Capital Budgeting | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Capital budgeting involves assessing investments and significant expenses to achieve optimal returns on investment. It encompasses decisions to allocate funds for projects where anticipated outcomes occur over a period longer than one year. Additionally, capital budgeting covers decisions related to divestment, such as selling off an entire business or a portion of it.
Objectives of Capital Budgeting:
- Choosing financially rewarding projects
- Managing capital expenditures effectively
- Identifying suitable funding sources
Capital Budgeting Process
Initiating Project Identification:
- The initial phase of capital budgeting involves creating investment proposals. Businesses may pursue investments for diverse reasons.
Project Screening and Assessment:
- This stage entails establishing appropriate criteria to evaluate proposals, aligning with the firm's goal of enhancing market value. Utilizing concepts like the time value of money aids in this evaluation process.
Project Approval:
- The method of selecting investment proposals varies among businesses, as each may have unique needs and priorities.
Execution:
- Funds are allocated and the proposal is put into action. Responsibilities are assigned for executing the proposals, ensuring timely project completion, and controlling costs.
Performance Evaluation:
- The last phase of capital budgeting entails comparing actual outcomes with predetermined standards. Any unfavorable results are pinpointed, and addressing project challenges aids in refining future proposal selection and execution.
Importance of Capital Budgeting
- Capital budgeting serves as a critical instrument in financial management.
- It offers financial managers a comprehensive framework to assess various projects' viability for investment.
- It illuminates the risks and uncertainties associated with different projects.
- It aids in preventing over or under-investment.
- Management gains effective control over the costs of capital expenditure projects.
- Ultimately, the fate of a business hinges on how efficiently available resources are utilized.
Capital Budgeting Methods
Traditional Approaches
- Payback Period
- Accounting Rate of Return Method
Discounted Cash Flow Methods
- Net Present Value Method
- Profitability Index Method
- Internal Rate of Return
Payback Period Method
The Payback Period Method, as implied by its name, denotes the duration required for the project's cash flows to cover the initial investment. This approach focuses solely on cash inflows, the project's economic lifespan, and the initial investment without regard for the time value of money. However, since it relies on a rule of thumb, it overlooks the significance of the time value of money and other profitability aspects.
The formula for calculating the payback period is:
- Payback Period = Initial Investment / Annual Cash Inflow
Accounting rate of return method (ARR)
This approach serves to address the drawbacks associated with the payback period method. The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is the average annual net income anticipated from an asset, divided by its average capital cost, expressed as a percentage. It is a formula employed in making decisions regarding capital budgeting, particularly in scenarios where companies must determine whether to proceed with a specific investment (such as a project or acquisition) based on the projected future net earnings compared to the capital cost. However, similar to the payback period method, ARR also neglects the time value of money and fails to consider the project's lifespan. Additionally, it may not align with the firm's objective of maximizing shareholder wealth.
The formula for ARR is:
- ARR = Average Income / Average Investment
Discounted cash flow method
The discounted cash flow method involves assessing the cash inflows and outflows over the lifespan of an asset. These cash flows are then discounted using a discounting factor. By comparing the discounted cash inflows with the outflows, this method incorporates the interest factor and evaluates the return beyond the payback period.
Net Present Value (NPV) Method
The Net Present Value (NPV) Method is a commonly employed approach for assessing capital investment proposals. It involves discounting the expected cash inflows at various time intervals using a specific rate. The present values of these cash inflows are then compared to the initial investment. A positive difference indicates acceptance, while a negative difference leads to rejection.
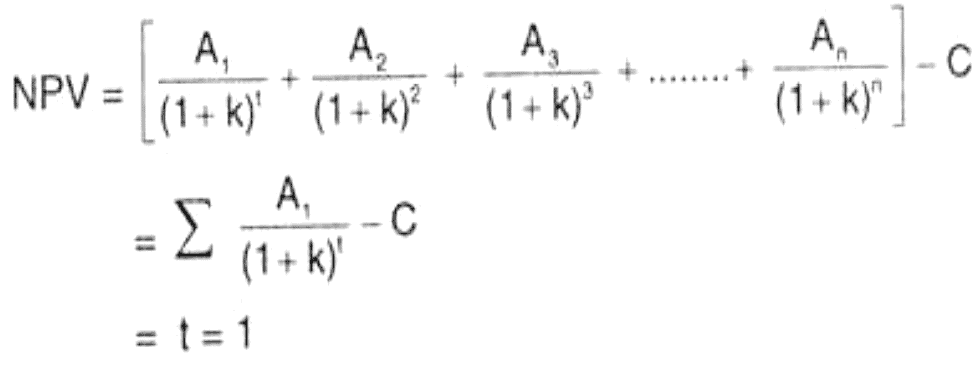
In the equation, A1, A2,... denote the cash inflows, K represents the firm's cost of capital, C signifies the cost of the investment proposal, and n denotes the expected lifespan of the proposal. It's crucial to recognize that the cost of capital, K, is presumed to be fixed; otherwise, the net present value cannot be determined.
The NPV formula is expressed as follows:
NPV = PVB – PVC
Here,
- PVB represents the present value of benefits, and
- PVC denotes the present value of costs.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is the rate at which the net present value of the investment becomes zero. It occurs when the discounted cash inflow equals the discounted cash outflow. This method acknowledges the time value of money and aims to determine the interest rate at which the funds invested in the project could be fully recovered from the cash inflows. Nonetheless, calculating the IRR can be a complex and time-consuming process.
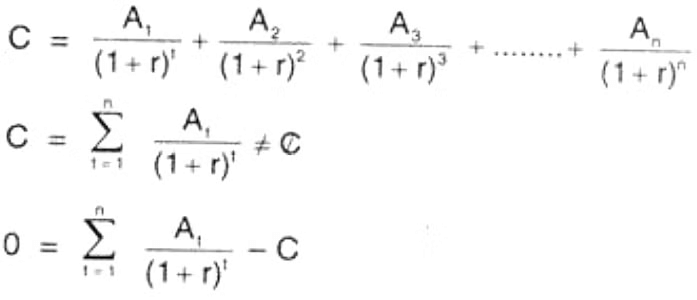
If IRR > WACC then the project is profitable.
- If IRR > k = accept
- If IR < k = reject
Profitability Index (PI)
Profitability Index (PI) is the ratio of the present value of future cash benefits, considering the required rate of return, to the initial cash outflow of the investment. It can be either gross or net, where the net index is simply the gross index minus one. The formula to compute the Profitability Index (PI) or Benefit-Cost (BC) ratio is as follows:
- PI = Present Value of Cash Inflows / Initial Cash Outlay.
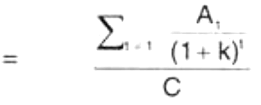
- PI = NPV (benefits) / NPV (Costs)
- All projects with PI > 1.0 is accepted
|
196 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Capital Budgeting - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is capital budgeting and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods used in capital budgeting? |  |
| 3. What is the Payback Period method in capital budgeting? |  |
| 4. What is the Net Present Value (NPV) method in capital budgeting? |  |
| 5. What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) method in capital budgeting? |  |
















