CBSE Class 11 History Sample Paper 2023 - 3 | History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D and E. There are 34 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – Question 1 f021 are MCQs of I mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 22 to 27 are Short Answer Type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60-80 words.
- Section C – Question no 28 to 30 are Long Answer Type questions, carrying 8 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 300-350 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 31 to 33 are Source-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section-E – Question no. 34 is Map-based, carrying 5 marks that includes the identification and location of significant test items. Attach the map with the answer book.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
Section-A
Objective Type Questions.
Q1: When did the excavation at Mesopotamia begin?
(a) 1850
(b) 1804
(c) 1840
(d) 1871
Ans: (c)
The excavations in the Mesopotamia began around the year 1840.
Q2: The Native American tribe forcibly evicted by US President Andrew Jackson was known as ______.
(a) Hopis
(b) Cherokees
(c) Metis
(d) Ottawas
Ans: (b)
The Cherokee was the Native American tribe which was forcibly evicted by the then American President Andrew Jackson.
Q3: Which of these was the oldest Mesopotamian town?
(a) Ur
(b) Sumeria
(c) Urrr
(d) Raur
Ans: (a)
The oldest Mesopotamian town was Ur where several archaeological remains have been found which were important for the reconstruction of the Mesopotamian history.
Q4: Who were the Plebeians?
(a) Plebeians were the royal people of the Roman Empire
(b) Plebeians were the slaves of the Roman Empire
(c) Plebeians were the nomads of the Roman Empire
(d) Plebeians were the common people of the Roman Empire
Ans: (d)
Plebeians were the common people of the Roman empire. In ancient Rome, society was divided into ti%’o main classes: the patricians and the plebeians. Patricians were the aristocratic elite, while plebeians were the common citizens, including farmers, merchants, and labourers.
Q5: Fill in the blank.
Monasteries were constructed.
(a) in the middle of towns
(b) away from town and in forest
(c) far away from human inhabitation
(d) in the vicinity of Churches.
Ans: (c)
The monasteries in the Europe were constructed far away from the human inhabitation.
Q6: Why did China build the fortifications?
(a) To protect their subjects from frequent nomadic raids.
(b) They were fond of huge walls.
(c) It helped in giving an extravagant look to their kingdoms.
(d) None of these.
Ans: (a)
The Chinese built several fortifications. The most well-structured was the Great Wall of China to protect them from nomadic invasions.
Q7: What was the real name of Genghis Khan?
(a) Temujin
(b) Louvre
(c) Miam
(d) Tenzing
Ans: (a)
The real name of the famous Mongol ruler Genghis Khan was Temujin.
Q8: Who were the Franks?
(a) Germanic tribe
(b) Sung tribe
(c) Scottish tribe
(d) French tribe
Ans: (a)
The Franks were a Germanic tribe that lived in what is now western Germany and northern France. They were one of the most powerful tribes in Europe during the Middle Ages. The Franks were originally a group of small tribes that lived along the Rhine River.
Q9: Assertion (A): Public Baths was an essential feature of the urban cities of Roman Empire.
Reason (R): Public Baths was only used for spiritual purposes.
Choose the correct statements:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is correct but R is incorrect
(d) A is incorrect but R is correct.
Ans: (c)
Public Baths were a common architectural feature of the Roman Empire and they were used for several purposes apart from spiritual matters. They were also used for social and recreational purposes.
Q10: Which of these factors was responsible for the rise of nation-states during the century?
(a) End of feudalism and the rise of middle class
(b) End of monarchy
(c) End of peasantry
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
The rise of the nation-state in the 16th century was a complex process with many contributing factors. However, one of the most important factors was the end of feudalism and the rise of the middle class.
Q11: Which of this Italian city contributed to the growth of Renaissance?
(a) Turin
(b) Iucca
(c) Venice
(d) Ban
Ans: (c)
The beginning and the growth of the Renaissance took place from the city of Venice in Italy.
Q12: I launched the Cultural Revolution in China. Identify me: 
(a) Dr. Sun Yat Sen
(b) Mao Zedong
(c) Kiang-Sheik
(d) Zhou Enlai
Ans: (b)
The Cultural Revolution in China was started by the Communist leader Mao Zedong.
Q13: Fill in the blank.
________ painted the Sistine Chapel.
(a) Leonardo Da Vinci
(b) Michelangelo
(c) Voltaire
(d) Picasso
Ans: (b)
The famous Sistine Chapel in the Italy was painted by the famous artist Michelangelo.
Q14: Who were the early European/British settlers in Australia?
(a) Convicts who had been deported from Africa
(b) Convicts who had been deported from England
(c) The Australian tribals
(d) All of these
Ans: (b)
The earliest settlers in Australia were convicts who had been deported from England.
Q15: Choose the correct option.
The imperialist country Germany is located on the continent of
(a) Australia
(b) Europe
(c) Asia
(d) America
Ans: (b)
Germany is a nation geographically located in the Europe continent.
Q16: Onon river is present in:
(a) China
(b) Turkmenistan
(c) Mongolia
(d) Pakistan
Ans: (c)
The Onon River originates in the Khentii Mountains in Mongolia and flows northeast to Russia.
Q17: Which of these Emperors promoted Christianity in Roman Empire?
(a) Constantine
(b) Diocletian
(c) Tiberius
(d) Tacitus
Ans: (a)
The faith of Christianity in the Roman Empire was promoted by the Emperor Constantine.
Q18: What is the correct chronology?
(i) Chinese Communist Party founded
(ii) First Opium War
(iii) Meiji Restoration
(iv) Long March
(a) (ii), (iii), (i) & (iv)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) & (iv)
(c) (i), (ii), (i) & (iv)
(d) (iv), (i), (iii) & (ii)
Ans: (a)
The First Opium war took place between 1839 to 1842. The Meiji Restoration took place in Japan in the year 1868. The Chinese Communist Party was founded in the year 1921. The Long March in China took place in the year 1934.
Q19: CCP emerged victorious after …………………. revolution.
(a) 1911
(b) 1921
(c) 1931
(d) 1901
Ans: (a)
The emergence of the CCP as a dominant force in the China took place after the 1911 Revolution.
Q20: What do you understand by ‘Meiji Restoration’?
(a) Restoration of power back to the public.
(b) Restoration of power back to the army head.
(c) Restoration of power back to the emperor.
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Ans: (c)
The Meiji Restoration of 1868 was the restoration of power back to the emperor.
Q21: What is meant by the term Shogun?
(a) In Japanese history, the hereditary Commander-in-Chief of the army.
(b) In Chinese history, the hereditary Commander-in-Chief of the army.
(c) In French history, the hereditary Commander-in-Chief of the army.
(d) In American history, the hereditary Commander-in-Chief of the army.
Ans: (a)
In Japanese history, the Shoguns were the hereditary Commander-in-chief of the army.
Section-B
Short answer Type Questions
Q22: What is the importance of clay tablets as evidence for Mesopotamian history?
OR
What kind of trade relations did Mesopotamia have with Turkey and Iran and across the Gulf region?
Ans:
- Hundreds of day tablets occur at Mesopotamian sites and offer a wealth of information for the reconstruction of Mesopotamian history.
- These helps to understand the trade transactions within and outside Mesopotamia.
- These helps to understand the transfer deeds of kings and changes in the customary law.
- They helps us to understand the development of script from pictographic to cuneiform.
- The Gilgamesh epic and the poem about Enmarker throw a lot of light on kingship.
- Also, these tablets give us important information about the progress that they had made in the fields of science, mathematics and astronomy.
OR
Mesopotamia was rich in food resources but lacked stones for tools, seals, and jewels. There was no metal even for tools. Wood, copper, tin, silver, gold, shell, and various types of stones were available in Turkey, Iran, and across the Gulf region. These regions, on the other hand, had enough mineral resources but less agricultural produce. Thus, Mesopotamians had flourishing trade relations with these regions. They regularly traded their abundant textiles and agricultural produce for wood, copper, tin, and other minerals.
Q23: Who constituted the First Order? Describe its role.
Ans: The clergy constituted the First Order. The priests derived their importance from the eminence of the Catholic Church in feudal society. The Church had its own laws, it owned the lands given by the rulers and could levy taxes. At the head of the western church was the Pope who lived in Rome. The bishops and clerics who constituted the first order guided the Christians in Europe. Most villages had their own church under Bishops where people assembled for the Sunday mass. The Bishops and the clerics were the religious nobility, and like lords owned vast landed estates, lived in grand palaces and they could levy taxes like the ‘tithe’. Money also came in the form of endowments from the rich.
Q24: What led to the fame of Florence in the 15th century?
Ans: Florence was not a centre of trade or learning by the 13th century. But by the 15th century, it had become a famous city due to its citizens Like Dante Alighieri and Giotto. Dante was a layman who wrote on religious themes. Giotto was an artist who painted life-like portraits which were very different from the stiff figures done by the earlier artists. It developed as the most exciting intellectual city in Italy and as a center of artistic creativity.
Q25: What was the objective of the European countries to establish colonies? What was their nature of control over the colonies?
Ans: The main objective of the European countries to establish colonies was to earn profit. The nature of control was different in different colonies:
- In South Asia, the East India Company was established to trade with India but ultimately succeeded in becoming a political power by defeating the local rulers and annexing their territories.
- In Africa, the Europeans initially traded on the coast, but later the Imperialist powers agreed to divide Africa as colonies for themselves.
- The Europeans settled in countries like Ireland, New Zealand Australia, and South Africa and came to be known as ‘Settlers’.
Q26: Why did the US and Canadian governments end all special provisions for the natives?
Ans: In the 1950s and 1960s, the US and Canadian governments thought of ending all provisions for the natives in the hope that they would join the mainstream and adopt the European culture. But the natives did not want this. In 1954, with the Declaration of Indian Rights, prepared by them, they agreed to take up the US citizenship on the condition that their reservations would not be taken away and their traditions would not be interfered with. A similar development occurred in Canada.
In 1969, the government announced that they would not recognise aboriginal rights. The natives organised a series of demonstrations and debates but the question could not be resolved until 1982, when the Constitution Act accepted the existing aboriginal and treaty rights of the natives. Today, even though the natives have been greatly reduced in numbers, they have been able to assert their right to their own culture and particularly in Canada to their sacred land in a way their ancestors could not have done in the 1880.
Q27: What is meant by the ‘Great Leap Forward’? What were its benefits?
OR
Describe the military and the economic reforms introduced under the Meijis.
Ans: The Great Leap Forward movement was launched in 1958, based and designed to meet the Chinese situation. It was a policy to galvanise rapid developments in both industry and agriculture and increase output and to adapt to the Chinese conditions. There was a complete change on the emphasis in industry, instead of large-scale works smaller factories were established. Large communes were established that were divided into brigades and work teams with elected council.
Its benefits included:
- Both agricultural and industrial production increased substantially.
- China managed to feed its massive population without facing a famine.
- The communes became efficient units of Local government which enabled Beijing to keep in touch with the local opinion.
- It enabled China to avoid the problem of growing unemployment and also helped the spread of welfare activities, education and improvement in the position of women in Society.
OR
Military: An army based on the European model was established. Military service declared universal and obligatory, soldiers were recruited at the age of twenty. They served for three years in the active army and four years in the reserve. A national army thus came into existence. European officers were called to train them. In addition, dockyards and arsenals were constructed. Military was put under the direct command of the emperor.
Economy: An agricultural tax was levied to raise funds. The first railway line was built in 1870-72 between Tokyo and Yokohama. Textile machinery was imported from Europe and foreign technicians were employed to train the workers. Japanese students were sent abroad to study. In 1872, modem banking institutions were established. Companies like Mitsubishi and Sumitomo were given subsidies add tax benefits to become major ship-builders so that the Japanese trade was from now on carried in Japanese ships.
Section-C
Long Answer Type Questions.
Q28: Justify the statement, “The ruling elites were wealthier and more powerful than ever before” in the Roman Empire during the sixth century.
OR
Discuss the main features of the Early Empire in Rome.
Ans: There is no doubt that the earlier ruling elites were richer or wealthier and powerful than ever before.
This was due to the following reasons:
- Urban prosperity was marked by new forms of architecture and an exaggerated sense of luxury. The ruling elites were wealthier and more powerful than ever before. In Egypt, hundreds of Papyri that survived showed us that the society was relatively affluent where money was in extensive use and rural estates generated vast incomes in gold. For example, Egypt contributed taxes of over 2.5 million solidi a year in the reign of Justinian in the sixth century.
- The general prosperity was especially marked in the eastern region where the population was still expanding till the sixth century, despite the outbreak of bubonic plague which affected the Mediterranean in the 540s. In the West, by contrast, the empire was fragmented politically as Germanic groups from the North (Goths, Vandals, Lombards, etc.) took over all the major provinces and established kingdoms that have been described as post-Roman. In the east, where the empire remained united, the reign of Justinian is the high water mark of prosperity and imperial ambition.
OR
The main features of the Early Empire were:
- The Emperor, the aristocracy, and the army were the three main players of the empire.
- The Emperor was called the ‘Principate’ but in practice he was an absolute ruler.
- The Senate represented the aristocracy i.e. the wealthiest families who were mainly landowners.
- The Romans had a professional and paid army.
- The soldiers had to put in a minimum 25 years of service. The army was the single largest organised body in the empire.
- By the fourth century, there were almost 600,000 soldiers.
- There was a gradual extension of the Roman direct rule.
- Dependent kingdoms were absorbed into Roman provincial territory. All the territories of the empire were organised into provinces and subject to taxation.
- The emperor controlled the vast empire through the cities and the local upper classes collaborated with the Roman state in administering their own territories and raising taxes from them. Most of the governing class people came from the provincial upper classes.
- Nuclear family system was prevalent, women enjoyed considerable legal rights in owning and managing property.
- Casual literacy varied greatly between different parts of the empire.
- The Roman empire was a cultural mosaic that had a variety of religious cults, languages, dress styles, food habits and social organisation.
- The empire had a good infrastructure of harbours, mines, brîckyards, olive oil factories.
- They had a flourishing trade with Spain, North Africa and Egypt.
- They were also technologically advanced and used diversified applications of water power as well as used advanced mining technology.
Q29: What caused Genghis Khan’s unpopularity in the conquered lands? Explain. [8]
OR
Describe the major events of the Mongol tribe that took place after the death of Genghis Khan. [8]
Ans:
Genghis Khan had undoubtedly built a great kingdom. The freshly conquered people showed little regard for their new lord. This was due to a number of factors.
The following were the primary causes:
- Several lovely cities and towns were destroyed by the Mongols during their invasion. After his on-slaught, the majority of these cities lost their glory.
- Their invasion had a negative impact on agriculture since standing crops were destroyed when the massive army withdrew.
- Trade and commerce were severely harmed throughout the war year or during the invasion.
- As a result of their invasion, a great number of people died. Many people became disabled and powerless.
- Several persons were enslaved.
- As a result of their invasion, the underground rivers in the arid region were not repaired in a timely manner.
- All of his expeditions resulted in the desertification of freshly captured territories.
- People from many walks of life were subjected to adversity.
OR
The major events that took place after the death of Genghis Khan are as follows:
- The Mongol military forces met with a few reversals in the decades after 1230 but quite noticeably after 1260 the original impetus of campaigns could not be sustained in the West. Although Vienna, and beyond it western Europe as well as Egypt was within the grasp of Mongol forces, their retreat from the Hungarian steppes and defeat at the hands of the Egyptian forces signaled the emergence of new political trends There were two facets to this, one the internal politics of succession within the Mongol family. These interests were more important than the pursuit of campaigns in Europe.
- The second compulsion occurred as Jochi and Ogodei lineages were marginalised by the Toluyid branch of Genghis Khan’s descendants. Toluyid interests in the conquest of China increased during the 1260s, forces and supplies were increasingly diverted into the heartland of the Mongol dominion.
- As a result, the Mongols fielded a small under-staffed force against the Egyptian military. Their defeat and the increased preoccupation with China of the Toluyid family marked the end of western expansion. Consequently, conflict between the Jochid and Toluyid descendants along the Russian-Iranian frontier diverted the Jochids away from the European campaigns.
- This did not arrest their campaigns in China which was reunited under the Mongols. Paradoxically at this moment of the greatest successes, the internal turbulence between the members of the ruling family manifested itself.
Q30: How did Japan escape colonisation?
OR
Did Japan’s policy of rapid industrialisation lead to wars with its neighbours and destruction of the environment?
Ans:
After the news of China’s defeat, fear gripped Japan that it too might be made into a colony. To escape the similar fate as China and India, the government launched a policy with a slogan, “Fukoku Kyohei” (rich country, strong army). They realised that they needed to develop their economy and build a strong army. To this, they needed to create a sense of nationhood among the people and to transform subjects into citizens.
To achieve these ideals the government took the following measures:
- It built the ‘emperor system’.
- New system of education was introduced based on the European model with special emphasis on ‘moral culture’ and an attitude of extreme nationalism and chauvinism. By 1910, schooling was almost universal,
- To integrate the nation, a new administrative structure altering the old village boundaries was imposed.
- A modern military force was developed. Conscription was introduced for all young men over 20 years.
- Civil liberties and open political struggles were curbed and a legal system was set up to regulate formation of political groups, control holding of meetings, and imposed strict censorship.
- The Diet and the military were put under the direct command of the emperor. The state was controlled by an oligarchy and the military and the police were given wide powers.
- The economy was modernised in less than four decades. State capitalism was undertaken with the help of Daimyos and big merchant houses. State industries were sold to ‘Zaibatsu’. Companies Like Mitsubishi and Sumitomo were helped by subsidies and tax benefits.
- Initially the stress was on strategic industries but was soon followed by other like textiles and cement.
OR
- Yes, Japan’s policy of rapid industrialisation was one of the leading factors which led to wars with its neighbours, Russia and China, and destruction of environment.
- Japan as a country is poor in natural resources and land is not suitable for agriculture. She needed minerals and raw materials like tin, iron and raw cotton to develop and feed her growing industries.
- The unstable political conditions in China fuelled her ambitions for expansion. Demand for natural resources like timber led to environmental destruction. There were increasing incidents of cadmium poisoning and mercury poisoning and air pollution that led to a lot of health issues.
- Japan desired a larger market for its products. It started pursuing her colonial ambitions. The Korean victory suited them as it could be used as a market for her products. In the Sino-Japanese war of 1894-95, China was defeated and Taiwan was annexed.
- In 1902, by entering into an alliance with Britain, Japan became the first Asian country to enjoy an equal status with the other colonial power. In the Russo-Japanese war of 1905, Russia too recognised Japan’s interest in Korea.
- Japanese industries expanded rapidly during the First World War because of trading boom of the war years. The size of their factories increased. In 1921, when Europe began to revive and recover its lost markets, unemployment and industrial unrest developed. At the same time peasants were hit by rapidly falling price of rice due to bumper harvest.
- The world economic crisis of 1929-32 further worsened the situation. It was largely to safeguard and expand her economic interests in the Pacific that Japan bombarded the Pearl Harbour, which resulted in its humiliating defeat and bombardment of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in World War II.
Section-D
Source-based Questions.
Q31: Read the below passage and answer the following questions.
A man of the southern marshes, Nabopolassar, released Babylonia from Assyrian domination in 625 BCE. His successors increased their territory and organised building projects at Babylon. From that time, even after the Achaemenids of Iran conquered Babylon in 539 BCE and until 331 BCE when Alexander conquered Babylon, Babylon was the premier city of the world, more than 850 hectares, with a triple wail, great palaces and temples, a ziggurat or stepped tower, and a processional way to the ritual centre. Its trading houses had widespread dealings and its mathematicians and astronomers made some new discoveries. Nabonidus was the last ruler of independent Babylon. He writes that the god of Ur came to him in a dream and ordered him to appoint a priestess to take charge of the cult in that ancient town in the deep south. He writes: ‘Because for a very long time the office of High Priestess had been forgotten, her characteristic features nowhere indicated, I bethought myself day after day …‘ Then, he says, he found the stele of a very early king whom we today date to about 1150 BCE and saw on that stele the carved image of the Priestess. He observed the clothing and the jewelry that was depicted. This is how he was able to dress his daughter for her consecration as Priestess.
On another occasion, Nabonidus’s men brought to him a broken statue inscribed with the name of Sargon, king of Akkad. (We know today that the latter ruled around 2370 BCE.) Nabonidus, and indeed many intellectuals, had heard of this great king of remote times. Nabonidus felt he had to repair the statue. ‘Because of my reverence for the gods and respect for kingship,’ he writes, ‘I summoned skilled craftsmen, and replaced the head.’
(a) Who was Nabopolassar?
(b) Who won Babylonia, the world-famous city of the time in 539-331 BCE?
(c) Which is correct about Nabopolassar:
(i) He was the last ruler of Babylon.
(ii) He was a slave ruler.
(iii) He repaired the statue of Sargon, the king of Akkad.
(iv) Both (i) and (iii) are correct. [
Ans:
(a) Nabopolassar was the conqueror of Babylonia who took over from the Assyrian dynasty in 625 BCE.
(b) Achaemenids of Iran conquered the city of Babylon in 539 BCE and ruled it till Alexander conquered it in 331 BCE.
(c) Both (i) and (iii) are correct.
Nabopolassar was the last ruler of the Babylon. He led to the repairing of the last statue of Sargon, who was the King of Akkad.
Q32: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Apart from the Church, devout Christians had another kind of organisation. Some deeply religious people chose to live isolated lives, in contrast to clerics who lived amongst people in towns and villages. They lived in religious communities called abbeys or monasteries, often in places very far from human habitation. Two of the more well-known monasteries were those established by St. Benedict in Italy in 529 and of Cluny in Burgundy in 910. Monks took vows to remain in the abbey for the rest of their lives and to spend their time in prayer, study and manual labour, like farming. Unlike priesthood, this life was open to both men and women/men became monks and women nuns. Except in a few cases, all abbeys were single-sex communities, that is, there were separate abbeys for men and women. Like priests, monks, and nuns did not marry. From small communities of 10 or 20 men/women, monasteries grew to communities often of several hundred, with large buildings and landed estates, with attached schools or colleges and hospitals. They contributed to the development of the arts. Abbess Hildegard was a gifted musician and did much to develop the practice of community singing of prayers in church. From the thirteenth century, some groups of monks called friars chose not to be based in a monastery but to move from place to place, preaching to the people and living on charity.
(a) Who was Abbes Hildegard?
(b) Was he in favour of the Three Orders?
(c) What examples does he give to prove it?
Ans:
(a) Abbess Hildegard was a gifted musician who contributed to the development of the practice of community singing of prayers in church.
(b) Yes, he was in favour of the three orders.
(c) In support of the division of three orders, Hildegard gives the following examples:
- How a herder never herds his entire cattle in one stable but differentiates between cows, donkeys, sheep, and goats.
- Though God is the creator of all, yet he does not make all equal. There are distinctions among his creations.
- God loves all human beings but he does not treat all equally on earth or in heaven.
Q33: Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
William Tyndale (1494-1536), an English Lutheran who translated the Bible into English in 1506, defended Protestantism thus: ‘In this they be all agreed, to drive you from the knowledge of the scripture, and that ye shall not have the text thereof in the mother tongue, and to keep the world still in darkness, to the intent they might sit in the consciences of the people, through vain superstition and false doctrine, to satisfy their proud ambition, and insatiable covetousness, and to exalt their own honour above king and emperor, yea, and above God himself… Which thing only moved me to translate the New Testament. Because I had perceived by experience, how that it was impossible to establish the lay-people in any truth, except the scripture were plainly laid before their eyes in their mother-tongue, that they might see the process, order, and meaning of the text’.
(a) Who was William Tyndale?
(b) What did he seek to achieve by translating the Bible into English?
(c) What were the issues on which the Protestants criticised the Catholic Church?
Ans:
(a) William Tyndale was an English Lutheran who translated the Bible into English in 1506. He was a defender of Protestantism.
(b) By translating the Bible into English, he sought to make the Bible available to the layman. He also wanted to expose the false practices indulged in by the church in the name of the sacred text.
(c) The issues criticised were: immoral and luxurious life of the churchmen, sale of “letters of Indulgence”, their practice of selling offices, Pope’s authority to raise taxes and fees, and divergence from the religious texts and emphasis on rituals.
Section-E
Map-based Questions.
Q34:
(i) On a given map of Australia locate the following.
(a) Tasmania
(b) Darwin
(c) Canberra
Ans:
(a) Pacific Ocean
(b) Southern Ocean
(ii) On same map, A & B has been marked as an important sea bodies of Australia. Identify them and write their names.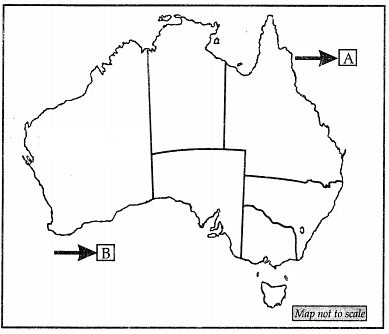 Ans:
Ans: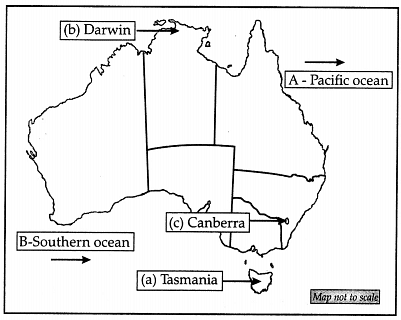
|
27 videos|157 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on CBSE Class 11 History Sample Paper 2023 - 3 - History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the important topics covered in CBSE Class 11 History curriculum? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively prepare for the CBSE Class 11 History exam? |  |
| 3. What is the marking scheme for the CBSE Class 11 History exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any recommended reference books for CBSE Class 11 History preparation? |  |
| 5. How can students improve their writing skills for the CBSE Class 11 History exam? |  |





















