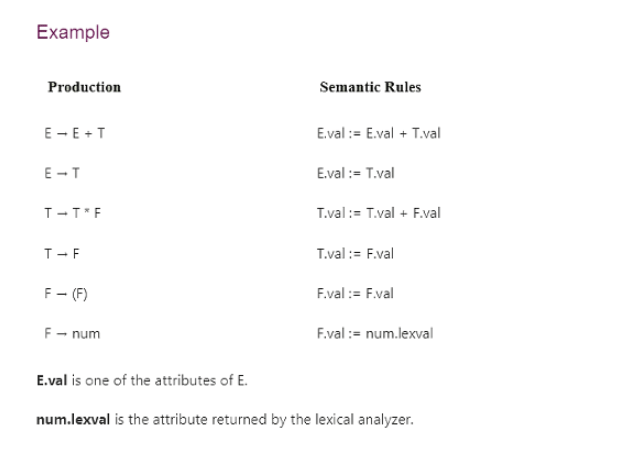
Syntax Directed Translation - GATE PDF Download
In syntax directed translation, along with the grammar we associate some informal notations and these notations are called as semantic rules.
So we can say that
- In syntax directed translation, every non-terminal can get one or more than one attribute or sometimes 0 attribute depending on the type of the attribute. The value of these attributes is evaluated by the semantic rules associated with the production rule.
- In the semantic rule, attribute is VAL and an attribute may hold anything like a string, a number, a memory location and a complex record
- In Syntax directed translation, whenever a construct encounters in the programming language then it is translated according to the semantic rules define in that particular programming language.
Syntax directed translation scheme
- The Syntax directed translation scheme is a context -free grammar.
- The syntax directed translation scheme is used to evaluate the order of semantic rules.
- In translation scheme, the semantic rules are embedded within the right side of the productions.
- The position at which an action is to be executed is shown by enclosed between braces. It is written within the right side of the production.

Implementation of Syntax directed translation
Syntax direct translation is implemented by constructing a parse tree and performing the actions in a left to right depth first order.
- SDT is implementing by parse the input and produce a parse tree as a result.
 Parse tree for SDT:
Parse tree for SDT: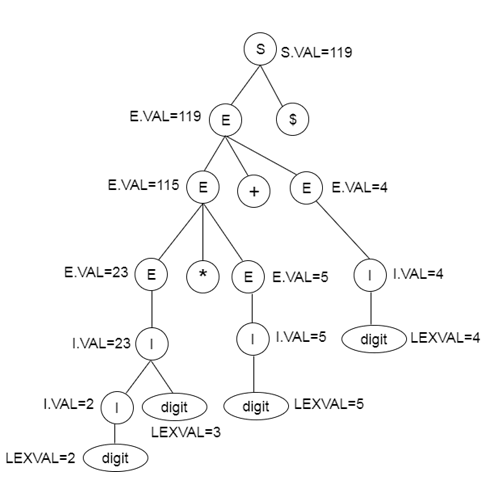
Intermediate code:
- Intermediate code is used to translate the source code into the machine code. Intermediate code lies between the high-level language and the machine language.
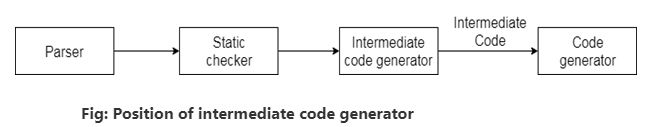
- If the compiler directly translates source code into the machine code without generating intermediate code then a full native compiler is required for each new machine.
- The intermediate code keeps the analysis portion same for all the compilers that's why it doesn't need a full compiler for every unique machine.
- Intermediate code generator receives input from its predecessor phase and semantic analyzer phase. It takes input in the form of an annotated syntax tree.
- Using the intermediate code, the second phase of the compiler synthesis phase is changed according to the target machine.
Intermediate representation
Intermediate code can be represented in two ways:
1. High Level intermediate code:
High level intermediate code can be represented as source code. To enhance performance of source code, we can easily apply code modification. But to optimize the target machine, it is less preferred.
2. Low Level intermediate code
Low level intermediate code is close to the target machine, which makes it suitable for register and memory allocation etc. it is used for machine-dependent optimizations.
Postfix Notation
When you create a parse tree then it contains more details than actually needed. So, it is very difficult to compiler to parse the parse tree. Take the following parse tree as an example:
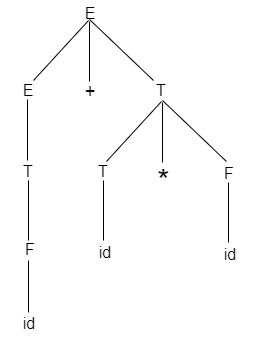
- In the parse tree, most of the leaf nodes are single child to their parent nodes.
- In the syntax tree, we can eliminate this extra information.
- Syntax tree is a variant of parse tree. In the syntax tree, interior nodes are operators and leaves are operands.
- Syntax tree is usually used when represent a program in a tree structure.
A sentence id + id * id would have the following syntax tree:
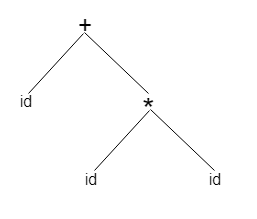
Abstract syntax tree can be represented as:
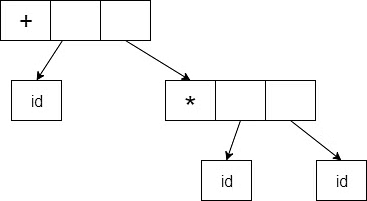
Abstract syntax trees are important data structures in a compiler. It contains the least unnecessary information.
Abstract syntax trees are more compact than a parse tree and can be easily used by a compiler.
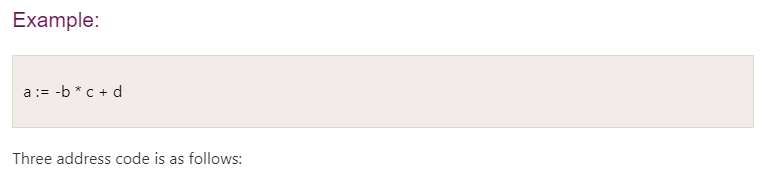
Three address code
- Three-address code is an intermediate code. It is used by the optimizing compilers.
- In three-address code, the given expression is broken down into several separate instructions. These instructions can easily translate into assembly language.
- Each Three address code instruction has at most three operands. It is a combination of assignment and a binary operator.
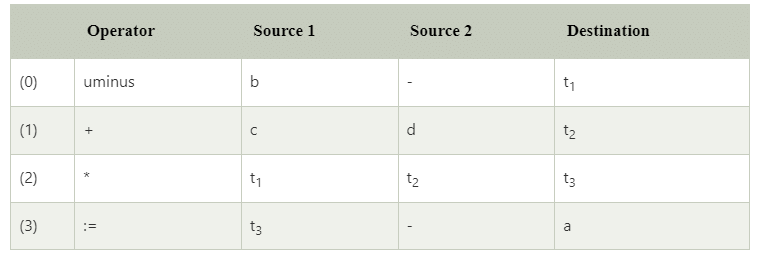
 Quadruples
Quadruples
The quadruples have four fields to implement the three address code. The field of quadruples contains the name of the operator, the first source operand, the second source operand and the result respectively.


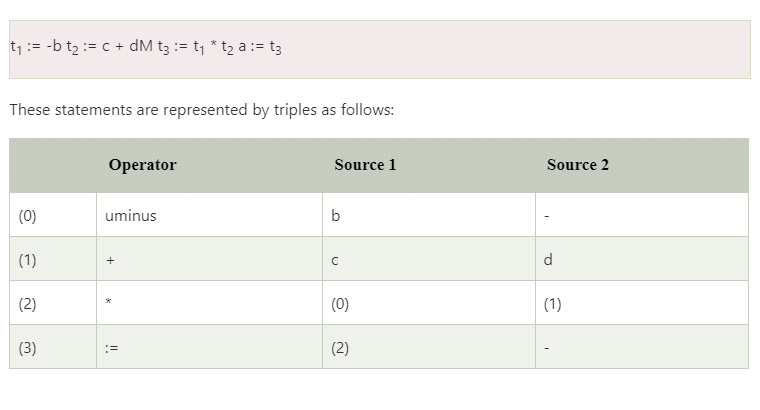
 Triples
Triples
- The triples have three fields to implement the three address code. The field of triples contains the name of the operator, the first source operand and the second source operand.
- In triples, the results of respective sub-expressions are denoted by the position of expression. Triple is equivalent to DAG while representing expressions.

Translation of Assignment Statements
- In the syntax directed translation, assignment statement is mainly deals with expressions. The expression can be of type real, integer, array and records.
Consider the grammar
The translation scheme of above grammar is given below:
| Production rule | Semantic actions |
|---|---|
| S → id :=E | {p = look_up(id.name); If p ≠ nil then Emit (p = E.place) Else Error; } |
| E → E1 + E2 | {E.place = newtemp(); Emit (E.place = E1.place '+' E2.place) } |
| E → E1 * E2 | {E.place = newtemp(); Emit (E.place = E1.place '*' E2.place) } |
| E → (E1) | {E.place = E1.place} |
| E → id | {p = look_up(id.name); If p ≠ nil then Emit (p = E.place) Else Error; } |
Boolean expressions
Boolean expressions have two primary purposes. They are used for computing the logical values. They are also used as conditional expression using if-then-else or while-do.

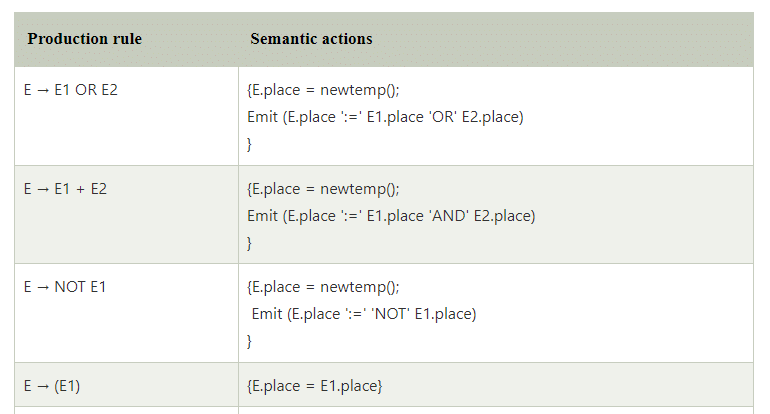

- The EMIT function is used to generate the three address code and the newtemp( ) function is used to generate the temporary variables.
- The E → id relop id2 contains the next_state and it gives the index of next three address statements in the output sequence.
Here is the example which generates the three address code using the above translation scheme:
 Statements that alter the flow of control
Statements that alter the flow of control
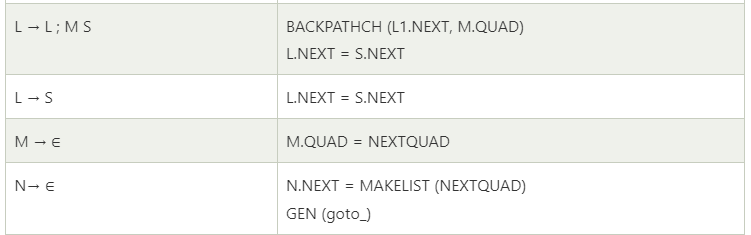
- The goto statement alters the flow of control. If we implement goto statements then we need to define a LABEL for a statement. A production can be added for this purpose:
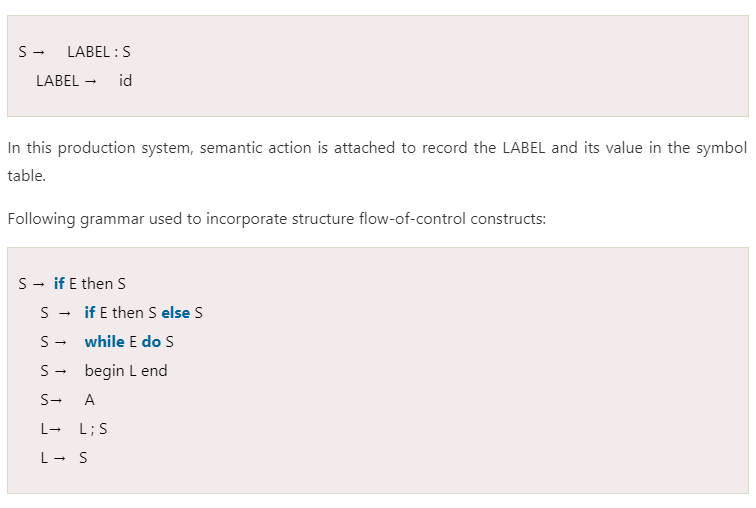 Here, S is a statement, L is a statement-list, A is an assignment statement and E is a Boolean-valued expression.
Here, S is a statement, L is a statement-list, A is an assignment statement and E is a Boolean-valued expression.
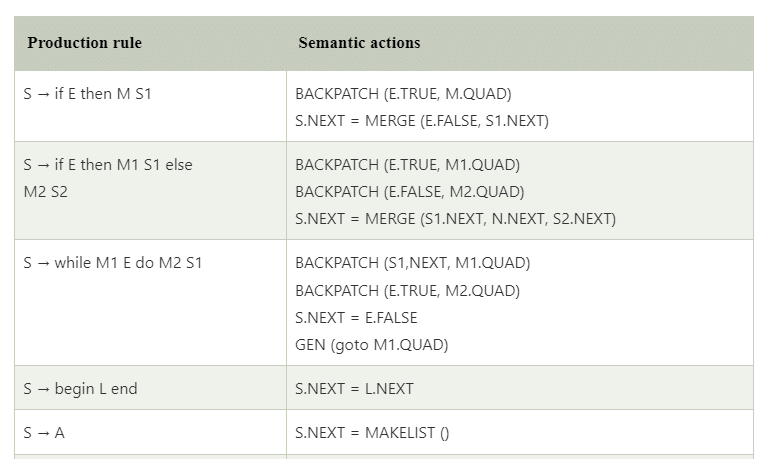
Translation scheme for statement that alters flow of control
- We introduce the marker non-terminal M as in case of grammar for Boolean expression.
- This M is put before statement in both if then else. In case of while-do, we need to put M before E as we need to come back to it after executing S.
- In case of if-then-else, if we evaluate E to be true, first S will be executed.
- After this we should ensure that instead of second S, the code after the if-then else will be executed. Then we place another non-terminal marker N after first S.

 |
Download the notes
Syntax Directed Translation
|
Download as PDF |
Postfix Translation
In a production A → α, the translation rule of A.CODE consists of the concatenation of the CODE translations of the non-terminals in α in the same order as the non-terminals appear in α.
Production can be factored to achieve postfix form.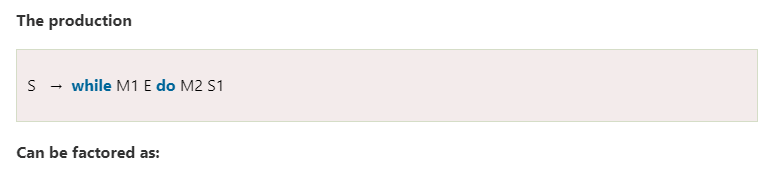

A suitable transition scheme would be 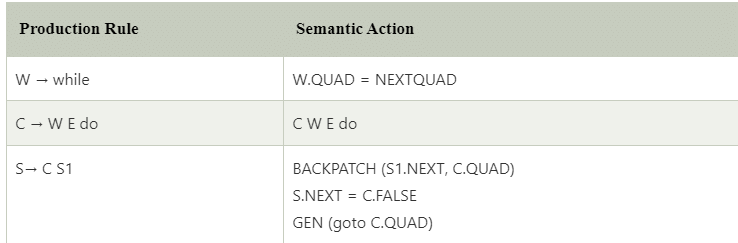
Postfix translation of for statement
Elements of arrays can be accessed quickly if the elements are stored in a block of consecutive location. Array can be one dimensional or two dimensional.
For one dimensional array:
 Multi-dimensional arrays:
Multi-dimensional arrays:
Row major or column major forms
- Row major: a[1,1], a[1,2], a[1,3], a[2,1], a[2,2], a[2,3]
- Column major: a[1,1], a[2,1], a[1, 2], a[2, 2],a[1, 3],a[2,3]
- In raw major form, the address of a[i1, i2] is
- Base+((i1-low1)*(high2-low2+1)+i2-low2)*width
Translation scheme for array elements
- Limit(array, j) returns nj=highj-lowj+1
- place: the temporary or variables.
- offset: offset from the base, null if not an array reference.


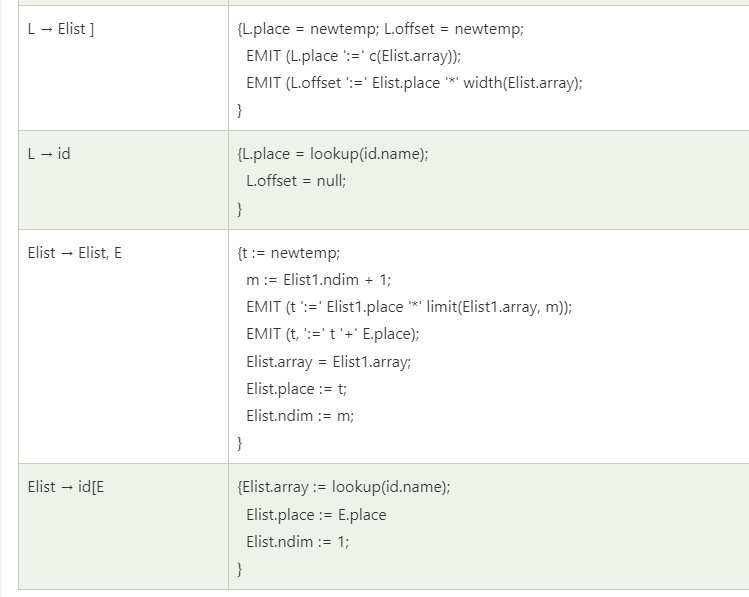
Where:
- ndim denotes the number of dimensions.
- limit(array, i) function returns the upper limit along with the dimension of array
- width(array) returns the number of byte for one element of array.
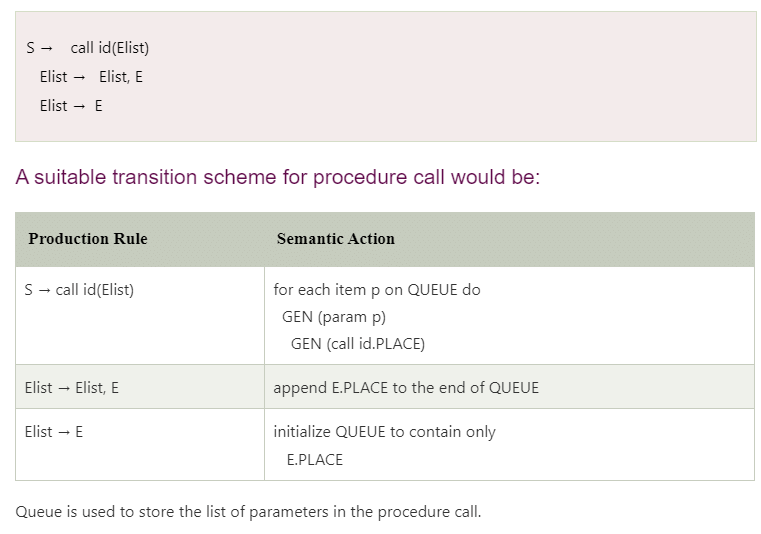
Procedures call
Procedure is an important and frequently used programming construct for a compiler. It is used to generate good code for procedure calls and returns.
Calling sequence:
The translation for a call includes a sequence of actions taken on entry and exit from each procedure. Following actions take place in a calling sequence:
- When a procedure call occurs then space is allocated for activation record.
- Evaluate the argument of the called procedure.
- Establish the environment pointers to enable the called procedure to access data in enclosing blocks.
- Save the state of the calling procedure so that it can resume execution after the call.
- Also save the return address. It is the address of the location to which the called routine must transfer after it is finished.
- Finally generate a jump to the beginning of the code for the called procedure.
Let us consider a grammar for a simple procedure call statement
FAQs on Syntax Directed Translation - GATE
| 1. What is a syntax directed translation scheme? |  |
| 2. How is syntax directed translation implemented? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between postfix notation and infix notation? |  |
| 4. What is the purpose of three-address code in syntax directed translation? |  |
| 5. How are boolean expressions translated in syntax directed translation? |  |






















