Science & Technology - 5 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Deepfakes |

|
| Wi-Fi 7 Technology |

|
| CAR-T Cell Therapy |

|
| Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership |

|
| Ultra-processed Food |

|
Deepfakes
A fact-checking website recently revealed that a widely circulated video featuring an actor entering an elevator was, in fact, a deepfake. This discovery triggered significant discussions, prompting other actors to advocate for legal measures to address the proliferation of deepfake content.
- In response, the Minister of State for Electronics and Information Technology highlighted potential regulations within the IT Act, 2000, aimed at curbing the dissemination of such deceptive videos.
- Nevertheless, a comprehensive strategy for deepfake regulation should consider the synergies between platform governance and Artificial Intelligence (AI) regulations, while also devising safeguards for the broader integration of emerging technologies.
What are the Uses of Deepfake Technology?
- Film Dubbing: Deepfake technology can be used to create realistic lip-syncing for actors who speak different languages, making the film more accessible and immersive for global audiences.
- For example, a video was created to launch a petition to end malaria, where celebrities like David Beckham, Hugh Jackman, and Bill Gates spoke in different languages using deepfake technology.
- Education: Deepfake technology can help teachers deliver engaging lessons by bringing historical figures to life in the classroom, or creating interactive simulations of different scenarios.
- For example, a deepfake video of Abraham Lincoln giving his Gettysburg Address could be used to teach students about the American Civil War.
- Art: Deepfake technology can be used as a creative tool for artists to express themselves, experiment with different styles, or collaborate with other artists.
- For example, a deepfake video of Salvador Dali was created to promote his museum in Florida, where he interacted with visitors and commented on his artworks.
- Autonomy and Expression: Deepfake technology can empower people to control their own digital identity, protect their privacy, or express their identity in different ways.
- For example, a deepfake app called Reface allows users to swap their faces with celebrities or characters in videos or gifs, for fun or personalization.
- Amplification of the Message and its Reach: Deepfake technology can help amplify the voice and impact of people who have important messages to share, especially those who face discrimination, censorship, or violence.
- For example, a deepfake video of a journalist who was killed by the Saudi government was created to deliver his final message and call for justice.
- Digital Reconstruction and Public Safety: Deepfake technology can help reconstruct missing or damaged digital data, such as restoring old photos or videos, or enhancing low-quality footage.
- It can also help improve public safety by creating realistic training materials for emergency responders, law enforcement, or military personnel.
- For example, a deepfake video of a school shooting was created to train teachers on how to react in such a situation.
- Innovation: Deepfake technology can spur innovation in various fields and industries, such as entertainment, gaming, or marketing. It can enable new forms of storytelling, interaction, diagnosis, or persuasion.
- For example, a deepfake video of Mark Zuckerberg was created to demonstrate the potential of synthetic media and its implications for society.
What are the Challenges Associated with Deepfake Technology?
- Dissemination of False Information: Deepfakes have the potential to deliberately spread false information or misinformation, leading to confusion on critical issues. For instance, deepfake videos featuring politicians or celebrities may be employed to sway public opinion or influence elections.
- Harassment and Intimidation: Deepfakes can be crafted with the intention to harass, intimidate, belittle, and undermine individuals. An unethical application of this technology includes the creation of revenge porn, disproportionately affecting women. Deepfake porn infringes on privacy and consent, causing psychological distress and trauma.
- Blackmail and Ransom: Deepfake technology can be exploited to generate materials for blackmail or ransom, such as fake videos depicting someone engaging in criminal activities, having an affair, or being in jeopardy. A notable example involves a deepfake video of a politician being used to extort money in exchange for not making it public.
- Fabrication of Evidence: Deepfakes can be instrumental in fabricating evidence, potentially defrauding the public or compromising state security. This form of evidence manipulation can also influence legal proceedings or investigations. Instances include the use of deepfake audio or video to impersonate someone's identity or voice, making false claims or accusations.
- Tarnishing Reputations: Deepfakes can create nonexistent images or videos of individuals, portraying them saying or doing things they have never done. Synthesizing a person's voice in an audio file can be employed to tarnish reputations. This misuse of deepfake media may damage the credibility or trustworthiness of individuals or organizations, resulting in reputational or financial losses.
- Financial Frauds: Deepfake technology can be leveraged to impersonate executives, employees, or customers, manipulating them into disclosing sensitive information, transferring funds, or making erroneous decisions. A case in point involves a deepfake audio of a CEO being used to deceive an employee into wiring USD 243,000 to a fraudulent account.
What Should be done to Address the Menace of Deepfakes?
- Learning from Other Countries: The life cycle of deepfakes can be divided into three parts – creation, dissemination and detection. AI regulation can be used to mitigate the creation of unlawful or non-consensual deepfakes.
- One of the ways in which countries such as China are approaching such regulation is to require providers of deepfake technologies to obtain consent of those in their videos, verify the identities of users, and offer recourse to them.
- The Canadian approach to prevent harm from deepfakes includes mass public awareness campaigns and possible legislation that would make creating and distributing deepfakes with malicious intent illegal.
- Adding Watermarks to all AI-generated Videos: Adding watermarks to AI-generated videos is essential for effective detection and attribution. Watermarks reveal the content's origin and ownership, serving various purposes. They aid in attribution by clarifying the content's creator or source, especially when shared in different contexts.
- Visible watermarks also act as a deterrent against unauthorized use, making it clear that the content can be traced back to its source.
- Furthermore, watermarks support accountability by providing evidence of the original creator's rights, simplifying the enforcement of copyright and intellectual property protections for AI-generated content.
- Deterring Users to Upload Inappropriate Content: Online platforms should take steps to educate and inform users about their content policies, and perhaps implement measures to deter the upload of inappropriate content.
- Developing and Improving Deepfake Detection Technologies: This can involve using more sophisticated algorithms, as well as developing new methods that can identify deepfakes based on their context, metadata, or other factors.
- Strengthening Digital Governance and Legislation: This can involve creating clear and consistent laws and policies that define and prohibit the malicious use of deepfakes, as well as providing effective remedies and sanctions for the victims and perpetrators of digital harm.
- Enhancing media Literacy and Awareness: This can involve educating the public and the media about the existence and potential impact of deepfakes, as well as providing them with the skills and tools to verify and report suspicious content.
- Promoting Ethical and Responsible use of Deepfake Technology: This can involve establishing and enforcing codes of conduct and standards for the creators and users of deepfake technology, as well as encouraging its positive and beneficial applications.
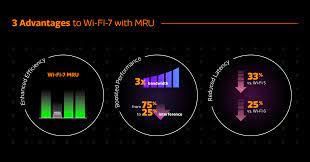
Wi-Fi 7 Technology
Wi-Fi stands as a wireless networking technology facilitating the connection of computers (both laptops and desktops), mobile devices (such as smartphones and wearables), and various other devices like printers and video cameras to the Internet. This technology empowers these devices and others to engage in communication, establishing an interconnected network.
What is Wi-Fi Technology?
- Wi-Fi, as defined by the Wi-Fi Alliance, refers to "wireless local area network (WLAN) products based on the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers' (IEEE) 802.11 standards." However, since the majority of modern WLANs adhere to these standards, the term "Wi-Fi" is commonly used interchangeably with "WLAN." Wi-Fi serves as a wireless networking technology utilized for data exchange among two or more devices.
- Initially designed for mobile computing devices like laptops, Wi-Fi has expanded its applications to include various consumer electronics such as televisions, DVD players, and digital cameras. A wireless network access point facilitates the connection of these devices to a network resource, such as the Internet. An access point or hotspot of this nature typically covers an indoor range of about 20 meters (66 feet) and an extended range outdoors.
- Wi-Fi technology eliminates the need for cables or wiring, enabling local area networks to operate wirelessly. Its popularity is on the rise for both home and business networks. In a Wi-Fi network, a computer's wireless adapter converts data into a radio signal, transmitted via an antenna. The setup involves a wireless router directly connected to the modem, serving as a hub to broadcast the internet signal to all Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
- This configuration allows continuous internet connectivity within the network's coverage area, providing users the flexibility to stay connected as long as they are within the designated range.
Wi-Fi Technology – Working Principle
- Electromagnetic waves are used by Wi-Fi to transmit networks.
- To avoid interference and high traffic, these Wi-Fi frequencies are divided into multiple channels.
- When a user connects to the internet via his device, the requested information is converted into binary code.
- With the help of the Wi-Fi chip embedded in your devices, this binary code is further translated into wave frequencies.
- Wi0fi, among all Electromagnetic waves, uses radio waves to transmit information via frequencies between the router and your device.
- Depending on the data being sent, a frequency of 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz is used. The greater the frequency, the more data is transmitted per second.
- The following three media are available for Wi-Fi signal transmission:
- Base station/Ethernet (802.3) connection: This is the primary host network that connects the router to the internet.
- Access point: It accepts wired Ethernet connections and converts them to wireless connections. It then uses radio waves to extend the connection.
- Accessing devices: These are the physical devices that have Wi-fi and allow us to surf the internet.
- These frequencies pass through radio channels and are picked up by Wi-Fi routers connected to your device.
- These frequencies are converted into binary code by the router, which is then translated into the requested internet traffic.
- The data is then received by the router via a hardwired internet cable. This is an extremely fast process.
- The Wi-Fi range is determined by the environment, whether it is indoor or outdoor.
- Wi-Fi cards read the signals and establish an internet connection between the user and the network.
- The speed of the device connected via Wi-Fi increases as the computer gets closer to the main source and decreases as the computer gets further away.
What is a Wi-Fi Hotspot?
- Establishing a Wi-Fi hotspot involves installing an access point connected to an internet source. The access point emits a wireless signal covering a limited range, typically around 300 feet. When a Wi-Fi-enabled device, such as a Pocket PC, encounters a hotspot, it can establish a wireless connection to that network.
- Hotspots are predominantly found in public areas like airports, coffee shops, hotels, bookstores, and educational campuses. The prevalent specification for hotspots globally is 802.11b. The primary providers of public Wi-Fi networks are private internet service providers (ISPs), who charge users for internet access.
- Connecting to certain hotspots may require a WEP key for private and secure access, while open connections allow anyone with a Wi-Fi card to connect. Almost every smartphone includes a mobile hotspot feature, enabling the wireless sharing of the network connection with other devices for internet access once activated by the mobile operator.
- A particularly practical form of Wi-Fi hotspot is the mobile hotspot provided by a cell phone carrier. This portable device communicates with cellular towers to broadcast signals, offering a convenient and mobile solution for wireless connectivity.
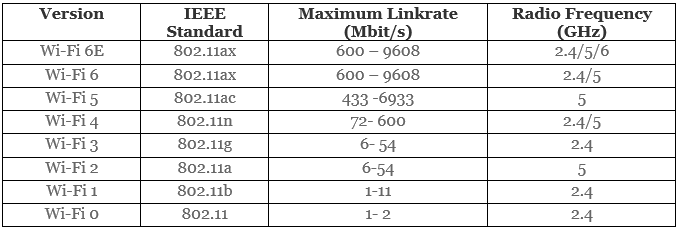
Types of Wi-Fi Standards
Wi-Fi Applications:
- Wi-Fi facilitates wireless communication, allowing tasks like streaming audio or video to various devices.
- It supports file and data sharing between multiple computers or mobile phones.
- Wi-Fi printers enable document printing wirelessly.
- Wi-Fi hotspots provide temporary internet connectivity in specific locations, utilizing the primary network connection for users of Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
- Point-to-point networks can be established using Wi-Fi, connecting challenging locations without the need for physical wiring.
- VoWi-Fi (voice-over Wi-Fi) enables calls over a home Wi-Fi network.
- Offices often connect computer systems to the internet via Wi-Fi, avoiding the need for complex wiring.
- Wi-Fi network disruptions don't result in a loss of connectivity, unlike cable breaks.
- Cities can offer network connectivity by strategically deploying Wi-Fi routers, and educational institutions have adopted Wi-Fi networks for their flexibility.
- Wi-Fi doubles as a positioning system, identifying a device's location through Wi-Fi hotspot detection.
Advantages of Wi-Fi:
- Convenience: Wireless networks allow users to access resources from almost any location within their primary environment (home or office).
- Mobility: Public wireless networks provide internet access beyond the usual work environment.
- Productivity: Users can maintain a constant network affiliation as they move between locations.
- Deployment: Setting up an infrastructure-based wireless network requires only a single access point, unlike the complexity of wiring in a traditional network.
- Expansion: Existing wireless networks can serve a large number of clients without additional wiring.
- Cost: Wireless networking hardware is only slightly more expensive than wired counterparts, with cost and labor savings from not running physical cables.
Limitations of Wi-Fi:
- Signal Range: Wi-Fi signal range is limited by obstacles, and speeds decrease with distance from the base station.
- Interference: Other devices on the same frequency, like Bluetooth, cordless phones, or microwaves, can cause interference.
- Security Concerns: Security issues, such as vulnerabilities in WEP technology, have slowed Wi-Fi adoption in businesses.
- Compatibility and Interoperability: Incompatibility issues arise among different Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11a and 802.11b) and products from different vendors.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi is a pervasive wireless networking technology that uses radio frequencies for data transfer, providing high-speed internet access without the need for cables. Offering freedom from wires, Wi-Fi allows internet connectivity from various locations, such as coffee shops, hotels, or conference rooms. Wi-Fi is significantly faster than standard dial-up connections. Wi-Fi-enabled devices, like laptops or PDAs, can wirelessly send and receive data wherever Wi-Fi access is available.
CAR-T Cell Therapy
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has recently approved the market authorization for NexCAR19, marking a significant milestone as India's inaugural indigenously-developed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell (CAR-T cell) Therapy.
- This achievement establishes India as one of the pioneering developing nations to possess its own indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
Description of NexCAR19
About:
- NexCAR19, created by ImmunoACT, an incubated company at IIT Bombay, represents an indigenous development in CAR-T and gene therapy within India. Specifically engineered to target cancer cells expressing the CD19 protein, NexCAR19 utilizes this protein as a marker on cancer cells.
- This unique mechanism enables CAR-T cells to identify and bind to cancer cells, initiating the elimination process. Notably, some developed nations rely on imports from the United States or Europe for their CAR-T therapies, underscoring the significance of India's independent development in this field.
Patient Eligibility:
- NexCAR19 therapy is designed for individuals diagnosed with B-cell lymphomas who have not responded to conventional treatments such as chemotherapy, experiencing relapse or cancer recurrence. Initially, the therapy is authorized for patients aged 15 years and above.
Procedure:
- The procedure begins with the patient donating blood at a transfusion center. Within a 7-10 day timeframe, the T-cells undergo genetic modifications and are subsequently reintroduced into the patient.
Efficacy:
- The therapy demonstrates a notable reduction in drug-related toxicities, causing minimal harm to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition referred to as neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicity may arise when CAR-T cells recognize the CD19 protein, entering the brain and potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- Additionally, the therapy results in Minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), characterized by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a substantial number of tumor cells. CAR-T cells are engineered to target and eliminate cancer cells, contributing to this syndrome.
Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership
The CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CSIR-CCMB), located in Hyderabad, is poised to join the Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP).
About the Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)
- DEEP is a groundbreaking integrated genomics and epigenomics study aimed at unraveling the genetic factors behind Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in diverse populations, including South Asians.
- The project seeks to illuminate the impact of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk observed in global populations, spanning Asia, Africa, and North and South America. It is a five-year international initiative.
- Researchers will investigate individuals representing diverse genetic and environmental contexts to discern DNA methylation patterns contributing to disease risk in each setting. The study will involve developing software, infrastructure, and conducting advanced statistical analyses to create new resources. These resources will be integrated into international health and genetics databases to analyze trends in DNA methylation variation.
Significance of the Initiative
- This research aims to identify common global disease-causing mechanisms and those unique to specific groups or regions. It addresses questions about the universality of medicines developed in one part of the world and their effectiveness for diverse populations.
- Ultimately, the DEEP study aspires to facilitate targeted interventions or treatments, thereby reducing global health disparities and inequities.
DNA Methylation:
- DNA methylation is a process wherein chemical groups attach to DNA to regulate the activation and deactivation of genes. This epigenetic modification helps the body respond to environmental signals and contributes to overall systemic health and disease status.
- Understanding the relationships between DNA methylation, genetics, and the environment is crucial for comprehending health and disease pathways and their consequences.
Ultra-processed Food
A report, co-released by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER), brings attention to a notable and troubling surge in the sales of ultra-processed foods in India over the past decade.
- The study indicates that the sales of items like chocolate and sugar confectioneries experienced a decline from 10% in 2019 to 1% in 2020 due to the pandemic but swiftly rebounded to 9% in 2021. Similarly, the retail sales of salty snacks and beverages decreased from 14% each in 2019 to 9% and 1% in 2021, respectively.
- The report forecasts that by 2032, despite a decrease in market share, ultra-processed foods such as chocolate, sugar confectioneries, salty snacks, and ready-made food will continue to dominate the market.
Concerning Ultra-processed foods
- Ultra-processed foods belong to a category of food items that have undergone extensive processing, involving multiple stages that often include the incorporation of various artificial ingredients like preservatives, colors, flavors, and additives.
- Typically, these foods have minimal whole or natural ingredients and are distinguished by their convenience, extended shelf life, and frequently addictive taste profiles.
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|