Techniques of Cost Control and Cost Reduction | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Cost Control |

|
| Cost Reduction |

|
| Difference between Cost Control and Cost Reduction |

|
| Cost Management |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
- Many businesses aim to maximize profits, a goal achievable through minimizing production costs. To achieve this, management employs two effective tools: cost control and cost reduction. Cost control ensures that actual costs align with budgeted costs by providing essential information to the management.
- On the other hand, cost reduction focuses on lowering the unit cost of a product without compromising its quality. The primary objective of organizations is to attain maximum profit, which can be realized by either increasing revenue or decreasing production costs. Various concepts in cost accounting are utilized to minimize costs, and understanding these concepts is crucial for management to achieve the ultimate goal of maximizing profit.
Cost Control
Cost Control is a process that concentrates on managing the overall cost through competitive analysis, ensuring that production costs do not exceed predetermined limits. The process includes a series of activities, starting with budget preparation for production. Subsequently, actual performance is evaluated, variances between actual and budgeted costs are computed, and reasons for discrepancies are identified. Finally, corrective actions are implemented.
Concept of Cost Control
Cost control is a fundamental aspect of cost accounting. Within cost control, the cost accountant assesses actual costs, compares them with standards, and identifies deviations. Remedial actions are then taken to reduce variances. The focus is on various measures to maintain costs within budgeted standards and prevent them from exceeding predefined limits. The primary goal of Cost Control is to reduce the overall cost of production.
Features of Cost Control
Cost control possesses the following characteristics:
- It is an effort to maintain expenses within manageable limits.
- It is an ongoing process involving the establishment of standards and the creation of budgets to establish targets, followed by continuous comparisons of actual performance against these standards.
- It necessitates the production of regular cost control reports to identify variances that need resolution.
- It serves as motivation and encouragement for employees to attain budgetary goals and keep costs in check.
- It is not solely focused on cost reduction but also emphasizes the efficient utilization of resources to achieve improved outcomes with the available resources.
For instance: If the current cost of producing a unit is Rs. 100 per unit, cost control endeavors to curtail costs so that they do not exceed Rs. 100. The organization strives to reach this target, and if the actual cost is found to be Rs. 120, a deviation of Rs. 20 is identified. Efforts are then made to discover methods to bring the cost back to Rs. 100. This process is referred to as cost control.
Benefits of Cost Control
The advantages of cost control include:
- Achieving the expected return on the capital invested in a company by addressing deviations between actual and anticipated standards.
- Enhancing production standards with the company's limited resources.
- Lowering prices or maintaining them through cost reduction.
- Ensuring the economic use of resources.
- Increasing the profitability and competitive standing of a company.
- Improving the creditworthiness of the company.
- Contributing to the prosperity and economic stability of the industry.
- Boosting company sales and sustaining employment levels.
Drawbacks of Cost Control
The disadvantages of cost control encompass:
- Restricting flexibility and inhibiting process improvement within a company.
- Hampering innovation by prioritizing adherence to preset standards.
- Demanding skilled personnel for setting standards.
- Lack of creativity as it is primarily concerned with adhering to existing standards.
- Not fostering improvements in standards.
Cost Control Techniques
- Budgetary Control: Budgetary control is an ongoing process involving the creation of budgets and continuous comparison of these budgets with actual figures. It aims to identify deviations, understand the reasons behind them, and revise budgets accordingly. This technique aids in planning, coordination, and overall control.
- Standard Costing: Standard costing involves setting a standard cost and comparing it with actual costs to analyze variances. It facilitates the identification of variance causes and helps in cost estimation.
- Inventory Control: Inventory control focuses on regulating the purchase and usage of materials to maintain production without tying up excess funds. It aims to minimize material wastage and enhance effective resource utilization.
- Ratio Analysis: Ratio analysis establishes relationships among different variables, aiding in identifying organizational trends. This technique is also employed for comparing performance across various organizations and against external standards.
- Variance Analysis: Variance analysis is a cost control method that entails identifying and analyzing the reasons behind variations from established standards. Variances can be favorable or unfavorable, and this analysis helps in understanding and addressing them effectively.
Features of an Effective Cost Control System
As per Backer and Jacobson, a sound cost control system should possess the following characteristics:
- Delineation of Responsibility Centers: This involves clearly defining the responsibilities of various centers, known as responsibility centers.
- Delegation of Prescribed Authority: Empowering individuals with prescribed authority to make decisions within their designated responsibilities.
- Various Cost Standards: Implementing diverse cost standards to assess and compare performance against established benchmarks.
- Relevance of Controllable Cost: Ensuring that the costs under consideration are controllable by the responsible centers.
- Cost Reporting: Providing regular and comprehensive reporting on costs to enable effective monitoring and decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: Incorporating measures for continuous cost reduction to enhance efficiency and profitability.
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction plays a crucial role in achieving savings in the cost per unit and maximizing enterprise profits. The objective of cost reduction is to eliminate unnecessary expenses incurred during the production process, such as those related to storage, selling, and distribution of the product. To identify areas for cost reduction, emphasis should be placed on the following key elements: achieving savings in per unit production cost, maintaining product quality, and ensuring that the savings are sustainable and non-volatile.
Concept of Cost Reduction
Cost reduction involves a real and lasting reduction in the unit cost of goods and services provided by an organization without compromising their quality and efficiency. Various techniques, including budgetary control, standard costing, material control, labor control, and overhead control, can be employed for cost reduction. The primary focus of cost reduction is to decrease the per unit cost of a product. It is an ongoing and continuous process with no discernible endpoint.
Characteristics of Cost Reduction
Features of cost reduction include:
- Genuine Cost Reduction: Cost reduction involves authentic decreases in production costs.
- Permanent Cost Reduction: It entails lasting reductions primarily driven by internal factors. Changes in government taxes, for instance, are not considered cost reduction as they are not permanent.
- Maintained Production Quality: Cost reduction does not compromise the quality of production; it remains consistent.
- Unit Cost Reduction: Achieved by reducing expenditures at a given level of output.
- Quantity Increase for Cost Reduction: Another approach involves maintaining expenditures while increasing the quantity produced.
Advantages of Cost Reduction
Advantages of cost reduction encompass:
- Increased Profitability: Cost reduction contributes to higher organizational profitability.
- Enhanced Cash Flow: It positively impacts the company's cash flow.
- Goal Achievement: Cost reduction programs aid in achieving organizational goals.
- Long-Term Impact: Being permanent, cost reduction positively affects organizational performance over the long term.
- Quality Preservation: Cost reduction does not compromise the quality of production during the cost-cutting process.
Drawbacks of Cost Reduction
Challenges associated with cost reduction are commonly encountered and include the following:
- Resistance from Workers and Employees: Implementation of cost reduction programs is often met with resistance from workers and employees, making them challenging to execute.
- Adhoc Implementation: While cost reduction programs are inherently continuous, many organizations implement them on an adhoc basis, lacking a consistent and sustained effort.
- Limited Applicability: Not all cases are suitable for the application of cost reduction techniques, and their effectiveness may vary.
- Research Requirement: Cost reduction techniques often necessitate extensive research, adding to the overall cost burden of the company.
- Need for Planned Implementation: Successful implementation of cost reduction techniques requires a well-planned approach, which can pose additional challenges for organizations.
Cost Reduction Techniques
Achieving the goal of cost reduction can be pursued through two primary approaches:
- Reducing the Cost of the Product: Focuses on minimizing the expenses associated with a particular product.
- Increasing Efficiency: Aims to enhance overall efficiency to boost productivity in the production unit, ultimately lowering the per-unit cost.
Techniques of Cost Reduction
Cost reduction results from reduction of wastage, improvement in efficiency, identifying alternatives, and continuous reduction of the cost. There can be different methods for cost reduction which can be as follows:
- Value Analysis and Value Engineering: Analyzing and engineering the value of products or processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Job Evaluation and Merit Rating: Assessing job roles and assigning merit ratings to employees based on their performance.
- Quality Control: Implementing measures to ensure and enhance the quality of products.
- Economic Order Quantity: Determining the optimal order quantity to minimize costs associated with ordering and holding inventory.
- Standardization and Simplification: Establishing uniform standards and simplifying processes to streamline operations.
- Inventory Management: Efficiently managing the levels of inventory to reduce holding costs and wastage.
- Benchmarking: Comparing performance against industry benchmarks or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Business Process Reengineering: Overhauling and redesigning business processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Job Study, Works Study, and Motion Study: Analyzing job roles, work processes, and motion to identify areas for optimization.
- Job Evaluation and Merit Rating: Assessing job roles and assigning merit ratings to employees based on their performance.
- Value Analysis: Evaluating the value of products or processes to identify opportunities for cost reduction.
Key Requirements for the Success of Cost Reduction Programs
A cost reduction program is geared towards enhancing human efforts across all organizational levels to lower costs, whether in the short or long term. Short-term programs may address immediate issues, such as controlling wastages and inefficiencies in specific departments, potentially requiring capital expenditure. These programs involve setting target returns on capital employed and devising schemes to achieve them through various cost reduction measures.
Successful implementation of a cost reduction program necessitates the following essential elements:
- Establishment of a Dedicated Cost Reduction Cell: A dedicated cell should be in place for effective planning and execution of the cost reduction program.
- Efficient Management Reporting System: An efficient reporting system at all management levels ensures timely and accurate information dissemination.
- Top Management Support: The program should garner support from top management, preventing it from becoming a routine and ensuring its continuous nature.
- Operational and Research Procedures: A structured approach involving operational and research procedures is essential for successful implementation.
- Close Cooperation Among Executives: Different executives involved in the program should collaborate closely, with each department head assigned specific areas for achieving cost economies.
- Regular Follow-Up and Continuous Appraisal: Continuous follow-up and appraisal are necessary to assess the program's performance against actual cost reduction achievements.
- Holistic Examination of Expenditure: The program should extend beyond cost reduction and scrutinize whether expenditures are genuinely necessary, emphasizing the elimination of uneconomic and unnecessary activities.
Difference between Cost Control and Cost Reduction
Cost control and cost reduction, two distinct concepts in cost accounting, serve different purposes. In cost control, the aim is to minimize costs to meet predetermined targets. Conversely, in cost reduction, the goal is to further decrease costs beyond the budgeted amount, striving to enhance existing standards. Cost control concludes once the standards are achieved, whereas there is no defined endpoint for cost reduction, allowing for continuous improvement in standards. Cost reduction is an ongoing, broader process that extends beyond the limitations of cost control, beginning where control ends.
The differentiation between these two concepts is elucidated as follows:
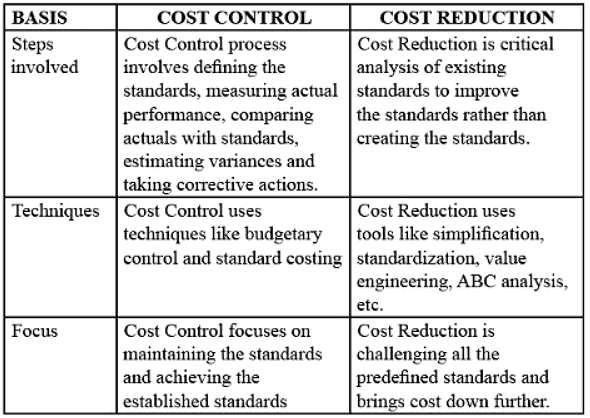
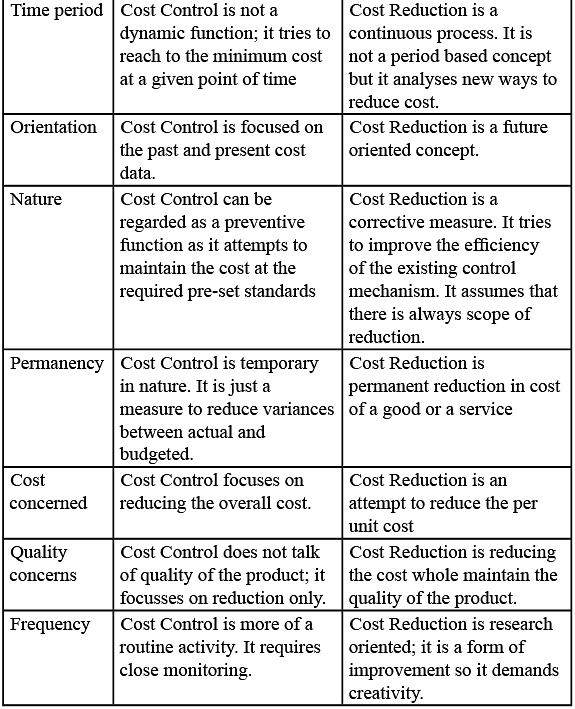
Both the cost reduction and cost control are different concepts; they do not overlap each other and cannot be substituted with each other. They both perform different functions in an organization having their own importance.
Cost Management
Cost management encompasses various cost accounting techniques with the objective of enhancing business cost efficiency through cost reduction or implementing measures to constrain cost escalation. The cost management system plays a crucial role in identifying, gathering, categorizing, and compiling information that managers can utilize for planning, control, and informed decision-making to maintain costs within acceptable limits. Defined as the process of planning and controlling the business budget, cost management aids in forecasting and anticipating business expenses.
Understanding Cost Management
Cost management involves the systematic gathering, analysis, and presentation of data for the purpose of planning, monitoring, and controlling costs. Techniques employed in cost management determine the allocation of organizational resources to various projects and assess their value or outcomes. Within cost management, the focus is on identifying, collecting, and reporting the necessary information for managers and other users. The primary goal is to furnish internal users within an organization with relevant information. Effective cost management enhances the business's potential by providing managers with information for optimizing costs and improving cost-effectiveness.
Goals of Cost Management
The primary goal of cost management is to curtail organizational expenses while fortifying the strategic standing of the firm. Various techniques can be employed to achieve this objective, including:
- Implementing Systems for Transaction Streamlining: Establishing systems to enhance the efficiency of transactions between corporate support departments and operating units.
- Designing Transfer Pricing Systems: Devising transfer pricing systems to coordinate buyer-supplier interactions between decentralized operating units within the organization.
- Utilizing Pseudo Profit Centers: Introducing pseudo profit centers to instill profit-maximizing behavior in units that were traditionally considered cost centers.
Categories of Cost Management
There are three categories of cost management:
- Strengthening Competitive Position: Techniques falling under this category aim to enhance the organization's competitive position. For instance, a hospital redesigning its patient admission process to make it more efficient and user-friendly strengthens its strategic position by attracting more patients.
- No Impact on Competitive Position: Some cost management techniques, like an insurance company reevaluating its accounts payable system for internal efficiency, may not directly impact the organization's competitive position but aim to enhance profitability.
- Weakening Competitive Position: Techniques in this category have the potential to weaken the organization's competitive standing. For instance, a large airline having only two ticket administration desks might initially save costs but could lead to long customer queues, dissatisfaction, and a negative reputation, ultimately reducing ticket sales compared to competitors. As a guiding principle, organizations should avoid practices predicted to weaken their position.
Cost Management Techniques
Effectively managing business costs is crucial for sustained success. The following techniques outline ways to control and maintain overall business costs within the desired limits:
- Time Management: Emphasizing the value of time throughout the organizational hierarchy can increase productivity without escalating labor costs. Educating employees on time efficiency fosters a culture of effectiveness.
- Inventory Management: Strategically planning inventory requirements, including quantity, vendor costs, and stock levels, enables businesses to optimize capital usage. This prevents excess inventory accumulation, freeing up capital for other purposes.
- Outsourcing: Utilizing third-party employees for one-time projects or outsourcing certain tasks allows businesses to avoid adding permanent costs to their books. However, quality standards of outsourcing partners must be maintained to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Updated Market Sense: Staying informed about market trends is crucial for survival. Regularly engaging with vendors and negotiating contract renewals based on current market prices allows businesses to secure the best possible rates.
- Control of Headcount: Employee costs are a significant portion of overall business costs. Managing headcount by either hiring fewer employees or opting for lower-cost alternatives helps reduce the associated expenses, including salaries, workplace costs, licenses, and software expenditures. The focus is on optimizing resources while maintaining workforce efficiency.
Benefits of Cost Management
- Control of Project and Business Costs: Enables effective control of project-specific costs, consequently influencing overall business costs.
- Expense Prediction: Facilitates the anticipation of future expenses and costs, allowing businesses to align their strategies with expected revenues.
- Record Maintenance: Predefined costs can be systematically recorded, providing a structured overview of business expenses.
- Alignment with Objectives: Supports the implementation of actions necessary to ensure that resources and business operations are directed towards achieving set objectives and goals.
- Long-Term Trend Analysis: Allows for the analysis of long-term trends within the business, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making.
- Budget Comparison: Facilitates the comparison of actual costs incurred with budgeted ones, helping identify areas where expenditures exceed expectations.
- Business Positioning Analysis: Assists in analyzing the business's position, particularly in making acquisitions, by considering and evaluating the associated cost components.
Conclusion
- Cost accounting encompasses two essential functions: cost control and cost reduction. Cost control strives to maintain costs within predetermined limits, while cost reduction seeks to lower costs further by redefining standards.
- Under cost control, the process involves setting standards for the organization, measuring actual performance, comparing it with predefined standards, identifying deviations, and implementing corrective actions. This approach contributes to achieving expected returns, reducing costs, capitalizing on economies of scale, and enhancing the economic stability of the company. Techniques employed in cost control include inventory control, budgetary control, standard costing, ratio analysis, and variance analysis.
- Cost reduction, on the other hand, entails real and permanent reductions without compromising quality. It can be achieved by lowering costs or increasing output, ultimately improving profitability and impacting the organization in the long run. Techniques for cost reduction include value engineering, job evaluation, quality control, standardization, simplification, and job evaluation.
- The distinction between cost control and cost reduction lies in various aspects such as the techniques used, focus, frequency, orientation, permanency, and nature.
- Cost management involves the collection, analysis, and presentation of data to plan, monitor, and control costs. Its primary objective is to provide relevant information to the internal users of an organization.
|
180 videos|153 docs
|
FAQs on Techniques of Cost Control and Cost Reduction - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is cost control? |  |
| 2. What is cost reduction? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between cost control and cost reduction? |  |
| 4. What is cost management? |  |
| 5. What are some techniques of cost control and cost reduction? |  |
|
180 videos|153 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















