Understanding Ionic Bonds | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Ionic Bond? |

|
| Electrovalent Bond |

|
| Electronegativity and Ionic Bonding |

|
| Ionic Bond Vs Covalent Bond |

|
What is an Ionic Bond?
The ionic bond is defined as the electrostatic force of attraction that binds together two ions of opposite charges. A chemical bond arises between two atoms through the complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the attainment of their nearest inert gas configuration. There are primarily three mechanisms by which two atoms combine to release energy and achieve stability. One of these mechanisms involves the donation or acceptance of electrons to achieve an octet configuration. This type of bond is referred to as an ionic bond or electrovalent bond, formed when one atom gains electrons while the other loses electrons from its outermost level or orbit.
Electrovalent Bond
Electrovalent bonds emerge through the transfer of electrons from atoms of one element to those of another, yielding positive and negative ions. This bond, resulting from electron transfer, is termed an electrovalent or ionic bond. Electrovalent bonds exclusively occur between metals and non-metals; they do not form between two non-metals.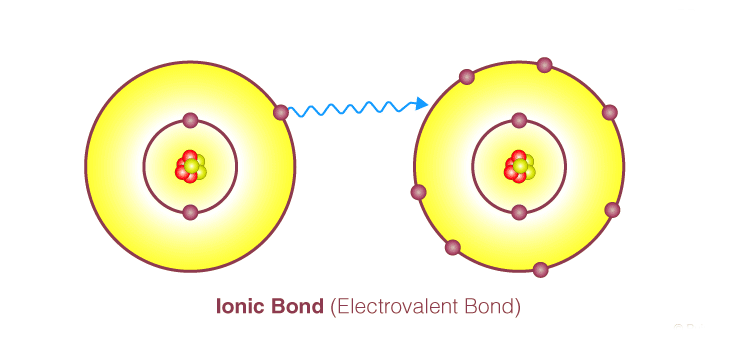
In essence, an electrovalent bond involves the transfer of a specific number of electrons to another dissimilar atom, which possesses a tendency to acquire electrons, thereby enabling both atoms to achieve stable inert gas configurations. This process of electron transfer is accompanied by a decrease in potential energy due to the electrostatic attraction between the ions, resulting in a lower overall potential energy of the system post-ionic bond formation.
Electronegativity and Ionic Bonding
- An Ionic bond arises from the complete transfer of valence electrons, aiming to achieve stability.
- This transfer generates two ions with opposite charges: positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
- The strong attractive force between these ions constitutes the ionic or electrovalent bond.
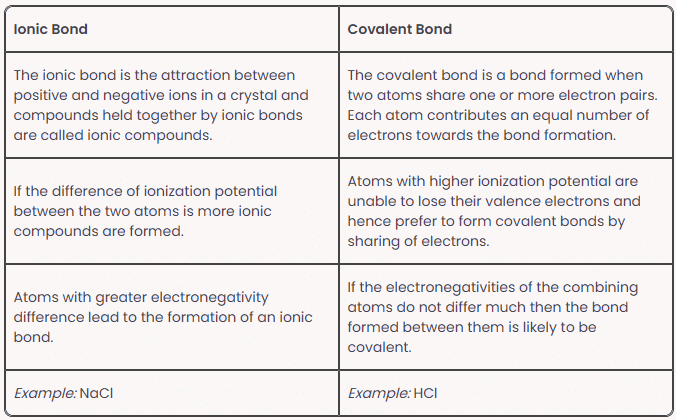
- Ionic bonds typically occur between atoms exhibiting significant disparities in electronegativity, as opposed to covalent bonds, which form between atoms with smaller differences in electronegativity.
- The compound resulting from the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions is termed an ionic compound.
Ionic Bond Vs Covalent Bond
Ionic Bond Properties
The robust attraction between cations and anions within molecules bonded by ionic bonds results in the following characteristics:
- Ionic bonds exhibit the highest strength among all bond types.
- With charge separation inherent in the ionic bond, these bonds are highly reactive in suitable environments.
- Molecules bonded by ionic bonds typically possess high melting and boiling points.
- Ionic bonded molecules, whether in aqueous solutions or in a molten state, serve as effective conductors of electricity. This conductivity arises from the presence of ions, which act as charge carriers.
Examples of Ionic Bonds
The following table shows the elements and the ions formed by them when they lose or gain e‑. 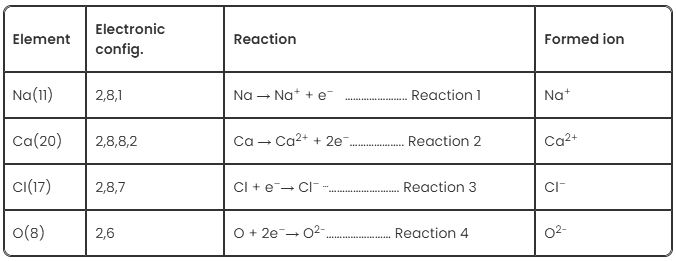
- Now when Na reacts with Cl, reaction 1 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be NaCl.
- When Na reacts with O, reaction 1 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be Na2
- When Ca reacts with Cl, reaction 2 and reaction 3 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaCl2.
- When Ca reacts with O, reaction 2 and reaction 4 will take place and the resultant compound will be CaO.
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Ionic Bonds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is an ionic bond? |  |
| 2. How do ionic bonds differ from covalent bonds? |  |
| 3. What properties do compounds with ionic bonds exhibit? |  |
| 4. Can ionic bonds form between two nonmetals? |  |
| 5. How do you determine the formula of an ionic compound formed from two elements? |  |















