Shankar IAS Summary: Environmental Pollution- 3 - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Environmental Pollution and Health |

|
| Acid Rain |

|
| Sources of Compounds Causing Acid Rain |

|
| Categorization of Industrial Sectors |

|
Environmental Pollution and Health
First: Pollution Inventory and Health Impact
- Assess the relative contribution of sources in a coherent health protection framework.
- Prioritize sources leading to greater exposure to health-damaging pollutants, not just based on emission quantities.
- Vehicles globally contribute significantly to particulates in cities.
Second: Exposure Levels and Health Risks
- People are exposed to higher health-damaging pollutants than ambient conditions.
- Each breath contains three to four times more pollutants than ambient air concentration.
- Highest exposure to vehicular fumes occurs on roads and within 500 meters.
 Environmental Pollution
Environmental Pollution
Third: Multi-Pollutant Approach for Health Benefits
- People are exposed to a mixture of pollutants with serious health impacts.
- Benefits increase when pollution sources are regulated for multi-pollutants.
- Delhi's air contains particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, ozone, and toxins.
- Focus on diesel emissions, a class one carcinogen linked to lung cancer.
Fourth: Disconnect Between Policies and Health Realities
- Air quality policies are disconnected from reported health realities.
- India is undergoing a rapid health transition with a rising burden of chronic diseases.
- Chronic diseases like cancer, stroke, and lung diseases are strongly influenced by air pollution.
- Policies must align with the health sector's reported reality for effective solutions.
Acid Rain
Acid rain refers to precipitation that has undergone acidification, resulting from the interaction of sulfur and nitrogen oxides with atmospheric moisture. With a pH below 5.6, acid rain harms ecosystems, particularly lakes, streams, and forests, impacting the flora and fauna residing in these environments.
 Acid Rain
Acid Rain
Types of Acid Deposition
"Acid rain" is a comprehensive term encompassing a blend of wet and dry deposition from the atmosphere.
A. Wet Deposition
- Acidic chemicals in the air, when carried to wet weather regions, can precipitate as rain, snow, fog, or mist.
- As this acidic water moves over and through the ground, it impacts a variety of plants and animals.
- The effects' intensity depends on factors such as water acidity, soil chemistry, buffering capacity, and the reliance of living organisms on the water.
- Precipitation removes atmospheric gases and particles through rain-out (particles incorporated into cloud drops) and washout (materials swept down by rain or snow).
B. Dry Deposition
- In dry-weather areas, acid chemicals may mix with dust or smoke and fall to the ground via dry deposition, adhering to surfaces like the ground, buildings, vegetation, and vehicles.
- Rainstorms can wash dry-deposited gases and particles from surfaces through runoff, making the mixture more acidic.
- Approximately half of atmospheric acidity returns to Earth through dry deposition.

The pH Scale
- The pH scale gauges a solution's acidity or basicity (alkalinity), ranging from 0 to 14.
- A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic.
- Devised in 1909, it's a logarithmic index for hydrogen ion concentration.
- pH values decrease as hydrogen ion levels increase.
- A solution with pH 4 is ten times more acidic than pH 5, and a hundred times more acidic than pH 6.
- Although the pH range is typically stated as 0 to 14, theoretically, lower and higher values are possible.
Sources of Compounds Causing Acid Rain
A. Sulphur
(i) Natural Sources:
- Seas and oceans.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Biological processes in the soil, such as the decomposition of organic matter.
(ii) Man-made Sources:
- Burning of coal (contributing to 60% of SO) and petroleum products (30% of SO).
- Smelting of metal sulfide ores for obtaining pure metals.
- Industrial production of sulfuric acid in metallurgical, chemical, and fertilizer industries.

B. Nitrogen Natural Sources:
- Lightning.
- Volcanic eruptions.
- Biological activity.
Anthropogenic Sources:
- Forest fires.
- Combustion of oil, coal, and gas.
C. Formic Acid
- Biomass burning during forest fires releases formic acid (HCOOH) and formaldehyde (HCHO) into the atmosphere.
- A significant portion of formaldehyde undergoes photo-oxidation, forming formic acid.
Other Acids
- Chlorine.
- Phosphoric acid.
- Hydrochloric acid (from smokestacks).
- Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide from automobiles can become carbonic acid.
Common Characteristics of Areas Prone to Acid Rain
- Concentrated in the industrialized belt of the northern hemisphere.
- Often upland and/or mountainous, well-watered by rain and snow.
- Abundance of water, with numerous lakes, streams, and extensive vegetation-covered land.
- Upland areas often have thin soils and glaciated bedrock.
 Great Smoky MountainsWorld Scenario
Great Smoky MountainsWorld Scenario
- Regions in Scandinavia, Canada, the North and Northeast United States, and Northern Europe, including parts of West Germany and upland Britain, share these characteristics.
- Acid rain hot spots across the Atlantic include Nova Scotia, Southern Ontario, Quebec in Canada, the Adirondack Mountains in New York, the Great Smoky Mountains, parts of Wisconsin, Minnesota, and the Colorado Rockies in the US.
In India
- Bombay reported the first instances of acid rain in 1974.
- Acid rain cases are now reported in metropolitan cities.
- Annual SO2 emissions in India have nearly doubled in the last decade due to increased fossil fuel consumption.
- Lowering of soil pH is noted in northeastern India, coastal Karnataka and Kerala, parts of Orissa, West Bengal, and Bihar.
Chemistry of Acid Rain
Six fundamental steps contribute to the formation of acid rain:
- The atmosphere receives sulfur and nitrogen oxides from both natural and man-made sources.
- Some of these oxides precipitate directly to the ground as dry deposition, either near the source or at a distance.
- Sunlight induces the formation of photooxidants, including ozone, in the atmosphere.
- These photo-oxidants react with sulfur and nitrogen oxides, resulting in the production of H2SO4 and HNO3 through oxidation.
- The sulfur and nitrogen oxides, photo-oxidants, and other gases (such as NH3) are involved in the process.
- Acid rain, containing ions of sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, and hydrogen, falls as wet deposition.
 Infertile Soil
Infertile Soil
Impact of Acid Rain
A. Soil
- Exchange between hydrogen ions and nutrient cations like potassium and magnesium causes the leaching of nutrients, leading to soil infertility.
- Decreased respiration of soil organisms is observed.
- An increase in ammonia due to decreased nutrients reduces the rate of decomposition.
- The nitrate level in the soil is found to decrease.
- Acid rain impact on soil is less in India due to predominantly alkaline soils with good buffering capacity.
B. Vegetation
- Acid rain affects trees and undergrowth, causing reduced or abnormal growth.
- Symptoms include discoloration and loss of foliar biomass, loss of feeder-root biomass (especially in conifers), premature aging of older needles in conifers, increased susceptibility to damage, death of herbaceous vegetation under affected trees, and prolific lichen production on affected trees.
C. Microorganisms
- pH influences the proliferation of microbial species, leading to a shift from bacteria-bound to fungi-bound microflora.
- This shift causes a delay in the decomposition of soil organic material and an increase in fungal diseases in aquatic life and forests.
D. Wildlife
- Effects on wildlife are not always evident but can impact productivity and survival.
- Direct effects include damage to eggs and tadpoles of breeding frogs and salamanders.
- Indirect effects involve the release of metals from soils into the aquatic environment, where they may be ingested by animals, leading to potential toxic effects.
- Other indirect effects include loss or alteration of food and habitat resources.
 WildlifeE. Humans
WildlifeE. Humans
- Acid rain affects human health in various ways.
- Obvious effects include bad smells, reduced visibility, and irritation of the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
- Direct effects encompass chronic bronchitis, pulmonary emphysema, and cancer.
- Indirect effects involve food poisoning through contaminated drinking water and food.
- Increased levels of toxic heavy metals like manganese, copper, cadmium, and aluminum contribute to adverse effects on human health.
F. Acid rain damage on Materials
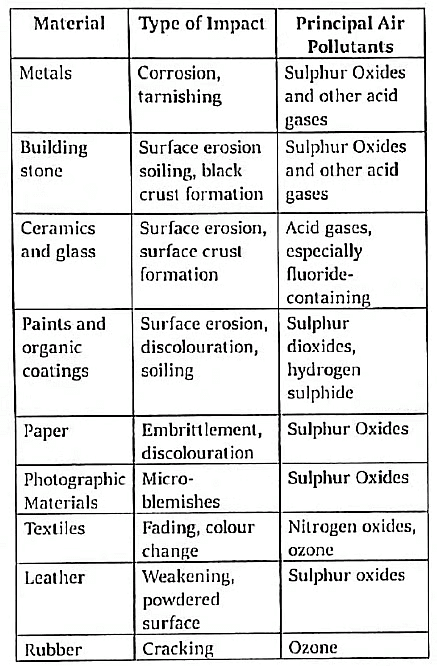
G. Socio-economic Impacts of Acid Rain: The detrimental effects of acid rain on agriculture and fishing contribute to the degradation of key life quality indicators, including Gross National Product (GNP) and per capita income. This impact is particularly pronounced in predominantly agricultural and developing nations such as India.
Trigger Effect of Acid Rain on Pollutants
Mercury
- Methyl mercury and related alkyl mercurial compounds accumulate in edible fish tissue.
- Acid deposition may enhance the partitioning of methyl mercury into the water column.
- Use of lime effectively reduces mercury levels in fish.
Aluminium
- Acidified waters leach substantial amounts of aluminum from watersheds.
- Even at low levels, aluminum is linked to dialysis dementia, especially in those with impaired kidney function.

Cadmium
- Enters drinking water supply through corrosion of galvanized pipes or copper-zinc solder.
- A decrease in water pH (from 6.5 to 4.5) results in a fivefold increase in cadmium, potentially causing renal tubular damage.
Lead
- Fetuses and infants are highly susceptible to drinking water lead contamination.
- High blood lead levels in children (>30 µg/mL) induce biochemical and neurophysiological dysfunction.
- Lower-than-normal blood lead levels can cause mental deficiencies and behavioral problems.
Asbestos
- Asbestos in natural rock can be released by acidic waters.
Control Measures
- Implementing buffering techniques: Adding neutralizing agents like lime (calcium oxide and calcium carbonate) to acidified water to increase pH.
- Reducing SO2 emissions: Burn less fossil fuel, use alternative energy sources (tidal, wind, hydropower), employ low sulfur fuel, and apply desulfurization methods.
- Decreasing NOx emissions: Modify engines in power stations.
- Controlling SOx emissions: Convert to sulfuric acid, elemental sulfur, or neutralize for use in manufacturing other products.
 Industrialisation
Industrialisation
Categorization of Industrial Sectors
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has devised criteria for categorizing industrial sectors into Red, Orange, Green, and White categories.
- The categorization is based on the Pollution Index, a numerical value (0 to 100) derived from factors such as emissions (air pollutants), effluents (water pollutants), hazardous waste generation, and resource consumption.
- The Pollution Index (PI) signifies the degree of pollution load, with a higher PI indicating increased pollution from the industrial sector.
- The re-categorization process is a scientific exercise aimed at addressing challenges in the old categorization system, which did not accurately reflect industries' pollution levels.
- The newly introduced White category, representing practically non-polluting industries, does not require Environmental Clearance (EC) and Consent. This facilitates obtaining financing from lending institutions.
- No industries in the Red category, indicating higher pollution levels, will typically be permitted in ecologically fragile or protected areas.


















