Waste Management | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Impact of Economic Development on Waste Production |

|
| Types of Waste |

|
| Waste Minimization Techniques |

|
| Benefits of Waste Management |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Waste management is a complex field that draws upon various disciplines, including engineering, economics, urban and regional planning, management techniques, and social sciences. Its primary aim is to minimize wastage within a given system. Taking a systematic approach to waste management involves addressing waste at all stages and across all types of resources.
Defining Waste
According to the Environmental Protection Act of 1990, waste is defined as any unwanted material, including scrap, effluent, or other substances requiring disposal due to damage, contamination, or other factors. The Act distinguishes between materials that can be reclaimed or reused in their original form and those requiring specialized waste management processes.
Categories of Waste
The Department of the Environment identifies four main categories of potential waste:
- Functional but Worn Materials: These are items that are still operational, albeit in need of repair, and can be reused for their intended purpose.
- Materials for Immediate Reuse: Substances or objects that can be repurposed immediately without specialized waste recovery processes, such as ash from power stations used in construction materials.
- Degraded Materials: Items that require specialized waste recovery processes for reuse, such as polluted solvents or scrap materials. These remain classified as waste until they undergo recovery.
- Unwanted Substances: Materials that the holder wishes to dispose of and may need to pay for their removal.
Impact of Economic Development on Waste Production
The rapid pace of economic development has significantly enhanced living standards worldwide. However, this progress has led to a surge in material consumption, consequently increasing waste production, particularly in urban areas.
Classification of Solid Waste
Solid waste generated in urban areas encompasses various categories:
- Organic Waste
- Plastic Waste
- Metal Waste
- Glass Waste
- Paper Waste
- Electronic Waste
- Miscellaneous Waste (Ash, Sand, Grit, etc.)
- Diverse Forms of Waste
Types of Waste
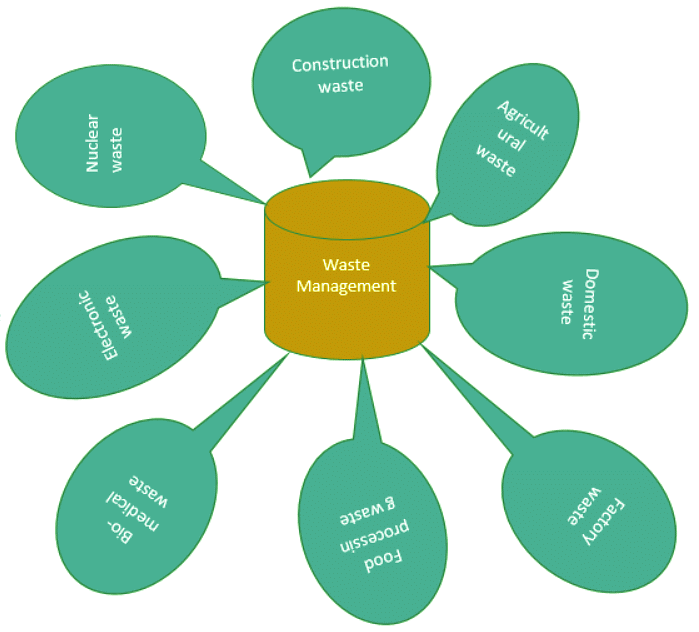
Organizations often dispose of items with significant residual value, spanning from production scrap materials to outdated plant and equipment, which are legally classified as waste. Some wastes are designated as hazardous, encompassing a broad spectrum of substances with varying levels of risk. For instance, toxic materials capable of causing cancer are deemed hazardous. Similarly, items like fluorescent tubes or cathode ray tubes found in televisions pose minimal immediate threat but may inflict long-term damage over time. The Environment Agency defines waste as any substance or object that has been unused, necessitating disposal or intended for discarding.
Waste Generation Process
The process of waste management involves various stages such as collection, transport, processing, recycling, or disposal of waste materials. Different methods and expertise are required for managing solid, liquid, gaseous, or radioactive substances. Waste management practices vary across regions and sectors, highlighting the need for tailored approaches.
Objectives of Waste Management
The primary objectives of waste management include waste reduction, promotion of reuse and recycling, energy recovery, and prevention of harmful impacts on the environment and public health. Effective waste management contributes to cost savings, worker safety, and community well-being.
Resource and Waste Management Relationship
Resource management and waste management are interrelated concepts aimed at optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste generation. Understanding their complementary nature is essential for developing comprehensive sustainability strategies.
Concept of Wastivity
The concept of wastivity provides a measure of system performance by evaluating the ratio of waste to input. Differentiating between gross wastivity and net wastivity helps in assessing productivity and efficiency.
Current Trends in Waste Management
The evolving landscape of waste management emphasizes waste minimization, reuse, recycling, and responsible disposal. Companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable procurement practices and efficient waste management procedures to achieve financial returns and environmental goals.
Waste Management Hierarchy
The waste management hierarchy prioritizes waste reduction, reuse, recycling, recovery, and disposal, highlighting the importance of minimizing waste generation and maximizing resource recovery.
Waste Minimization Techniques
- Landfill Management: Landfills are commonly used for waste disposal, where garbage is buried in designated areas. Modern landfill operations include measures to reduce odors and hazards, such as compacting waste and covering it with soil daily.
- Incineration: Incineration involves burning municipal solid waste at high temperatures to reduce its volume and convert it into residues and gases. This process, also known as combustion or thermal treatment, helps minimize the space needed for waste disposal and reduces stress on landfills.
- Resource Recovery: Resource recovery involves collecting useful materials from discarded items for further use or converting them into energy, such as heat, electricity, or fuel.
- Recycling: Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new products to conserve energy, reduce landfill volume, minimize pollution, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and preserve natural resources.
- Plasma Gasification: Plasma gasification uses electrically charged gas to decompose waste into its basic molecular structure, producing syngas. This method provides renewable energy and is effective for municipal solid waste disposal.
- Composting: Composting is a natural decomposition process that converts organic waste into nutrient-rich compost, suitable for fertilizing plants. It's a simple and environmentally friendly method of waste management.
- Waste-to-Energy: Waste-to-energy processes convert non-recyclable waste into usable heat, electricity, or fuel, offering a renewable energy source and reducing carbon emissions.
- Waste Minimization/Avoidance: Waste minimization involves reducing the creation of waste materials through practices such as recycling, repairing items, avoiding disposable products, reusing items, and choosing products with minimal packaging.
- Biological Reprocessing: Biological reprocessing methods, including composting and digestion, break down organic waste into compost or biogas through aerobic or anaerobic processes.
Waste Management in the Indian Perspective
India faces challenges in waste management due to its large population and increasing waste generation rates. Limited land for waste treatment and disposal in urban areas exacerbates the problem. Comprehensive data collection and systematic assessment of waste quality and pollution potential are needed for effective waste management strategies.
Benefits of Waste Management
- Waste management offers numerous benefits to both the environment and society, encompassing various functions such as waste removal and recycling. Urban areas have developed methods to separate organic waste from non-recyclable materials, enabling the creation of compost for public spaces. Some cities even sell this compost for profit, contributing to a circular economy. Recycling and reprocessing waste not only reduce the consumption of natural resources but also decrease the need for waste disposal.
- Additionally, proper waste management significantly improves public health. Previous practices like burning waste in landfills or backyards posed serious health risks due to the emission of particulate matter. Inhalation of these pollutants can lead to various respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. By implementing effective waste disposal methods, such as containment or safe incineration, communities can mitigate health hazards, reduce exposure to biohazards, and minimize pest infestations.
- Moreover, waste reduction initiatives offer substantial cost savings for businesses by minimizing expenditures on raw materials, equipment, and office supplies. Streamlining operations to minimize waste not only enhances efficiency and productivity but also demonstrates environmental responsibility, fostering customer loyalty. Companies adopting waste reduction strategies contribute to the preservation of natural resources, reduction of pollution associated with resource extraction and manufacturing, and conservation of landfill space.
Conclusion
Waste management is crucial for treating solid wastes and promoting recycling practices. Businesses worldwide must adopt effective waste management processes to ensure safe and efficient disposal of products and substances. By implementing waste reduction measures, companies can minimize their environmental footprint while achieving cost savings and enhancing their financial performance. Incorporating waste reduction standards into daily operations is essential for addressing environmental concerns and promoting sustainable business practices.
FAQs on Waste Management - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. How does economic development impact waste production? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of waste? |  |
| 3. What are some waste minimization techniques? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of waste management? |  |
| 5. How does waste management contribute to sustainable development? |  |

















