Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Notes > Civil Law for Judiciary Exams > Written Statement Format
Written Statement Format | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
What is a Written Statement?
- In the legal realm, a written statement, as per the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC), refers to a formal document submitted by the defendant in response to the plaintiff's complaint or petition. This document outlines the defendant's defenses, denials, and any counterclaims they might have. It is crucial for focusing on the main issues of the case and plays a pivotal role in shaping the lawsuit's direction.
- When drafting a written statement, the defendant must either admit or deny each allegation made by the plaintiff and assert any affirmative defenses they possess. Moreover, if there are any claims against the plaintiff, they can be included as counterclaims in the written statement. It is imperative to adhere to the legal guidelines and deadlines while filing a written statement in compliance with the CPC.
Components of a Written Statement Format
- Title: The title of a written statement, as per the Civil Procedure Code (CPC), should prominently indicate it as a "Written Statement" under the CPC. It must also include the case number and the names of the parties involved.
- Introduction: Commence the written statement with an opening paragraph that identifies the defendant, their address, and their role in the case.
- Background: Offer a concise overview of the case, outlining the plaintiff's claims and the events that led to the lawsuit. Mention the court where the case is filed.
- Response to Allegations: Address each allegation made by the plaintiff in their complaint. Clearly state whether the defendant admits, denies, or lacks knowledge of each specific claim. Utilize a numbered list for better clarity.
- Affirmative Defenses: Include any affirmative defenses that the defendant intends to raise. These defenses are legal arguments that, if validated, could excuse the defendant from liability.
- Counterclaims: If the defendant has any claims against the plaintiff stemming from the same circumstances, present them as counterclaims in the written statement.
- Witnesses and Evidence: Specify any witnesses or evidence that the defendant plans to rely on during the trial to bolster their defense.
- Legal Citations: Reference any pertinent legal statutes, case law, or precedents that support the defendant's stance within the written statement.
- Relief Sought: Clearly outline the relief or remedy that the defendant is seeking from the court. This may involve a request for case dismissal, a specific judgment, or any other appropriate relief.
- Verification: The written statement typically necessitates verification by the defendant or their legal representative, affirming that the contents are accurate to the best of their knowledge and belief.
- Date and Signature: Conclude the written statement by signing and dating it, including the name and designation of the signatory.
- Annexures: Attach any pertinent documents, exhibits, or evidence that support the defendant's case, referring to them within the written statement.
Question for Written Statement FormatTry yourself: What is the purpose of a written statement in the legal realm?View Solution
Sample Written Statement Format
The written Statement on Behalf of the Defendant’s format is given below: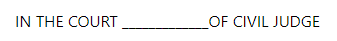
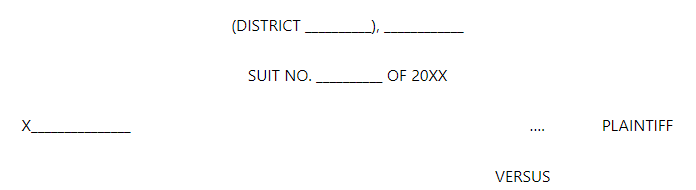

Preliminary Objections
- The plaintiff's claim is time-barred under the relevant article of the Limitation Act and should be dismissed solely on this basis.
- This court lacks jurisdiction to hear and decide this case due to [reason].
- The suit has not been correctly valued for court fees and jurisdictional purposes and should therefore be summarily rejected.
- There is no valid cause of action in favor of the plaintiff against the defendant, warranting dismissal of the suit.
- The suit is deficient due to the non-joinder of necessary parties, specifically [name].
- The inclusion of Z as a party to the suit is improper.
- The suit is precluded by the principle of res judicata due to a prior decree in Suit No. ____, rendering it liable for dismissal.
- The suit should be stayed as there is a pending suit between the same parties in another court.
- The suit lacks proper verification as required by law.
- The plaintiff's claim for permanent injunction is not viable under Section 41(h) of the Specific Relief Act, as a more appropriate remedy is available through specific performance.
- The plaintiff's claim for permanent injunction is also barred under Section 41(i) of the Specific Relief Act due to the plaintiff's alleged misconduct.
- The plaintiff's claim for declaration is barred under Section 34 of the Special Relief Act, as further consequential relief has not been sought.
- Enforcement of the contract of personal service is prohibited under Section 14 of the Specific Relief Act, rendering the suit untenable.
- The suit is invalid as the mandatory notice under Section 80 of the Code of Civil Procedure/Section 14(1)(a) has not been provided by the plaintiff.
- The plaintiff firm lacks registration under Section 69 of the Indian Partnership Act, making it ineligible to bring forth this suit.
- The present suit is prohibited by Section 4 of the Benami Transaction (Prohibition) Act, 1988, warranting its dismissal.
On Merits
- The first paragraph of the plaint is accepted and acknowledged.
- The allegations in paragraph 2 of the plaint are denied due to lack of sufficient knowledge. The plaintiff is required to provide evidence to substantiate each claim made in this paragraph.
- The assertions in paragraph 3 of the plaint are wholly inaccurate and are thus denied. It is contested that the plaintiff is the rightful owner of the property in question. In reality, Mr. N is the lawful owner.
- Regarding paragraph 4 of the plaint, it is acknowledged that the defendant currently possesses the property in question. However, all other statements in this paragraph are categorically denied. Specifically, it is refuted that [specific allegations] are true.
- The remaining contentions in the plaint are refuted. Each allegation will be addressed individually based on the pertinent facts of the case. The response provided herein is merely illustrative and may vary depending on the circumstances of the case.
- Paragraph 11 of the plaint is contested and denied. There is no legal basis for the plaintiff's claim against the defendant. Consequently, the plaintiff's claims should be dismissed outright.
- Paragraph 21 is not admitted. This court lacks jurisdiction to adjudicate this matter as the subject of the suit exceeds the pecuniary jurisdiction of this court.
- Paragraph 13 is also not admitted. The suit has not been accurately valued for the purposes of determining court fees and jurisdiction. According to the defendant's assessment, the correct valuation of the suit is Rs. [amount].
Prayer
The defendant respectfully requests this Hon'ble Court to:
(a) Dismiss the plaintiff's suit in its entirety.
(b) Award costs to the defendant.
(c) Grant any other fair and reasonable relief as deemed appropriate in the interests of justice.
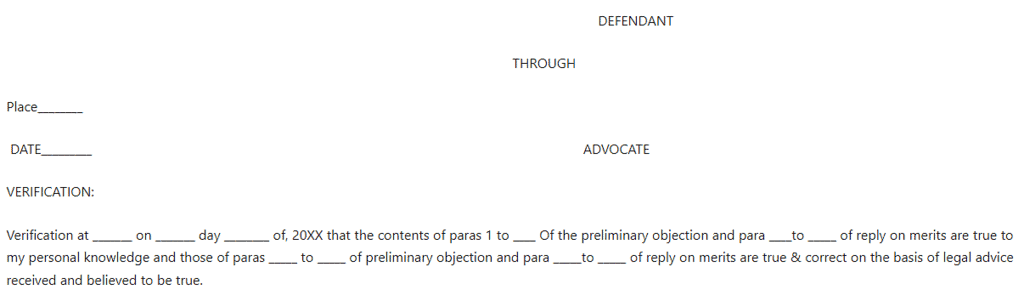
Defendant
- Absolutely, consulting with a legal professional is crucial to ensure that all legal requirements and strategies are properly addressed in any legal document or statement. This general guideline is provided for informational purposes only and should be used as a reference point when working with a lawyer or legal expert on your specific case.
The document Written Statement Format | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams is a part of the Judiciary Exams Course Civil Law for Judiciary Exams.
All you need of Judiciary Exams at this link: Judiciary Exams
|
363 docs|256 tests
|
FAQs on Written Statement Format - Civil Law for Judiciary Exams
| 1. How to write a strong written statement for judiciary exams? |  |
Ans. To write a strong written statement for judiciary exams, it is important to clearly state your position, provide supporting evidence, and use clear and concise language.
| 2. What is the purpose of a written statement in a judiciary exam? |  |
Ans. The purpose of a written statement in a judiciary exam is to present facts, arguments, and evidence in a clear and organized manner to support a legal case.
| 3. How long should a written statement be for a judiciary exam? |  |
Ans. The length of a written statement for a judiciary exam can vary depending on the specific requirements of the exam, but it is typically recommended to be concise and to the point.
| 4. What are the key components of a well-written statement for a judiciary exam? |  |
Ans. The key components of a well-written statement for a judiciary exam include a clear introduction, a detailed explanation of the facts, a thorough analysis of the legal issues, and a strong conclusion.
| 5. How can one ensure that their written statement is effective in a judiciary exam? |  |
Ans. To ensure that a written statement is effective in a judiciary exam, it is important to carefully review and revise the statement for clarity, accuracy, and relevance to the legal case.
Related Searches
















