Shankar IAS Summary: Environmental Impact Assessment - 2 | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Indian Policies Requiring EIA |

|
| The EIA Cycle and Procedures |

|
| Salient Features of the 2006 Amendment |

|
| Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification 2020 |

|
Introduction
Environmental protection and sustainable development have served as the fundamental principles guiding the policies and procedures regulating industrial and other developmental activities in India.
The Need For EIA
- Every human-made activity has an impact on the environment, often leaning towards harm rather than benefit.
- Despite this, contemporary human development relies on these activities for necessities such as food and security.

- Therefore, there is a vital need to align developmental activities with environmental concerns.
- Ensuring the sustainability of development options under consideration is highly desirable.
- To achieve this, it is crucial to identify and characterize environmental consequences early in the project cycle.
- These consequences should be incorporated into the project design to create a harmonious balance between development and environmental well-being.
Environmental Impact Assessment(EIA)
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a crucial tool for planners, aiming to align development activities with environmental concerns.
- EIA seamlessly integrates environmental considerations from the initiation phase, preparing feasibility reports.
- This integration allows for the inclusion of environmental concerns and mitigation measures during project development.
- EIA plays a preventative role, potentially avoiding future liabilities or costly alterations in project design.

- The primary objective of EIA is to anticipate and address potential environmental issues during the project's planning and design stages.
- EIA, coupled with an Environment Management Plan (EMP), assists planners and government authorities in decision-making by identifying key impacts and formulating mitigation measures.
- Widely recognized as an integral component of sound decision-making, EIA is an accepted planning tool.
- The Ministry of Environment & Forests (MOE&F) has implemented policy initiatives and legislation to prevent indiscriminate exploitation of natural resources.
- These efforts aim to promote the integration of environmental concerns in developmental projects.
- The Notification on Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) of developmental projects in 1994, under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, is a significant stride in this direction.
Indian Policies Requiring EIA
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in India began in 1976-77 when the Planning Commission tasked the Department of Science and Technology with evaluating river-valley projects for environmental considerations.
Initially, the assessment covered projects requiring approval from the Public Investment Board, but these were administrative decisions lacking legislative support.
In 1986, the Government of India enacted the Environment (Protection) Act to address environmental concerns comprehensively.
As part of the Act's objectives, a decision was made to make environmental impact assessment a statutory requirement.

Under the Environment (Protection) Act of 1986, the Government issued various notifications related to specific geographical areas, extending beyond the general EIA.
These notifications included prohibitions on industries within specific belts, restrictions in ecologically sensitive regions, and the classification of coastal stretches as coastal regulation zones with corresponding prohibitions.
Notable instances include restrictions in the Raigarh district of Maharashtra, the Doon Valley, coastal regulation in various stretches, Dahanu Taluka in Maharashtra, specified areas in the Aravalli Range, and the north-western region of Numaligarh in Assam.
The measures aimed to regulate industrial and other activities that could lead to pollution and congestion, providing a comprehensive framework for environmental protection in diverse regions.
The EIA Cycle and Procedures
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process in India comprises the subsequent stages:
Screening
- The screening process is conducted to determine whether a project necessitates environmental clearance in accordance with statutory notifications. Screening criteria are based on:
- Scales of investment,
- Type of development, and
- Location of development.
- A project requires statutory environmental clearance only if the provisions of the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) notification and/or one or more statutory notifications mentioned above encompass it.
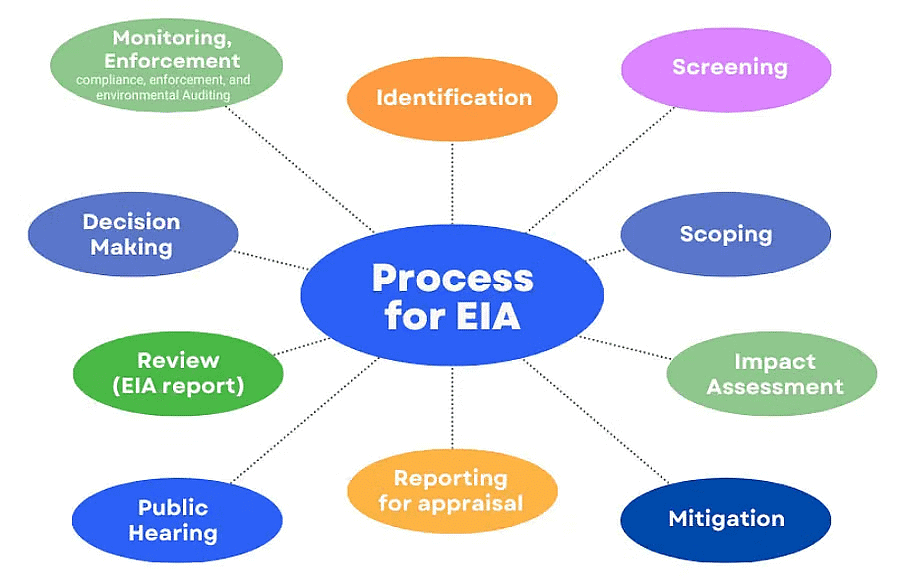
Scoping
Scoping involves detailing the terms of reference for the EIA. This task is undertaken by the consultant in collaboration with the project proponent, with guidance, if necessary, from the Impact Assessment Agency.
The Ministry of Environment and Forests has issued sector-wise guidelines (comprehensive terms of reference) delineating significant issues to be addressed in EIA studies.
Quantifiable impacts are assessed based on magnitude, prevalence, frequency, and duration, while non-quantifiable impacts (e.g., aesthetic or recreational value) are evaluated through socio-economic criteria.
Once areas with potentially significant impacts are identified, the baseline status of these areas should be monitored. Subsequently, predictions should be made regarding the anticipated changes in these areas due to the construction and operation of the proposed project.
Baseline Data
Impact Prediction
Impact prediction involves mapping the environmental consequences of the significant aspects of the project and its alternatives. Predicting environmental impact can never be done with absolute certainty, underscoring the importance of considering all possible factors and taking precautions to reduce uncertainty to the greatest extent possible.

The project's impacts should undergo assessment in the following categories:
Air
- Changes in ambient levels and ground-level concentrations resulting from total emissions from point, line, and area sources.
- Effects on soils, materials, vegetation, and human health.
Noise
- Changes in ambient levels due to noise generated by equipment and vehicle movement.
- Effects on fauna and human health.
Water
- Availability to competing users.
- Changes in quality.
- Sediment transport.
- Ingress of saline water.
Land
- Changes in land use and drainage patterns.
- Changes in land quality, including the effects of waste disposal.
- Changes in shoreline/riverbank and their stability.
Biological
- Deforestation/tree-cutting and shrinkage of animal habitat.
- Impact on fauna and flora (including aquatic species, if any) due to contaminants/pollutants.
- Impact on rare and endangered species, endemic species, and migratory paths/routes of animals.
Impact on Breeding and Nesting Grounds
1. Socio-Economic: Effect on the local community, involving demographic alterations.
2. Impact on Economic Status:
- Impact on human health.
- Impact of increased traffic.
 Breeding and Nesting Grounds
Breeding and Nesting Grounds
Assessment of Alternatives, Delineation of Mitigation Measures and Environmental Impact Assessment Report
Identify and compare potential alternatives for both project location and process technologies, considering a no-project option. Rank alternatives to select the most environmentally favorable option.
Develop a mitigation plan for the chosen option, supplemented with an Environmental Management Plan (EMP) for enhanced environmental practices. The EMP is crucial for monitoring clearance conditions, with detailed monitoring specifics included.
Provide clear information in the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report on different environmental scenarios:
- Without the project.
- With the project.
- With project alternatives. Transparently present uncertainties associated with the assessment.
Public Hearing
Legal provisions mandate that the public be notified and engaged in the evaluation of a proposed development following the conclusion of the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report.
Anyone anticipated to be impacted by the proposed project has the right to obtain the Executive Summary of the EIA. Potentially affected individuals may encompass:
- Genuine local residents.
- Local associations.
- Environmental groups actively engaged in the area.
- Any other individual situated at the project site or sites of displacement.

Environmental Groups
These individuals are entitled to present oral or written suggestions to the State Pollution Control Board, providing them with an opportunity to contribute to the decision-making process.
Environment Management Plan
- Delineation of mitigation and compensation measures for all identified significant impacts.
- Delineation of unmitigated impacts.
- Physical planning, including a work program, time schedule, and locations for implementing mitigation and compensation systems.
- Financial planning for implementing mitigation measures demonstrated through budgetary estimates and inclusion in the project budget.
Decision Making
- The decision-making process involves consultation between the project proponent (assisted by a consultant) and the impact assessment authority (assisted by an expert group if necessary).
- The decision on environmental clearance is reached through several steps, including the evaluation of the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Environmental Management Plan (EMP).
Monitoring the Clearance Conditions
- Monitoring should occur during both the construction and operation phases of a project. This is not only to ensure compliance with commitments but also to observe whether the predictions in the EIA reports were accurate.
- In cases where impacts exceed predicted levels, corrective action should be taken. Monitoring enables the regulatory agency to review the validity of predictions and the conditions of implementing the Environmental Management Plan (EMP).
Salient Features of the 2006 Amendment
These features include the decentralization of environmental clearance for developmental projects into two categories: Category A and Category B.
- Category A Projects:
- Appraised at the national level by the Impact Assessment Agency (IAA) and the Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC).

- Appraised at the national level by the Impact Assessment Agency (IAA) and the Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC).
- Category B Projects:
- Appraised at the state level by the State Level Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and State Level Expert Appraisal Committee (SEAC).
After the 2006 Amendment, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) cycle involves four stages:
- Screening
- Scoping
- Public hearing
- Appraisal
Category A projects necessitate mandatory environmental clearance and do not undergo the screening process. On the other hand, Category B projects undergo the screening process and are classified into two types:
- Category B projects (Mandatory requires EIA)
- Category B projects (Do not require EIA)
While Category A projects and Category B projects (Mandatory requires EIA) undergo the complete EIA process, Category B projects (Do not require EIA) are excluded from the complete EIA process.
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification 2020
The Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification 2020, introduced under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), replaces the 2006 notification.
Key provisions of the 2020 EIA Notification include:
- Reduction of the public hearing period from 30 to 20 days.
- Exemption of certain project classifications (A, B1, and B2) from public scrutiny.
- Changes in post-clearance compliance reporting, transitioning from semi-annual to annual submissions.
- Requirement for project proponents to exclusively prepare the EIA report.
- Omission of reporting violations and non-compliance by the public.
- Introduction of post-facto clearance, allowing projects operating without prior environmental clearance to apply for it.
- Imposition of penalties on firms found violating their establishment terms.
|
97 videos|203 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Environmental Impact Assessment - 2 - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the Indian policies that require Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)? |  |
| 2. What is the EIA Cycle and Procedures? |  |
| 3. What are the salient features of the 2006 Amendment to the EIA Notification? |  |
| 4. What is the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification 2020? |  |
| 5. How does the EIA help in environmental decision-making? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|





















