Plant Design | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Facility Layout |

|
| Location Decision |

|
| Warehouse Location |

|
Introduction
- One of the pivotal long-term decisions made by industrial engineers revolves around the positioning of their operational entities. The choice of location profoundly influences the cost structure of the production system, exerting a significant impact on the overall profitability of the company. Hence, determining the location of physically intensive entities holds paramount importance in achieving the desired profitability objectives. The plant location dilemma is ubiquitous across all industries involved in manufacturing, supply chain, transportation, or service provision. Once a firm delineates the nature and specifications of goods and services to be offered, the subsequent step involves deliberating on the location of the plant and its associated physical assets.
- The optimal location for a particular business hinges on its specific characteristics and goals, with the overarching aim of maximizing profitability. For instance, industrial location decisions are tailored to the nature of the business, while service organizations prioritize maximizing returns. In contrast, manufacturing organizations' location decisions are influenced by a blend of cost considerations and delivery rate optimization.
- The facility location predicament holds immense significance in two fundamental scenarios: for entirely new businesses and for existing establishments. Existing firms may seek new locations for various reasons, including adding new facilities, expanding current business capacity and infrastructure, or relocating existing facilities to larger premises elsewhere. Theoretically, both new and existing firms have a plethora of alternatives to consider when contemplating new locations.
Principal Factors in Locational Choice
For organizations, the decision on where to locate hinges on various factors, including accessibility from suppliers, proximity to customers, market proximity, and more. These factors can be classified into four sets:
- Fixed Costs: These are influenced by factors such as building design, facility layout, and the establishment and upkeep of departments.
- Variable Costs: These arise from factors like labor availability, access to raw materials, proximity to markets, etc.
- Revenue Factors: These encompass aspects affecting demand, such as proximity to customers, accessibility, usability, etc.
- Subjective Factors: These relate to individual preferences, the ambiance of the area, etc.
The need to select a location or site for a facility arises due to these factors. Common types of location problems include adding one or more new entities that interact with existing facilities. These new entities could be machinery, plants, warehouses, etc. The fundamental location problems include:
- Single Facility Location Problem: This concerns the location of a facility to serve a local community or customers, such as placing a cinema hall for public convenience.
- Multi-facility Location Problem: This arises when establishing a new organization with multiple facilities is necessary.
In addressing the facility location problem, the primary decision revolves around finding the right location for the firm based on its nature. Once the nature of the firm is determined, the subsequent decision involves selecting a layout conducive to efficient production and timely delivery. This entails choosing a layout capable of producing products swiftly and ensuring timely delivery. A key focus in achieving this goal is to minimize the costs associated with processing, transporting, and storing materials throughout the production system. To accomplish this, the design and layout of buildings must be harmonized with the design of material handling systems.
[Intext Question]
Facility Layout
In modern production and service operations, facility layout design has garnered significant interest, driven by the imperative to reduce material handling costs and the increasing adoption of flexible manufacturing systems.
Definition
- Facility layout refers to a technique for arranging machines, utilities, employee workstations, customer service areas, restrooms, etc., to achieve the highest possible output with improved quality at the lowest overall cost. A proper layout is crucial for success in factory management.
Main Objectives of Layout
The primary objectives of facility layout include:
- Enhancing product quality
- Maximizing space, labor, and machine utilization
- Minimizing scrap and waste
- Reducing production delays
- Providing space for future expansion
- Avoiding unnecessary changes
- Facilitating production control
- Minimizing wasteful efforts and expediting production
- Reducing accidents
- Ensuring proper lighting and ventilation
- Minimizing material handling costs
- Simplifying supervision
- Ensuring equipment and personnel safety
Categories of Layout
Various layout types have been developed to achieve these objectives, including:
- Fixed Position Layout: Pertains to the layout requirements of large, bulky projects such as ships and buildings, where tools, machines, and personnel need to be brought close to the work site.
- Process Layout: Addresses low-volume, high-variety production.
- Product Layout: Focuses on high-volume single-product production, maximizing personnel and machine utilization.
- Warehouse Layout: Concerns shelf space management and aims to strike a balance between space and material handling.
- Service Layout: Responds to customer behavior and deals with shelf space management.
Principles Related to Facility Layout
According to Muther, six basic principles related to facility layout are:
- Principle of Overall Integration: Involves integrating men, materials, and machinery.
- Principle of Minimum Distance: Emphasizes minimizing the distance traveled by men and materials.
- Principle of Flow: Advocates arranging the work area for each operation or process in the same order as material assembly.
- Principle of Cubic Space: Stresses optimal utilization of horizontal and vertical space.
- Principle of Satisfaction and Safety: Prioritizes worker safety and satisfaction.
- Principle of Flexibility: Aims for an efficient layout that minimizes costs and inconvenience during rearrangement.
These principles outline the criteria for achieving the best layout. The decision-makers' primary focus in achieving the best layout is selecting the space for locating the firm. The subsequent section provides brief details regarding location decisions and the factors influencing them.
Location Decision
Factors Influencing Location Decision
- Due to globalization and fierce competition, determining the facility's location poses a significant challenge for management. Product life cycles are shrinking, and organizations can now develop new and innovative products more efficiently due to several reasons:
- Effective utilization of IT tools
- Improved modes of transport and shipping
- Streamlined cash flow
- Availability of skilled labor
- Considering these factors, making a facility location decision involves extensive and costly location studies. Typically, several potential sites are evaluated during the selection process, each presenting its own strengths and weaknesses. Consequently, choosing the final location entails a careful tradeoff, weighing the pros and cons of each alternative.
- Understanding the factors commonly influencing the selection of a facility location can shed light on the decision-making process. The selection of a location follows a sequence of decisions, including national, regional, community, and site decisions.
- Initially, management must decide whether the facility will be located domestically or internationally, a choice that was less common just a few decades ago. Once this decision is made, management proceeds to determine the general geographic region within the chosen country for the facility's placement.
- After deciding on the geographic region, management then evaluates various communities within that region. Table 2.1 outlines several factors that affect the community decision.
- Finally, within the chosen community, management selects the specific site based on factors such as size, cost, proximity to transportation systems, and others detailed in Table 2.1.
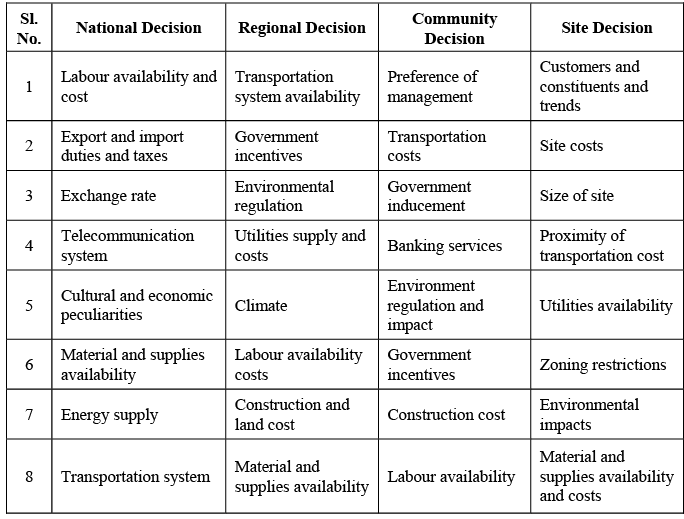
The above table lists the factors affecting the location decision. But along with these factors, one major factor affecting the location of the firm is the type of the firm going to be placed. The two examples are given to illustrate to consideration of these factors.
Warehouse Location
In recent years, manufacturing firms have dedicated significant efforts to reducing work-in-process inventory, leveraging flexible automation, set time reduction, and point-of-use storage. However, despite these advancements, the need for warehouses, particularly for receiving and distribution, remains essential.
While warehouses are often viewed simply as storage facilities, they encompass a variety of functions. A warehouse comprises the building shell, storage medium, storage/retrieval transportation mechanism, and its control policies. Please refer to Table for a brief description of each component.

Warehouse Location Objectives
The primary objectives considered when determining the location of a warehouse are as follows:
- Facilitate effective stock picking and order filling
- Enable efficient inventory counts
- Ensure smooth loading and unloading of vehicles
- Maintain accurate inventory records
Among all facility location decisions, selecting a warehouse location is one of the simplest and most straightforward. The primary factors influencing warehouse location are the costs associated with incoming and outgoing transportation. It is essential to position the warehouse near the market to establish effective communication with recipients of outgoing products and respond promptly to customer orders while minimizing transportation costs.
FAQs on Plant Design - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is facility layout and why is it important in a business? |  |
| 2. What factors should be considered when making a location decision for a business? |  |
| 3. How can a business determine the optimal location for a warehouse? |  |
| 4. What are the key considerations in designing a plant layout? |  |
| 5. How can a business determine the most suitable location for a new facility? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















