Understanding Hund's Rule | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Hunds Rule of Maximum Multiplicity |

|
| Explanation of Hund’s Rule |

|
| Electron Configuration and its Purpose |

|
| Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity |

|
Introduction
The Aufbau principle dictates that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals before filling higher energy ones. However, this principle doesn't provide a specific order for the filling of the three 2p orbitals.
According to Hund’s rule:
- Before any orbital is doubly occupied, each orbital in the sublevel is singly occupied.
- To maximize total spin, all electrons in singly occupied orbitals possess the same spin.
- An electron in a half-filled orbital won't pair with another electron since it can fill all its orbitals with similar energy. Consequently, many atoms in their ground state have unpaired electrons. When two electrons encounter each other, they exhibit behavior akin to magnets, striving to distance themselves before eventual pairing.
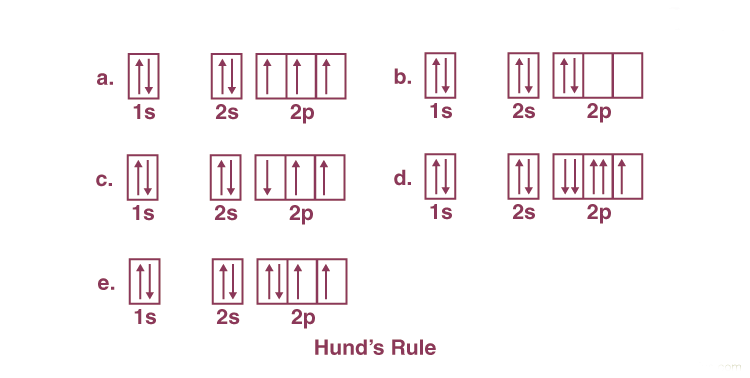
Hunds Rule of Maximum Multiplicity
Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity dictates that among electron configurations, the term with the highest multiplicity occupies the lowest energy level. As per this rule, electron pairing within p, d, and f orbitals is not permitted until each orbital within a given subshell is singly occupied.
Hund's Rule states:
- Within a sublevel, each orbital is singly occupied before becoming doubly occupied.
- Electrons in singly occupied orbitals share the same spin orientation.
Explanation of Hund’s Rule
Electrons occupy empty orbitals before undergoing pairing, primarily due to their negative charges, which induce repulsion between them. To minimize this repulsion, electrons avoid sharing orbitals.
According to the second rule, unpaired electrons within singly occupied orbitals exhibit identical spin orientations. The spin of the initial electrons in the sublevel determines the spin of subsequent electrons. For instance, in a carbon atom's electron configuration of 1s22s22p2, the two 2s electrons occupy the same orbital, while the two 2p electrons occupy different orbitals in accordance with Hund’s Rule.
Electron Configuration and its Purpose
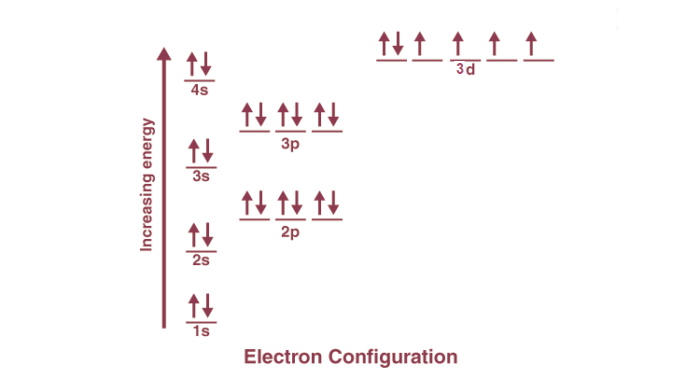
The image above aids in comprehending electronic configuration and its significance. When two atoms make contact, their valence shells interact first. An atom is deemed less stable when its valence shell is not fully occupied. The chemical properties of an element are heavily influenced by its valence electrons, and elements with similar valence numbers often exhibit comparable chemical characteristics.
Furthermore, electron configuration offers insights into stability prediction. An atom is considered most stable when all its orbitals are fully occupied. Orbitals with complete energy levels, such as those found in noble gases, are particularly stable and tend not to react with other elements.
Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity
The principle posits that within a given electron configuration, the term with the highest spin multiplicity corresponds to the lowest energy level. It suggests that when multiple orbitals of equivalent energy remain unoccupied, electrons first occupy them individually before pairing up. Derived from observations in atomic spectra, this rule aids in predicting the ground state of molecules or atoms with one or more open electronic shells. Friedrich Hund discovered this principle in 1925.
Uses of Hund’s Rule:
Hund’s Rule finds extensive utility in various fields such as atomic chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy, and other related disciplines.
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Hund's Rule - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is Hund's Rule of Maximum Multiplicity? |  |
| 2. How does Hund's Rule help in predicting stability through electron configuration? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of Hund's Rule in chemistry? |  |
| 4. How does Hund's Rule relate to the structure of an atom? |  |
| 5. Why is Hund's Rule important in the study of chemistry and atomic structure? |  |




















