The pituitary also secretes growth hormones crucial for normal growth.
Role of Hormones in Frog Metamorphosis
- In frog metamorphosis, insect hormones control the process.
- Thyroxine, produced by the thyroid, is necessary for tadpole growth into adults and requires iodine in water.
- Insufficient iodine in water can hinder tadpoles from becoming adults.
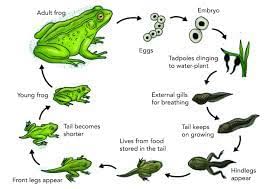 Frog Metamorphosis
Frog Metamorphosis
Reproductive Health
Health encompasses both physical and mental well-being of an individual. Maintaining a balanced diet, personal hygiene, and engaging in adequate physical exercise are essential for overall health.
Nutritional Needs of Adolescents
- Adolescence is a stage of rapid growth and development, making a carefully planned diet crucial during this period.
- A balanced diet includes proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins in proper proportions.
- Common Indian meals like roti/rice, dal, vegetables, and milk provide a balanced diet, while fruits also contribute to nourishment.
- Iron-rich foods such as leafy vegetables, jaggery, meat, citrus, and Indian gooseberry are beneficial for adolescents, helping in blood formation.
- Personal hygiene, including regular bathing and cleanliness, is crucial to prevent bacterial infections, especially for teenagers with increased sweat gland activity.
- Girls should maintain cleanliness during menstruation, using sanitary napkins or homemade pads and changing them every 4–5 hours.
- Engaging in physical exercise, walking, and playing outdoor games contributes to maintaining a fit and healthy body.
Say "NO" to Drugs Say No To Drugs
Say No To Drugs
- Adolescence is a period of normal growth and development, and individuals should not feel confused or insecure about the changes happening in their bodies and minds.
- Reject any suggestions to use drugs, as they are addictive, harmful to health, and can ruin both physical and mental well-being.
- Drugs can lead to long-term health issues and negatively impact happiness.
- Awareness of AIDS, caused by the HIV virus, emphasizes the dangers of sharing syringes and engaging in sexual contact with infected individuals.
- Saying "No" to drugs is crucial for maintaining a healthy and fulfilling life.Question for Short Notes: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceTry yourself:What is the role of thyroxine in frog metamorphosis?View Solution
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes: Reaching The Age of Adolescence - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the primary changes that occur during puberty in both males and females? |  |
| 2. How do hormones regulate the sexual maturation process during adolescence? |  |
| 3. What factors influence the determination of a baby's sex? |  |
| 4. What other hormones, besides sex hormones, are important for reproductive health? |  |
| 5. Why is reproductive health important during the reproductive phase of life in humans? |  |

















