External Environment of Organisation | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Industrial Organization Model |

|
| PESTLE Framework |

|
| External Factor Evaluation Matrix |

|
Introduction
- The macro-environment within which all organizations operate broadly encompasses the economic, political, legal, socio-cultural, and environmental aspects. Technological advancements have been a key driver behind the significant changes observed in the external environment, making it increasingly complex. These factors often overlap, and developments in one area may influence developments in others. For instance, the globalization of markets and increased competition between private and public organizations, as a result of the opening up of the economy, prompted the Indian government to revise its economic policies.
- The liberalization policy and economic reforms of 1991 led to the removal of regulations such as the MRTP Act, which restricted the size of businesses and inhibited their efficiency and competitiveness, thus positively impacting indigenous industries. Current political developments are likely to influence business people's perceptions regarding the future policy direction in certain sectors. Social considerations, particularly in the context of a developing nation like India, also play a crucial role in shaping the broader dynamics of the business environment. The clash between preserving Indian ethos and culture and allowing freedom of choice for individuals often creates challenges and uncertainties for businesses.
Industrial Organization Model
- The Industrial Organization (IO) Model is a framework that helps us understand how strategic decisions can lead to competitive advantage. It takes an external perspective, meaning it looks at how external factors influence an organization's strategic activities. In other words, this model assumes that the features and conditions of the external environment impact the formulation and implementation of strategies in order to generate above-average returns and thereby gain competitive advantage.
- Under this model, the organization is forced to develop strategies in response to external demands, which can limit the range of tactics that may be suitable and effective. Additionally, the model assumes that all organizations within an industry possess a similar set of resources, which means that most organizations in a given industry will have comparable skills and pursue similar tactics. The resources needed to execute strategies are highly transferable among organizations, and significant distinctions in strategically relevant resources across enterprises in an industry tend to diminish due to high resource mobility.
The Industrial Organization model follows a process for achieving competitive advantage, which involves several steps:
- Examine the external environment, including the general, industrial, and competitive environments, to identify external environmental attributes and both decide and limit the organization's strategic solutions.
- Based on the structural parameters of the industry, choose an industry (or industries) with high potential for returns.
- Develop strategies associated with above-average returns based on the features of the industry in which the organization plans to operate.
- Acquire or develop the key resources required for successful implementation of the formulated strategies and plans.
- Achieve competitive advantage by successfully implementing the strategic actions that enable the organization to utilize its resources to meet the demands of the external environment.
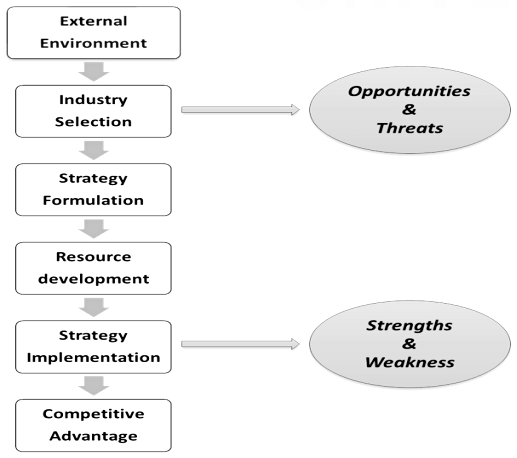
This model is important for the organizations as it helps them assess the strategic position of the organization.
PESTLE Framework
- The external forces that impact organizations can be categorized into six broad groups: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal Forces. Changes in these external forces can influence consumer demand for both industrial and consumer products and services. They can also affect the types of products produced, market positioning, market segmentation strategies, services offered, and business choices. Therefore, it's essential for organizations to identify and evaluate external opportunities and threats, which helps them develop a clear mission, design strategies to achieve long-term objectives, and create policies to meet short-term goals.
- In the following sections, we'll discuss each of these six forces individually and then draw conclusions about environmental analysis. A thorough analysis of these factors can help identify major trends in different industries. Exhibit-2 illustrates the PESTLE framework, which is a popular tool used for such analysis.
- While the PESTLE framework can help understand the most critical factors at the present time, it's essential to primarily use it to anticipate future impacts, which may differ from their current or past impacts.
Exhibit 2: PESTLE Framework
The PESTLE Framework - Macro-environmental influences. This framework primarily covers two areas:
- Environmental factors affecting the organization;
- Important factors relevant in the present context and in the years to come.
Political Factors
- Stability of Government
- Political values and beliefs influencing policies
- Regulations on trade and global business
- Taxation policies
- Priorities in the social sector
Economic Factors
- Trends in Gross National Product (GNP)
- Interest rates and savings rates
- Money supply and inflation rates
- Inflation rate
- Unemployment
- Disposable income
- Business cycles
- Trade deficit/surplus
Socio-cultural Factors
- Population demographics
- Ethnic composition
- Aging population
- Regional changes in population growth and decline
- Social mobility
- Lifestyle changes
- Attitudes towards work and leisure
- Education - spread or erosion of educational standards
- Health and fitness awareness
- Multiple-income families
Technological Factors
- Biotechnology
- Process innovation
- Digital revolution
- Government spending on research
- Government and industry focus on technological advancement
- New discoveries/developments
- Speed of technology transfer
- Rates of obsolescence
Legal Factors
- Legislation on monopolies/Antitrust regulations
- Employment laws
- Health and safety regulations
- Product safety regulations
Environmental Factors
- Carbon emissions
- Pollution levels
- Environmental sustainability
- Global warming
- Biodegradable materials
Political factors
- Political factors have a significant impact on the economic environment of a nation. Political ideology and stability or instability can strongly influence the pace and direction of economic growth. They can also create an economic environment that is conducive to the growth of some businesses, indifferent to others, or even present obstacles. Governments at various levels, including central, state, local, and foreign, all play a role in shaping the business environment. They are the primary regulators or deregulators. Businesses often rely on government contracts, subsidies, and other forms of support, which are a major part of the external environment. Any changes in laws, regulations, or tax policies can have a significant impact on organizations.
- Looking back at history, certain political ideologies led to the departure of some foreign organizations from India in the late 1970s. Entry barriers, protectionist policies, high tariffs, and nationalist agendas contributed to a closed economy until liberalization policies were introduced in 1991. This situation weakened the economy and made businesses less competitive internationally. However, in subsequent years, political consensus developed on issues such as labor reforms, power sector reforms, and infrastructure development, which have been beneficial for businesses.
Economic Factors
Exhibit 3 provides a comprehensive view of the broad economic indicators that paint the economic landscape of the general environment. These indicators should be carefully examined while conducting environmental analysis.
Exhibit 3: Common Economic Indicators
- National Income
- Gross National Product (GNP)
- Personal Disposable Income
Policy Initiatives
- Monetary Policy
- Fiscal Policy
- Labour and Employment Policy
Savings
- Personal Savings
- Corporate Savings
Foreign Sector
- Exchange Rates
- Exports/Imports
- Balance of Payments
Industry
- Industry Investment
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Flows
- Services
- Infrastructure
Sectoral Growth
- Agriculture
- Industry
Capital Market
- Equity Market
- Bond Market
Prices, Wages, Productivity
- Inflation
- Labour Productivity
Economic factors provide insights into the nature and direction of the economy in which an organization operates.
- Organizations must focus on economic trends in segments that affect their industry. For example, the trend of low interest rates on personal savings may prompt individuals to shift towards equity and bond markets, leading to an increase in capital market activity and the mutual fund industry. Consumption patterns are often influenced by the relative affluence of market segments, and organizations must understand them through factors like disposable income and consumer spending habits.
- Other economic influences that organizations should consider include interest rates, inflation rates, unemployment rates, trends in gross national product, government policies, and sectoral growth rates. The services sector's contribution to national income is increasing annually, and family incomes are rising faster than individual incomes, leading to a more diverse range of job opportunities. This presents different types of opportunities and challenges for businesses.
- With the opening up of the economy, trends in the global market require careful examination. The above factors need to be analyzed and incorporated into your conclusions about the general environment and how they, along with other forces, may collectively impact businesses.
Social Factors
Socio-cultural factors have a significant influence on markets, products, services, and customers. Nearly all organizations face challenges stemming from changes in demographic and cultural variables.
Let's briefly discuss these.
- Demographic Factors: Demographic characteristics such as population, age distribution, literacy levels, inter-state migration, rural-urban mobility, income distribution, etc., are key indicators for understanding the demographic impact on the environment. Shifts in age distribution, caused by improved birth control methods, have created opportunities for youth-centric products ranging from clothing to entertainment to media. The growing number of senior citizens and their livelihood needs have been highlighted, and the government is paying more attention in the form of social security benefits, etc.
- Literacy and the composition of literates in the nation create opportunities for particular industries and types of jobs. For example, the presence of a large number of English-speaking engineers has encouraged many software giants to set up shops in India, and on the other hand, the availability of cheap labor has made India a destination for labor-intensive projects. Moreover, large labor mobility across different occupations and regions, in recent times, has greatly reduced wage differentials, which has an impact on businesses that needs to be understood.
- Cultural Factors: Social attitudes, values, customs, beliefs, rituals, and practices also significantly influence business practices. Festivals in India offer great business opportunities for certain industries like clothing and garments, jewelry, gift items, sweets, and many others; the list could be endless.
- Social values and beliefs are important as they affect our buying behavior. For example, a multinational fast-food chain does not serve beef burgers in India because Indians do not consume cow meat, as the animal is considered holy and sacred. A related example from an entertainment giant clearly demonstrates the impact different cultures may have on businesses. This organization, which has been successful in the US market, could not replicate its success in European nations due to differences in the way people entertain themselves there.
- As a result, they had to customize their offerings to be successful in these markets. The spread of consumerism, the rise of the middle class with high disposable income, and the flashy lifestyles of people working in software, telecom, media, and multinational companies seem to have changed the socio-cultural scenario, and this needs to be deeply understood. The pandemic crisis, which introduced the Work from Home (WFH) culture, has also impacted the way the market is perceived. Values in society also determine the work culture, approach towards stakeholders, and the various responsibilities the organization considers owing to its stockholders and society.
Technological Factors
- Technological factors represent significant opportunities and threats that must be considered when formulating strategies. Technological breakthroughs can drastically impact an organization's products, services, markets, suppliers, distributors, competitors, customers, manufacturing processes, marketing practices, and competitive position.
- Advancements in technology can open up new markets, change the relative positions of industries, and render existing products and services obsolete. They can also reduce or eliminate cost barriers between businesses, create shorter production runs, create shortages in technical skills, and lead to changing values and expectations of customers and employees.
- The impact of information technology (IT), which combines the benefits of both telecommunications and computers, has been revolutionary in every field. It has not only opened up new business opportunities but has also changed the way businesses are conducted. IT has introduced a new dimension of "speed," which organizations recognize as an additional source of competitive advantage, beyond low cost and differentiation.
- Manufacturers, bankers, and retailers have used IT to carry out their traditional tasks at lower costs and deliver higher value-added products and services. The pandemic situation has further changed the way organizations operate. Artificial intelligence, robotics, cloud computing, blockchain technology, etc., have significantly penetrated the business world.
Legal Factors
- Licensing policies, quota restrictions, import duties, FOREX regulations, FDI regulations, controls on distribution and pricing of commodities, together made business difficult before liberalization. However, with economic reforms, things have changed, and legal formalities have eased.
- Nevertheless, with globalization, the rules of competition, trademark rights and patents, WTO rules and implications, price controls, product quality laws, and several other legal issues in individual nations have become important and need to be considered while understanding the general environment.
Environmental Factors
- Environmental conservation and protection have gained prominence due to deteriorating environmental balance, which threatens the sustainability of life and nature. Businesses are also held responsible for such situations, as emissions from industries pollute the air, excessive chemical effluents are drained out into water, making it poisonous and unfit for use, and the use of non-biodegradable resources affects the bio-chain adversely. The exposure of employees to hazardous radiations also puts their lives in danger.
- All these issues have been taken very seriously by different stakeholders in society, including the government, and legislations and movements are creating pressure for environmentally friendly businesses. These have far-reaching implications for businesses, ranging from the type of business, the product being manufactured, how it is manufactured, and how friendly it is for mankind and nature. Many multinationals that come under the purview of society regarding environmental hazards have started using more sustainable methods to survive in business. Businesses worldwide are now focusing more on preserving nature than harming it.
Competitive Environment
- The competitive environment refers to the situation that organizations face within their specific areas of operation. This can be understood at an industry level or with respect to smaller groups called strategic groups. An industry in the economy is recognized as a group of organizations producing the same principal product or, more broadly, the group of organizations producing products that are close substitutes for each other. In a given industry, different organizations have different intermediate bases for understanding their relative positions with respect to other organizations in the industry.
- Organizations within an industry with similar strategic characteristics, following similar strategies, or competing on similar bases are called strategic groups. These characteristics for a particular group will be different from those in other strategic groups in the same industry or sector. There may be many different characteristics that distinguish between strategic groups. For example, size, breadth of product range, geographical coverage, quality or service levels, or marketing spend. The concept of strategic groups, when used, helps in understanding who the direct competitor of any given organization is and on what basis competitive rivalry is likely to take place within each strategic group.
External Factor Evaluation Matrix
The External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE) is a strategic tool that assists strategists in summarizing and evaluating PESTEL factors. This process involves five steps, as outlined below:
- List Key External Factors: Once the PESTEL analysis is completed, the key external factors that determine opportunities and threats for the organization are identified. This typically includes 10 or 20 factors, which are then listed using percentages or ratios.
- Assign Weight to Each Factor: In this step, each factor is assigned a weight ranging from 0.0 (not very important) to 1.0 (extremely important). These weights represent the relative importance of each factor and are determined by comparing successful competitors with unsuccessful ones or through group discussions within the organization. The sum of all weights should equal 1.0, and these weights are industry-specific.
- Assign a Rating to Each Factor: Next, each factor is rated on a scale from 1 to 4 to indicate the effectiveness of the organization's present strategic response to the factor.
The rating scale is as follows:
- 1 = Poor response
- 2 = Average response
- 3 = Above-average response
- 4 = Superior response
These ratings are organization-specific.
- Determine a Weighted Score: In this step, the weight of each factor is multiplied by its rating to calculate a weighted score for each factor.
- Determine the Total Weighted Score: The final step involves considering the score of the weighted score of each variable, resulting in the total weighted score of the organization.
Exhibit 4 provides an example of an EFE matrix to illustrate these steps.
Exhibit 4: External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix of X Inc.
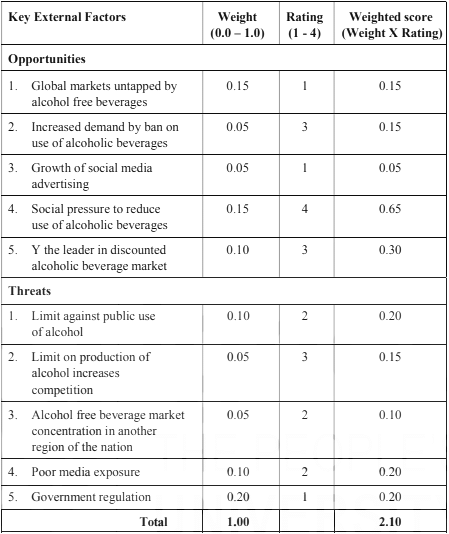
It is important to note that, regardless of the number of opportunities or threats in an EFE matrix, the maximum possible weighted score for an organization is 4.0, while the minimum possible score is 1.0. This signifies that if an organization achieves a weighted score of 4.0, its response to the opportunities and threats is deemed excellent, and conversely, if it scores 1.0, the organization is not effectively capitalizing on opportunities or mitigating threats. The example provided in the exhibit illustrates a total weighted score of 1.0, suggesting that the organization is not sufficiently leveraging opportunities or mitigating threats. Therefore, it is imperative for organizations to comprehensively understand these factors in order to maximize opportunities and minimize threats.
|
196 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on External Environment of Organisation - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the Industrial Organization Model? |  |
| 2. What is the PESTLE Framework? |  |
| 3. How is the External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFEM) used? |  |
| 4. How does the external environment of an organization impact its strategies? |  |
| 5. How can the PESTLE Framework be used in conjunction with the Industrial Organization Model? |  |




















