Introduction to Android Development - Software Development PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Android Development |

|
| Features of Android |

|
| Programming Languages used in Developing Android Applications |

|
| Advantages and Disadvantages of Android Development |

|
Introduction to Android Development
The Android operating system has become the dominant force among various mobile platforms worldwide, boasting the largest installed base. With hundreds of millions of devices powered by Android across more than 190 countries, its market share reached around 71% by the end of 2021, a figure continuing to grow rapidly.
Origin and Development
- Android was initially developed by the Open Handset Alliance, based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software.
- Google sponsored the project's early stages, eventually acquiring the entire company in 2005.
- The first Android-powered device was launched in September 2008, marking the beginning of its widespread adoption.
Features and Advantages
- User-Friendly Interface: Android provides an intuitive user interface, making it accessible to a broad audience.
- Community Support: It benefits from a large and active developer community, offering resources, tutorials, and assistance.
- Customization Options: Android allows extensive customization, enabling users to personalize their devices according to their preferences.
- Device Compatibility: A wide range of companies manufacture Android-compatible smartphones and devices, contributing to its ubiquity.
Evolution Beyond Mobile
Originally conceived as a mobile operating system, Android has evolved to power various other devices, including tablets, wearables, set-top boxes, smart TVs, and notebooks. This expansion is facilitated by the advancement of code libraries and its popularity among developers from diverse domains.
Features of Android
Android, as a powerful open-source operating system, offers a plethora of features catering to various user needs and preferences. Below are some of the key features:
Features
Android Open Source Project
- The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) provides the flexibility to customize the operating system according to specific requirements. This open nature fosters innovation and enables developers to tailor Android to diverse use cases.
Connectivity
- Android supports a wide range of connectivity options including GSM, CDMA, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, facilitating telephonic conversations, data transfer, and internet access.
- Wi-Fi technology allows seamless pairing with other devices for activities such as gaming or collaborative use of applications.
Location Tracking
- Multiple APIs within Android support location-tracking services like GPS, enabling applications to access precise location data for various purposes such as navigation, geotagging, and location-based services.
Data Management
- Android provides a robust file manager, allowing users to efficiently manage all data storage-related activities, including file organization, transfer, and deletion.
Media Support
- Android offers extensive support for various media formats such as AVI, MKV, FLV, MPEG4 for audio and video playback or recording, enhancing multimedia experiences on Android devices.
- It also supports a range of image formats like JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, ensuring compatibility with diverse visual content.
Hardware Integration
- Android supports seamless integration with multimedia hardware, enabling control over playback or recording using cameras and microphones, enhancing the user experience in multimedia applications.
Web Browsing
- Android features an integrated open-source WebKit layout-based web browser, offering support for modern web technologies like HTML5 and CSS3, ensuring a rich browsing experience on Android devices.
Multi-Tasking
- Android supports multi-tasking, allowing users to run multiple applications simultaneously and switch between them seamlessly, enhancing productivity and multitasking capabilities.
Graphics Support
- Android provides robust support for virtual reality and 2D/3D graphics, enabling immersive gaming experiences and sophisticated graphical user interfaces.
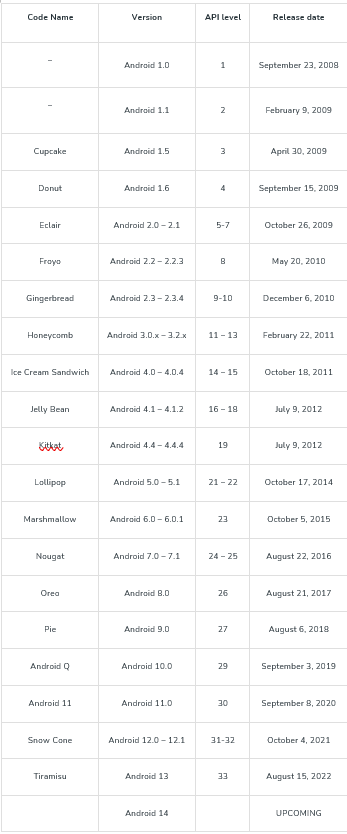
Android Version History
Google officially introduced Android in November 2007, with the first release occurring on September 23, 2008, through the HTC Dream featuring Android 1.0. Since then, Google has launched numerous Android versions, including Apple Pie, Banana Bread, Cupcake, Donut, Éclair, Froyo, Gingerbread, Jellybeans, Kitkat, Lollipop, Marshmallow, Nougat, Oreo, etc., each introducing additional functionalities and new features, further enriching the Android ecosystem.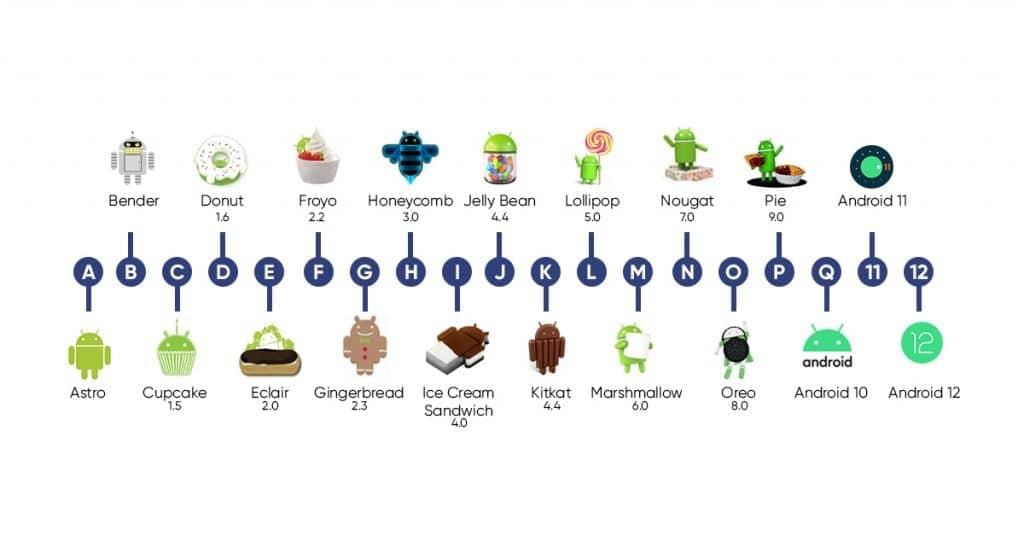 Android Versions
Android Versions
The following table shows the version details of android which is released by Google from 2007 to date.
Programming Languages used in Developing Android Applications
When it comes to developing Android applications, developers have primarily relied on two programming languages: Java and Kotlin. Each language has its own strengths and considerations.
Java
- Java has been the traditional and longstanding choice for Android development.
- It offers robustness, versatility, and a vast ecosystem of libraries and tools, making it suitable for building complex and scalable applications.
- Many developers are already familiar with Java, given its widespread use in enterprise and web development.
- Java's object-oriented nature facilitates code organization and maintenance, promoting clean and modular design practices.
Kotlin
- Kotlin, developed and maintained by JetBrains, emerged as a modern alternative to Java for Android development.
- It offers concise syntax, enhanced readability, and advanced features such as null safety and coroutines, which contribute to improved code quality and developer productivity.
- Google announced Kotlin as an official language for Android development during Google I/O 2017, indicating its endorsement and preference for Kotlin-based projects.
- Kotlin's interoperability with Java allows developers to seamlessly integrate Kotlin code into existing Java projects and vice versa, easing the transition for developers familiar with Java.
- The adoption of Kotlin by Google underscores its commitment to providing developers with modern and efficient tools for Android app development.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Android Development
Advantages of Android Development
- Open-Source Nature: Android being an open-source operating system fosters a vast community for support, encouraging collaboration and innovation among developers.
- Guidelines for Design: Google provides design guidelines for Android applications, facilitating the creation of more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that align with modern design principles.
- Fragmentation: Android's fragmentation allows applications to run multiple activities on a single screen, providing flexibility and enhancing user experience.
- Easy Distribution: Releasing Android applications on the Google Play Store is relatively straightforward compared to other platforms, enabling developers to reach a broader audience efficiently.
Disadvantages of Android Development
- Fragmentation Challenges: While fragmentation enhances user experience, it presents challenges for developers, requiring adaptation to various screen sizes and device features, which can be time-consuming.
- Testing Complexity: The wide variety of Android devices available in the market leads to significant variability in hardware and software configurations, making thorough testing of applications more difficult and resource-intensive.
- Increased Development Cost: Due to the complexities associated with development and testing in the Android ecosystem, the cost of building an application may escalate, especially for projects with high complexity and extensive features.
FAQs on Introduction to Android Development - Software Development
| 1. What are some key features of Android development? |  |
| 2. What programming languages are commonly used in developing Android applications? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of Android development? |  |
| 4. What are the disadvantages of Android development? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions related to Android development software development? |  |


















