Accounting Standards | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Concept of Accounting Standards
- Significance of Accounting: Accounting is recognized as the language of business, offering comprehensive financial information about various aspects such as financial activities, position, results, trends, and future prospects. This information is communicated through financial statements to both internal and external users.
- Role of Financial Statements: Financial statements play a crucial role in conveying financial information to users. They encompass details about the nature of financial activities, current financial position, results, trends, and future prospects. The preparation and presentation of financial statements involve adhering to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to ensure consistency in the language of business communication.
- Definition of Accounting Standards: According to Kohler, accounting standards are defined as a 'code of conduct imposed on accountants by custom, law, or professional body.' These standards serve as guidelines for maintaining and preparing accounts in a uniform manner.
Nature of Accounting Standards
Accounting standards serve various roles in the accounting process:
- Guide to Accountants: They act as a guide for accountants, providing a basis for preparing accounts. For example, they specify methods for valuing inventories.
- Dictator in Accounting: Like a dictator, accounting standards mandate certain practices in accounting. Accountants are required to adhere to standards, such as the prescribed format for preparing a Cash Flow Statement.
- Service Provider: Accounting standards define terms, present accounting issues, specify standards, explain disclosures, and outline implementation dates. They serve as a descriptive service provider in the accounting field.
- Harmonizer: Accounting standards bring uniformity by removing the impact of diverse accounting practices and policies. They act as harmonizers in resolving conflicts on accounting issues and facilitating solutions for accountants.
Benefits of Accounting Standards
- Standardized Accounting: The key benefit of FASB standard setting is the promotion of a uniform set of accounting principles for businesses. The FASB establishes generally-accepted accounting principles, preventing inconsistencies in methods used by businesses. For instance, it ensures that businesses cannot switch accounting methods during a fiscal year, maintaining accuracy in financial data presented to investors.
- Problem Identification: FASB standard setting offers a framework for identifying and addressing potential accounting problems. Since all U.S. businesses adhere to the same accounting principles, any issues or deficiencies in the accounting process are promptly recognized and reported to the FASB. The FASB then investigates and, if necessary, revises or introduces new accounting rules. For example, if a certain liability reporting method is found to unfairly lower net income, businesses can appeal to the FASB to address issues with standard setting.
- Private Regulation: The FASB, as a private entity independent of the U.S. government, plays a crucial role in setting accounting rules for all U.S. companies. While the SEC could theoretically establish its own accounting oversight board or government agency, relying on the FASB allows the private sector to dictate accounting rules, relieving the U.S. government of this responsibility.
- International Accounting Standard: The FASB is advantageous in actively promoting a globally recognized set of accounting rules. Given the interconnected nature of foreign financial markets due to globalization, having a standard set of accounting rules contributes to more accurate and fair financial reporting across countries. Collaborating with the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), one of the goals of the FASB is to achieve greater uniformity in global financial reporting.
Procedure for issuing as in India
- Determination of the Need for an AS: Initially, the Accounting Standard Board identifies the broad areas where the formulation of accounting standards is deemed necessary.
- Constituting Study Group: A Study Group is formed, comprising members of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, to assist the Accounting Standard Board in its activities.
- Drafting the Standard: The Study Group prepares a draft of the proposed standard, covering aspects such as the objective, scope, definitions, recognition and measurement principles, as well as presentation and disclosure requirements.
- Analyzing the Draft: The Accounting Standard Board reviews the preliminary draft from the Study Group. If revisions are needed, the Board takes steps to make necessary changes and refers the draft back to the Study Group.
- Circulation of the Draft: The Accounting Standard Board circulates the draft to the council members of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India and various specified bodies, including the Institute of Works & Cost Accountants of India, the Institute of Company Secretaries of India, Ministry of Company Affairs, Comptroller & Auditor General of India, Central Board of Direct Taxes, and others, for their comments.
- Holding Discussion and Finalizing Exposure Draft: The ASB conducts meetings with representatives of the aforementioned bodies to gather their views on the draft standard. Based on the discussions and analyses, the ASB finalizes the exposure draft of the proposed accounting standards.
- Circulation of Exposure Draft: The exposure draft of the proposed standards is issued for comments from members of the ICAI and the general public.
- Finalizing the Exposure Draft: Considering the received comments, the ASB finalizes the draft of the proposed standards. Subsequently, the ASB submits the finalized draft to the council of the ICAI.
- Modifying & Issuing the Accounting Standard: The council of the ICAI reviews the finalized draft, and if necessary, makes modifications in consultation with the ASB. The ICAI then issues the Accounting Standard, incorporating any modifications deemed necessary on the relevant subject.
Salient features of first time adoption of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind-AS): 101
- Introduction to Ind-AS 101: Ind-AS 101 outlines the rules for companies when they first start using Ind-AS. This happens when they switch from creating financial statements based on Indian Accounting Standards (Indian GAAP) to following Ind-AS.
- Transition Period Requirements: During the transition period, companies adopting Ind-AS for the first time need to fulfill specific requirements laid out in Ind-AS 101.
- Retrospective Application: Ideally, companies should apply Ind-AS retrospectively when transitioning from Indian GAAP. However, for a smoother transition, Ind-AS 101 provides some exemptions. These exemptions fall into two categories: mandatory (where the company must not apply Ind-AS retrospectively) and voluntary (where it's the company's choice to apply certain Ind-AS requirements retrospectively or not).
- Presentation and Disclosure: Ind-AS 101 includes rules for how companies should present and disclose information about the transition in their financial statements. This is to help users, like investors, understand the change.
- Impact on Financial Statements: Companies are required to explain how the transition to Ind-AS will affect their reported balance sheet, financial performance, and cash flows. This ensures transparency about the impact of the change.
- No Exemption from Other Ind-AS Disclosures: It's important to note that while there are exemptions for certain aspects in the transition, there are no exemptions from the disclosure requirements outlined in other Ind-AS. Companies still need to provide necessary information as per those standards.
- Summary: Ind-AS 101 guides companies in transitioning to Ind-AS from Indian GAAP. It offers exemptions for a smoother transition, outlines presentation and disclosure rules, and requires explanations on how the change impacts financial statements. Importantly, it emphasizes transparency, ensuring that companies disclose necessary information for users to understand the transition.
Objective of Ind-AS 101
The aim of Ind-AS 101 is to guarantee that an organization's initial Ind-AS Financial Statements, along with its interim financial reports during the corresponding period, present information of excellent quality that:
- Ensures transparency for users and comparability across all reported periods,
- Establishes a fitting foundation for accounting in accordance with the Indian Accounting Standards (Ind-AS), and
- Can be produced at a cost that is justified by the resulting benefits.
Scope of Ind-AS 101
An organization is required to adhere to Indian Accounting Standard-101 (First-time Adoption of Indian Accounting Standards) under the following circumstances:
- When preparing its initial Financial Statements subsequent to the implementation of Ind-AS.
- In each Interim Financial Report, following the guidelines of Ind-AS 34 Interim Financial Reporting, for the portion of the period encompassed by its inaugural Ind-AS Financial Statements.
International Financial Reporting Standards
- Purpose of Accounting:
- Accounting is like a common language used by companies, investors, and regulators to explain how well a business is doing financially.
- It provides a standardized way to describe a company's financial performance.
- Accounting Standards:
- These are a set of rules that guide companies when preparing their financial statements.
- They ensure consistency in how financial information is presented in the market.
- Legal Requirement for Public Companies:
- Companies listed on stock exchanges must legally publish financial statements following specific accounting standards.
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS):
- IFRS is a global set of accounting rules created by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
- It allows for consistent financial reporting globally, making it easier to compare companies internationally.
- Global Applicability:
- IFRS is used by over 100 countries, including the European Union and two-thirds of the G20 nations.
- It enables investors to compare the financial performance of companies worldwide on a level playing field.
- Support for IFRS:
- The G20 and other international organizations consistently endorse the mission of the International Accounting Standards Board in creating global accounting standards.
Need and Procedure of IFRS
- Globalization Impact on Financial Standards:
- The widespread globalization of financial markets and companies has led to the adoption of a single set of financial reporting standards globally.
- This approach enhances the comparability of financial statements across different countries.
- Consolidated Financial Statements Benefits:
- Utilizing a uniform set of standards reduces the costs associated with preparing consolidated financial statements for groups of companies operating worldwide.
- Post-Banking Crisis Focus on Standards:
- Financial reporting standards, particularly those related to the fair value measurement of financial assets and liabilities, gained attention following the banking crisis.
- G20 Leaders' Directive:
- In September 2009, G20 leaders in Pittsburgh directed the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and its US counterpart, the FASB, to collaborate on developing a single set of high-quality global accounting standards by June 2011.
- Challenges in Convergence:
- Although convergence towards a single set of standards was targeted, it has proven to be challenging and is likely to face delays.
- Development of IFRS:
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are crafted through a global consultation process known as the "due process," involving individuals and organizations worldwide.
- The due process includes six stages, with the IFRS Foundation Trustees overseeing compliance at various points, such as setting the agenda, project planning, publishing Discussion Papers and Exposure Drafts, and issuing the final Standard.
- Procedures after a Standard is issued are also part of the comprehensive due process.
The IFRS issued by IASB and the corresponding Ind- AS are given below: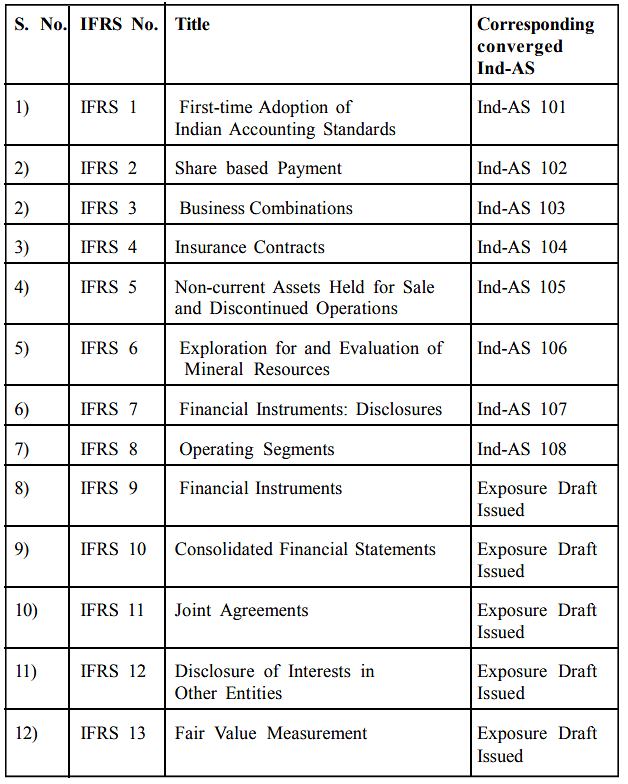
Convergence to IFRS
- Options for IFRS Implementation:
- Adoption:
- Country accepts IFRS without any alterations.
- No changes allowed in language or format as set by IASB.
- Convergence:
- Implementing IFRS with adjustments to suit a country's needs.
- India's Decision:
- India chooses to converge its existing accounting standards with IFRS, known as Ind-AS.
- Adoption:
- Challenges in Convergence:
- Fair Value Concept:
- Ind-AS relies on fair value measurement for assets and liabilities.
- Corresponding standards under the Income Tax Act are crucial for a smooth transition.
- Draft Income Computation and Disclosure Standards released by the Ministry of Finance in January 2015 are in the finalization stage.
- Exclusion of Sectors:
- Banks and Insurance Companies are excluded from the transition roadmap due to specific sector needs and concerns.
- Various Challenges:
- Challenges include compliance costs, capacity building, managing two sets of standards, and addressing exceptions or 'carve outs.'
- Coordination among MCA, DPE, and ICAI is crucial to effectively handle these issues.
- Fair Value Concept:
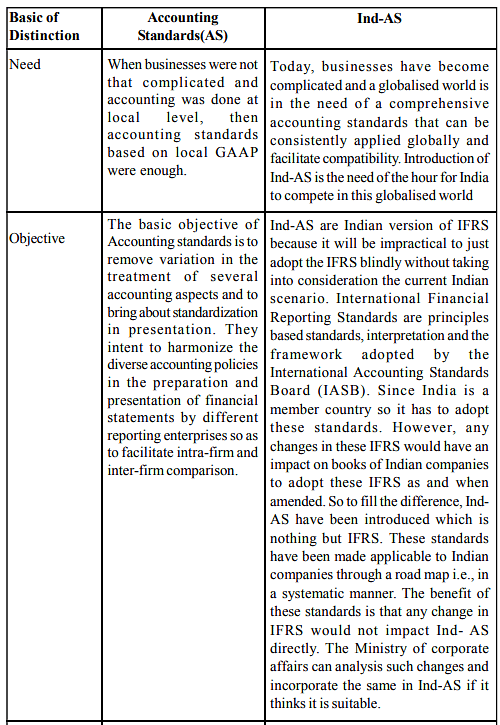
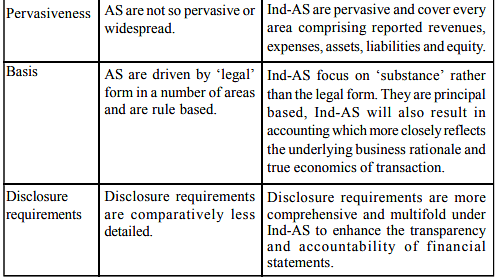
Distinction between Indian as and International
- Introduction to Accounting Standards and Ind-AS: Detailed differences between Accounting Standards and Ind-AS exist, impacting various industries and companies differently.
- Government Notification on Ind-AS: The Indian government has issued a notification outlining specific Ind-AS. Here is the list:
- Ind-AS 1: Presentation of Financial Statements
- Ind-AS 2: Inventories
- Ind-AS 7: Statement of Cash Flows
- Ind-AS 8: Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates, and Errors
- Ind-AS 10: Events after the Reporting Period
- Ind-AS 11: Construction Contracts
- Ind-AS 12: Income Taxes
- Ind-AS 16: Property, Plant and Equipment
- Ind-AS 17: Leases
- Ind-AS 18: Revenue
- Ind-AS 19: Employee Benefits
- Ind-AS 20: Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance
- Ind-AS 21: The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
- Ind-AS 23: Borrowing Costs
- Ind-AS 24: Related Party Disclosures
- Ind-AS 27: Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements
- Ind-AS 28: Investments in Associates
- Ind-AS 29: Financial Reporting in Hyper-inflationary Economies
- Ind-AS 31: Interests in Joint Ventures
- Ind-AS 32: Financial Instruments: Presentation
- Ind-AS 33: Earnings per Share
- Ind-AS 34: Interim Financial Reporting
- Ind-AS 36: Impairment of Assets
- Ind-AS 37: Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
- Ind-AS 38: Intangible Assets
- Ind-AS 39: Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement
- Ind-AS 40: Investment Property
Measurement of Business Income
- Concept of Income:
- One of the key accounting concepts is the "Concept of Income."
- For businesses, income refers to payments received for services or goods.
- Business Income:
- "Business Income" is the surplus revenue remaining after deducting incurred expenses.
- Measurement of Business Income:
- Two crucial factors in estimating income are revenues and expenses.
- Revenues:
- Generated through the sale of goods and services to customers.
- It represents the consideration received by the business for its services and goods.
- Expenses:
- Expenses are costs that have been consumed in the process of generating revenue.
- They indicate how assets decrease due to services performed by the business.
- Measurement of Revenue:
- Revenue measurement follows the accrual concept.
- Revenue is earned when realized, not necessarily when received in cash.
- Measurement of Expenses:
- Direct expenses, like delivery of goods, directly link to revenue.
- Indirect expenses, such as rent and office salaries, have an indirect association with revenue.
- Types of Expenditure:
- Expenses of the current year.
- Expenditure made before the current period but becomes an expense in the current year.
- Expenditure made this year but becomes an expense in future accounting periods, like purchasing fixed assets and depreciation.
- Expenses of the current year paid in future accounting years, known as outstanding expenses.
|
196 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Accounting Standards - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the benefits of implementing Accounting Standards? |  |
| 2. How are Accounting Standards issued in India? |  |
| 3. What are the salient features of first-time adoption of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind-AS): 101? |  |
| 4. What is the procedure for convergence to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)? |  |
| 5. What is the distinction between Indian Accounting Standards (Ind-AS) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)? |  |





















