Joint Ventures | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Definition: A joint venture is like a teamwork business where two or more people or companies join forces to share the costs and profits of a specific project.
Formation: It's when different entities, like companies, government bodies, or individuals, come together to combine their resources and skills for a common business goal.
Partnership Nature: In a joint venture, partners agree to share the profits and handle any losses together, promoting collaboration and risk-sharing.
Benefits: Joint ventures allow businesses to use each other's strengths, resources, and capabilities to achieve cost savings and efficiency. This helps in creating new products faster and more economically than if each company worked alone or through buying another company.
Historical Context: In the 1990s, many big companies like Chrysler, Shell, and IBM started restructuring their organizations globally, involving themselves in multiple joint ventures. This trend has historical roots, with joint ventures playing a crucial role in the development of industries like shipping, railroad, mining, and oil in the 1800s.
Current Importance: Today, joint ventures are still significant as they open up new possibilities for innovation and financial success, allowing businesses to expand their reach and collaborate on projects beyond their individual capacities.
Basic elements constituting a joint venture are as follows:
Contractual Agreement: A joint venture starts with a formal contract or agreement between the involved parties.
Intent to Collaborate: All parties must have the intention to work together in a joint venture.
Shared Property Interest: Each participant contributes something valuable, like money, skills, or assets, to the joint venture.
Joint Control: Everyone involved has a say in the decision-making and management of the venture.
Profit and Loss Sharing: The parties agree on how they will share both the profits and the losses of the joint venture.
Formation through Contract:
Joint ventures are created through contracts between individuals or organizations.
The contract can be informal and doesn't need to be very detailed.
A formal agreement isn't mandatory; the relationship can be formed through spoken agreements.
Intent and Purpose:
Usually established for a specific purpose and for a limited duration.
The key factor is the intent of the parties to create a joint venture.
Contributions and Goals:
Each member contributes something—whether it's money, skills, assets, or effort—for a common business purpose.
Shared beliefs about the expected financial and intangible goals of the joint venture.
Control and Management:
- Participants have the right to control decisions and management aspects.
Profit and Loss Sharing:
- The contract includes details on how the parties will share both the profits and losses.
Focus and Duration:
Goals and objectives of the joint venture are usually narrow and specific.
The joint venture is often for a particular purpose and a limited time.
Inference from Conduct:
- Even without a clear agreement, the existence of a joint venture can be inferred from the parties' behavior and actions.
Not Just a Contractual Relationship:
- It's more than just a business contract; it involves significant contributions to a new business venture.
Mutual Control and Shared Responsibilities:
- Members share control and specific responsibilities within the joint venture.
Reasons for Forming Joint Venture
Joint ventures can encompass companies operating in one or multiple countries, with international collaborations becoming increasingly prevalent, notably in industries requiring substantial capital investment like oil and gas exploration, mineral extraction, and metals processing. The primary motivation behind this trend is cost savings. The decision to form joint ventures is influenced by a combination of internal and external factors:
Internal Reasons to Form Joint ventures:
Sharing Costs:
- Business individuals and joint venture partners team up to divide costs related to marketing, product development, and other expenses, lightening the financial load.
Access to Financial Resources:
- By partnering in a joint venture, business people and their partners can tap into greater recognition and assets, enabling access to more financial resources like loans and grants than they could secure independently.
Technological Collaboration:
- When a company lacks the funds for technological resources, forming a joint venture allows for sharing innovative technology. This collaboration not only enhances product quality but also deepens the understanding of technological processes.
Expanding into New Markets:
- Companies and joint venture partners, by combining their customer contacts, can even create a joint product that opens doors to new markets.
Economies of Scale:
- Joint ventures enable businesses to work together in developing products or services, leading to reduced overall production costs through economies of scale.
External Reasons to Form a Joint venture:
Enhanced Product Innovation:
- When a business person and a joint venture partner collaborate, they can share ideas to create a more competitive product in the industry.
Faster Market Entry:
- By pooling financial, technological, and distribution resources, a business person and a joint venture partner can bring their joint product to the market more quickly and efficiently.
Strategic Edge Against Competitors:
- Teaming up in a joint venture allows partners to combine markets, technology, and innovation, giving them a strategic advantage over competitors in the industry.
Strategic Reasons:
Technology and Skills Enhancement:
- Two forward-thinking companies can share their technology, boosting each other's ideas and skills in the process.
Diversification Benefits:
- Diversification in joint ventures can happen for various reasons, like gaining entry into different markets, creating a range of products, and diversifying the pool of innovative talents.
Driving force for joint venture:
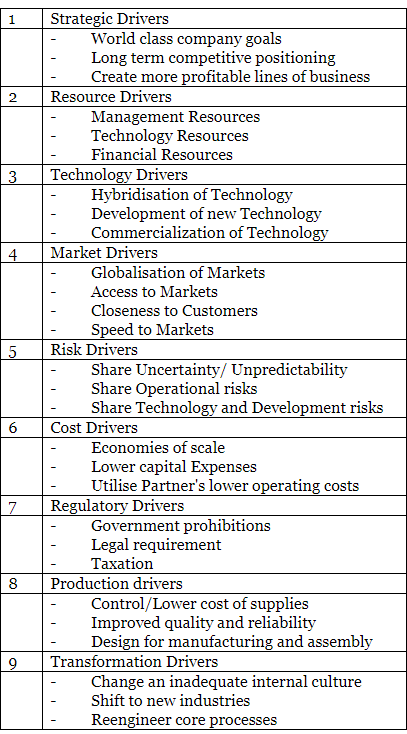
Characteristics of Joint Ventures
- Limited scope and duration
- Generally involve only two firms
- Involve only small fraction of participants' total activities
- Each participant offers something of value
- Joint production of single products
- No sharing of assets/information beyond venture
- Need not affect competitive relationships
- Joint property interest in subject matter of venture
- Right of mutual control or management of enterprise
- Right to share in cash flows of the enterprise
- Limited risk
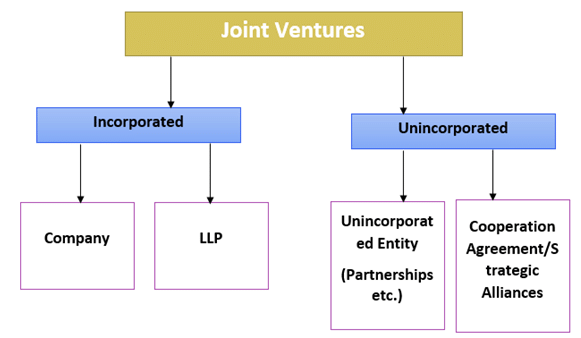
Forms of Joint Ventures
Types of Joint Ventures:
Contractual Joint Ventures:
- In this type of joint venture, parties do not establish a separate legal entity to carry out the venture.
- Instead, they enter into contracts and manage their own profits and losses.
- Taxes are paid only on individual profits.
- Contractual joint ventures are commonly used by parties to combine resources to bid for contracts or to undertake joint research.
- A significant advantage is that there is no joint and several liability for the losses of the venture.
Equity Joint Ventures:
- An equity joint venture involves the creation of a separate legal entity agreed upon by two or more parties.
- Parties contribute money or resources to the joint entity.
- This structure is best suited for long-term, broad-based ventures where a separate legal entity is needed.
- Equity joint ventures are often chosen for ventures involving significant capital investments, like large infrastructure projects or multinational ventures.
Partnership Structures in Joint Ventures:
Traditional Partnership:
- This is the simplest form of partnership, where all partners share equally in both responsibilities and liabilities.
- Partnerships do not have a separate legal existence from their owners.
Limited Partnership:
- In a limited partnership, there are general partners who manage the business and have unlimited liability, and limited partners who invest money but have limited liability.
- Limited partners are liable only up to the amount of their investment.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):
- LLPs are treated as separate legal entities.
- Partners have limited liability for the debts and obligations of the partnership.
- LLPs provide the flexibility of a partnership while limiting the personal liability of the partners.
Capital Asset Transfer and Tax Implications:
- If a joint venture partner transfers a capital asset into the partnership, the transfer will be treated as the disposal by the joint venture partner of a share in the asset in exchange for a share in the assets contributed by the other joint venture partners.
- This transfer could give rise to a tax liability for the joint venture partner, depending on the tax laws and regulations governing such transactions.
common structures employed to constitute a joint venture:
Importance of Joint Venture
- According to management experts, Joint Ventures serve as a tool for creating wealth and independence.
- They help small businesses not only survive but also thrive.
- Joint ventures foster strong relationships among skilled business individuals and help people regain their self-esteem.
- These collaborations are effective for strategic growth and provide quick access to new skills and technologies.
- They also help secure production capacity and reduce production costs.
- Joint ventures provide access to both local and distant markets, enabling businesses to reach a wider audience.
- They also help in creating economies of scale and market power, as noted by J. Peter Killing in 1983.
Strategies of Joint Venture
Choose Strong Partners:
- Always look for strong and reliable partners in joint ventures.
Ensure Equal Contributions:
- Make sure that each businessperson's contribution to the deal is fair and equal.
- An uneven partnership is not beneficial for either party.
Trustworthy Partners:
- Avoid partnering with individuals or businesses that are not trustworthy.
Start with Limited Scope:
- Initially, limit the scope of the venture and expand it gradually as trust grows.
Put Agreements in Writing:
- Keep agreements simple but put them in writing to avoid misunderstandings later.
Recognize Contributions:
- Acknowledge and value each partner's contributions from the start.
- Contributions can include skills, intellectual resources, marketing resources, capital, etc.
Fairness is Flexible:
- Understand that fairness is not an exact number but a range.
- Be flexible and favor partners who also show flexibility.
Establish Clear Protocols:
- Set clear protocols from the beginning for making changes or ending the relationship if expectations are not met.
Emphasize Goodwill:
- Goodwill is crucial for success in joint ventures.
- Ensure that both partners benefit from the relationship and work towards mutual success.
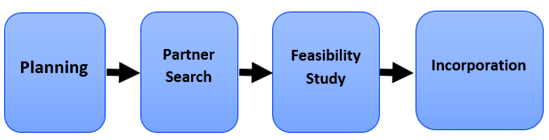
Steps in Forming Joint Venture
I. Planning Stage
Setting Goals and Objectives:
- Decision-making involves specifying the goals and objectives of the joint venture.
Product and Market Determination:
- Identifying the product and market for the venture is a crucial part of the planning stage.
Market Analysis:
- Conducting a thorough analysis of the market to understand its dynamics and potential.
Technology Decisions:
- Making decisions regarding the technology that will be employed in the joint venture.
Financial Requirements:
- Evaluating the financial needs and resources required for the venture.
Foreign Exchange Analysis:
- Considering the impact of foreign exchange rates on the joint venture.
Human Resource and Skill Requirements:
- Identifying the human resource and skill requirements for the successful implementation of the venture.
Revenue Predictions:
- Making predictions about the potential revenue the joint venture can generate.
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
- Evaluating the costs and benefits associated with the joint venture.
Personal SWOT Analysis:
- Conducting a personal SWOT analysis to understand individual strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
II. Searching for Partner
Financial Resources:
- Evaluating the financial resources of potential partners.
Technological Knowhow:
- Assessing the technological capabilities and know-how of prospective partners.
Market Presence:
- Examining the presence of partners in the target market.
Organizational Culture and Management Style:
- Considering the organizational culture and management style of potential partners.
Organizational Structure:
- Evaluating the type of organizational structure adopted by prospective partners.
Credibility Study:
- Conducting a credibility study to assess the reliability and trustworthiness of potential partners.
Ranking Criteria:
- Ranking prospective partners based on predefined criteria.
Feasibility Study Selection:
- Choosing partners for an in-depth feasibility study.
III. Feasibility Study
Culture and Structure Prediction:
- Predicting the culture and structure of the joint venture.
Adaptability Analysis:
- Analyzing partners' comfort and adaptability to new technology and the culture of the joint venture.
Responsibility and Gain/Loss Sharing:
- Examining the distribution of authority, responsibility, and financial gains and losses among partners.
Market Viability Analysis:
- Assessing the market viability of the joint venture.
Sustainability Analysis:
- Analyzing the sustainability of the joint venture in uncertain times.
Cost-Benefit Analysis (Again):
- Re-evaluating the costs and benefits associated with the joint venture.
Environmental Market Analysis:
- Conducting an environmental analysis of the joint venture in the market.
Growth Predictions:
- Predicting the potential growth of the joint venture.
IV. Incorporation
- Methods of Establishment:
- Outlining the ways a joint venture can be brought about, including a foreign investor buying into a local company, a local firm acquiring an interest in a foreign firm, or both forming a new enterprise together.
Benefits of Joint Ventures
- One of the primary advantages of joint ventures is the ability for partners to save costs and mitigate risks by sharing capital and resources. Joint ventures provide avenues for small firms to collaborate with larger companies, jointly engaging in the development, manufacturing, and marketing of new products.
- These partnerships afford companies, regardless of size, the chance to boost sales, expand into broader markets, and advance technological capabilities through collaborative research and development efforts involving multiple parties. Additional benefits of joint ventures include:
Access to New Technologies:
- Joint ventures provide access to modern technologies that a growing business might not afford on its own.
Cost Reduction:
- Businesses can benefit from cost reductions by pooling resources and capabilities in a joint venture.
Learning Opportunities:
- Joint ventures enable members to learn from each other, fostering knowledge transfer and collaboration in various business aspects.
Tax Transparency:
- Joint ventures offer tax transparency, treating profits and losses proportionately among partners for more effective tax planning.
No Public Filing:
- Joint ventures eliminate the need for public filings, avoiding publicity and associated expenses with regulatory bodies.
The findings suggest that a Joint Venture assists organizations in venturing into new markets or diversifying into new product lines. It aids in establishing credibility within a specific target market by selecting a reputable and well-established partner. This collaborative approach reduces business risks through the shared burden of losses and expenses. Furthermore, partners in Joint Ventures enjoy preferential treatment when it comes to acquiring shares from other partners and potentially taking over the entire company.
Drawbacks of Joint Venture
1. Loss of Competitive Edge:
- Forming alliances, especially with competitors, may jeopardize the unique advantages a business could have achieved independently. The business needs to weigh whether collaborating with competitors is essential for its goals and whether it's worth compromising its competitive position.
2. Lack of Control:
- Regardless of how an alliance is structured, participants inevitably surrender some control over the project. Gaining benefits often involves giving up control, requiring participants to strike a balance between retaining influence and fostering collaboration. Due diligence on participants is crucial to establish trust.
3. Governmental Relations:
- Collaborating with overseas entities can bring significant opportunities, but businesses must be cautious about local regulations and government reviews that may impact the alliance's operations.
4. Limited External Finance:
- Joint ventures offer fewer avenues for obtaining external finance compared to a corporate entity. Businesses may face limitations in accessing financial resources through this collaboration.
5. Liability Concerns:
- A notable drawback is the joint unlimited liability of each partner for the alliance's liabilities or actions taken by any partner within the alliance's scope. This means each partner is responsible for the debts and actions of the joint venture.
Key Elements for Success in a Joint Venture: There exist several pivotal factors for the success of a joint venture that enterprises should prioritize. These encompass:
- Effective communication, cooperation, and coordination among partners.
- Establishment of common goals and a shared vision among partners.
- Commitment to the success and enduring sustainability of the joint venture.
- Equitable distribution of profits and benefits among partners.
- Alignment of the joint venture's efforts towards the mutual benefit of all partners.
- Thorough planning and research before the establishment of the joint venture.
Joint Venture in India
From a global standpoint, India presents an enticing investment destination offering strategic advantages and lucrative commercial incentives. Here are some successful Indian companies with joint ventures:
Avi-Oil India Pvt. Ltd.:
- Established in 1993, it is a joint venture between Balmer Lawrie & Co Ltd and NYCO SA, France.
- Engages in mineral-based lubricating oil, defense, civil aviation, and hydraulic fluids.
Green Gas Ltd:
- Formed in 2005, it is a joint venture between GAIL (India) Ltd and IOCL.
- Distributes oil and gas in Agra and Lucknow.
Delhi Aviation Fuel Facility Pvt. Ltd.:
- Established in 2010, it is a joint venture between BPCL and DIAL.
- Specializes in construction, management, maintenance, and modernization of aviation facilities.
GSPL India Gasnet Ltd.:
- Joint venture partners include GSPL, HPCL, and BPCL.
- Operates in the natural gas pipeline selling sector in Gujarat.
Suntera Nigeria 205 Limited:
- Formed in 2006, joint venture partners include Sunetra Resources Ltd and Oil India Ltd.
- Invests in the gas and oil industry in Nigeria.
Indo Cat Pvt. Limited:
- Established in 2006 with joint venture partners from the USA and Intercat.
- Deals with manufacturing and marketing of FCC additives and catalysts.
Indian Oil PETRONAS Private Ltd.:
- Founded in 1998, it is a joint venture between Indian Oil and PETRONAS.
- Engages in importing and constructing facilities for LPG.
IOT Infrastructure & Energy Services Ltd.:
- Established in 1996, joint venture partners include GmBH, Germany, and Oil Tanking.
- Provides services for petrochemical products' building and operation.
Indian Synthetic Rubber Limited:
- Started in 2010 with joint venture partners from Marubeni Japan and TSRC Taiwan.
- Engages in rubber projects and styrene butadiene implementation.
Indian Oil Skytanking Limited:
- Formed in 2006, it is a joint venture between Indian Oil Corporation Ltd and IOT Infrastructure and Energy Services Ltd.
- Focuses on maintaining aviation fuel facility projects.
Indian Oil Ruchi Biofuels LLP:
- Established in 2010, it is a joint venture between Ruchi Soya and Indian Oil.
- Implements biodiesel value-chain projects in Uttar Pradesh.
NPCIL-IOCL:
- Founded in 2011, it is a joint venture between NPCIL and Indian Oil.
- Engages in the operation and development of nuclear power plants.
Lubrizol India Private Limited:
- Began operations in 2000 with joint venture partners from Lubrizol Inc., USA.
- Specializes in manufacturing and marketing of lubricants and additives.
Petronet LNG Limited:
- Established in 1998, joint venture partners include GAIL (India) Ltd, BPCL, ONGC, Gaz de France, and ADB.
- Focuses on LNG re-gasification and facility development.
Petronet VK Limited:
- Founded in 1998 with joint venture partners from various entities.
- Operates and constructs petroleum product transportation pipelines.
In summary, joint ventures serve as a means for companies to enter new markets and share profits with local partners. These collaborations help in creating new products, expanding into foreign markets, or both.
FAQs on Joint Ventures - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the reasons for forming a joint venture? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of joint ventures? |  |
| 3. What are the forms of joint ventures? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of joint ventures? |  |
| 5. What are the drawbacks of joint ventures? |  |




















