Worksheet Solutions: Basics of Computer - Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Do as Directed |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Fill in the blanks |

|
| True or False |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|

|
Do as Directed
Q1: Match each image to the type of data it processes: analog or digital.
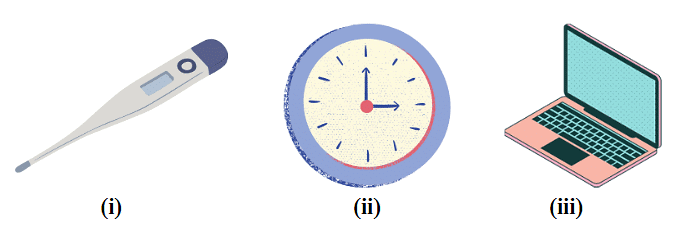
Ans: (i) Thermometer: Analog
(ii) Clock: Analog
(iii) Computer: Digital
Q2: Sort the images into two categories: large computers and small computers.
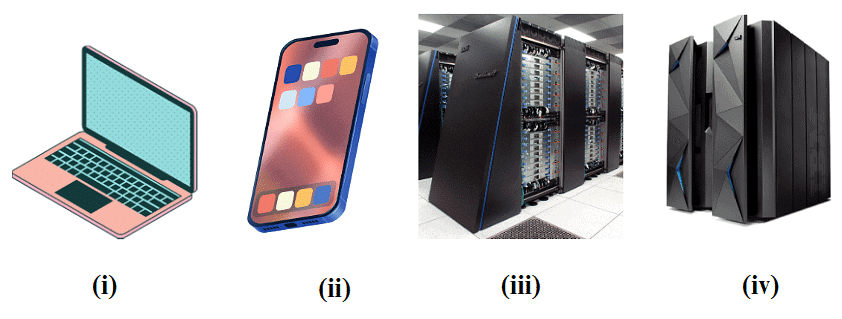 Ans: Large computers: Supercomputer, Mainframe computer
Ans: Large computers: Supercomputer, Mainframe computer
Small computers: Laptop, Smartphone
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Who is often credited as the inventor of the first mechanical computer?
(A) Charles Babbage
(B) Alan Turing
(C) Blaise Pascal
(D) Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Ans: Charles Babbage
Explanation: Charles Babbage is often credited as the inventor of the first mechanical computer due to his design of the Analytical Engine in the 19th century.
Q2: Which of the following devices was NOT part of the first generation of computers?
(A) Vacuum Tubes
(B) Transistors
(C) Magnetic Drum Memory
(D) Punch Cards
Ans: Transistors
Explanation: Transistors were not part of the first generation of computers. They replaced vacuum tubes in the second generation and made computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.
Q3: The ENIAC, one of the earliest electronic general-purpose computers, was primarily used for:
(A) Weather Forecasting
(B) Military Calculations
(C) Commercial Banking
(D) Scientific Research
Ans: Military Calculations
Explanation: The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was primarily used for military calculations during World War II, particularly for artillery firing tables.
Q4: Which computer programming language was developed by Grace Hopper in the 1950s?
(A) COBOL
(B) FORTRAN
(C) C++
(D) Java
Ans: COBOL
Explanation: Grace Hopper developed COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) in the 1950s. It was one of the first high-level programming languages designed for business applications.
Q5: The term "bug" in computing originated from:
(A) A software glitch
(B) An insect found inside a computer
(C) A hardware malfunction
(D) A programming error
Ans: An insect found inside a computer
Explanation: The term "bug" originated from an actual moth found inside the Harvard Mark II computer in 1947. Grace Hopper famously recorded the incident in the computer's logbook, coining the term "computer bug" to describe a malfunction.
Fill in the blanks
(i) The _____________ is considered the "Father of Computing" for his design of the Analytical Engine.
(ii) The first mechanical computing device is known as the _____________.
(iii) The key component that revolutionized computing by integrating the entire CPU onto a single chip is the _____________.
(iv) The first generation of computers primarily used _____________ for circuitry.
(v) Grace Hopper coined the term "computer bug" when an actual _____________ caused a malfunction in the Mark II computer.
Ans: (i) Charles Babbage
(ii) abacus
(iii) microprocessor
(iv) vacuum tubes
(v) moth
True or False
(i) The ENIAC and UNIVAC computers are examples of second-generation computers.
(ii) The microprocessor integrates only a portion of the central processing unit (CPU) onto a single chip.
(iii) The abacus is a modern electronic computing device.
(iv) The Analytical Engine, designed by Charles Babbage, was successfully built and operated during his lifetime.
(v) The Mark I computer, developed by IBM, used punch cards for data input and output.
Ans: (i) False
(ii) False
(iii) False
(iv) False
(v) True
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What are the two main characteristics of a computer?
Sol: It responds to instructions and follows a list of instructions.
Q2: What type of computer is the fastest and most powerful?
Ans: Supercomputer
Q3: What type of data does an analog computer process?
Ans: Continuous data, like temperature or speed.
Q4: What is the difference between RAM and storage in a computer?
Ans: RAM stores data temporarily, while storage holds data permanently.
Q5: Give an example of a microcomputer.
Ans: Laptop, smartphone, or tablet.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Imagine you have a recipe book with instructions for different dishes. How is this similar to a computer program?
Ans: Both a recipe book and a computer program provide step-by-step instructions that need to be followed in a specific order to achieve a desired outcome – a delicious dish or a completed task on the computer.
Q2: Why do you think people say "the computer crashed"? What does it actually mean?
Ans: People say "the computer crashed" when it unexpectedly stops working or malfunctions. It doesn't literally crash like a car, but it means the computer program encountered an error and can't continue functioning properly.
Q3: You want to play a game with your friend online, but their computer is too slow. What might slow down a computer, and how can we speed it up?
Ans: Several things can slow down a computer, like having too many programs open at once, inadequate storage space, or outdated software. To speed it up, you can close unnecessary programs, delete unused files, or update software.
Q4: What's the difference between the internet and a website? It might help to think of the internet like a library.
Ans: The internet can be thought of a massive library with countless books (websites) on various topics. The internet is the vast network connecting computers worldwide, while websites are individual pages within that network, each containing specific information or providing different services.
Q5: Why do you think computers need to be kept cool? What happens if they get too hot?
Ans: Computers generate heat while processing information. If they overheat, it can damage the internal components and cause malfunctions. Therefore, it's important to keep them cool with fans or proper ventilation.













