Covalent Bonds | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
A covalent bond arises when electrons are equally shared between the atoms involved. This shared pair of electrons, known as a bonding pair or shared pair, constitutes the essence of this bonding type. Covalent bonds are also referred to as molecular bonds. Through the sharing of bonding pairs, atoms achieve stability in their outer shells, resembling the stable electron configurations of noble gases.
What is Covalent Bond?
Elements with exceptionally high ionization energies cannot readily donate electrons, while those with very low electron affinities struggle to accept electrons. Consequently, atoms of such elements tend to engage in electron sharing with atoms of other elements or within atoms of the same element. This sharing enables both atoms to achieve octet configurations in their respective valence shells, thereby attaining stability. Such interactions, involving the sharing of electron pairs among different or identical elements, are termed Covalent Bonds.
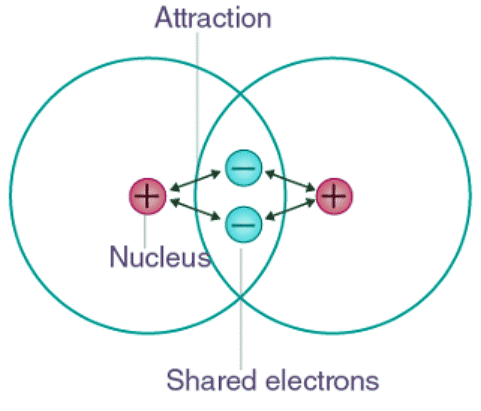
Covalent bonding can be achieved in two ways:
- Sharing of electrons between atoms of the same kind, for example, formation of H2, Cl2, O2, etc.
- Sharing of electrons between atoms of different kinds, for example, formation of CH4, H2O, NH3, etc.
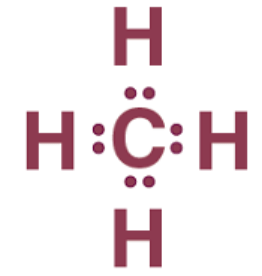
Covalent Bonding in Carbon Atom
According to carbon's electronic configuration, it requires either the gain or loss of 4 electrons to achieve stability, which presents challenges:
- Carbon cannot gain 4 electrons to become C4- due to the difficulty of 6 protons accommodating 10 electrons, resulting in instability.
- Similarly, carbon cannot lose 4 electrons to become C4+ as it demands significant energy to remove 4 electrons. Moreover, C4+ would possess only 2 electrons, leading to instability.
- Unable to gain or donate electrons, carbon shares electrons to establish a covalent bond in order to attain its nearest noble gas configuration.
Properties of Covalent Bond
When a single electron pair shared between atoms fails to satisfy the normal valence of an atom, multiple electron pairs may be shared. Here are some characteristics of covalent bonds:
- Covalent bonding entails the sharing of electrons rather than their creation.
- These bonds are highly robust and exist between atoms.
- Typically, a covalent bond contains an energy of approximately ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol).
- Once formed, covalent bonds seldom break spontaneously.
- Covalent bonds exhibit directionality, with bonded atoms displaying specific orientations relative to each other.
- Most compounds with covalent bonds tend to have relatively low melting and boiling points.
- Compounds formed by covalent bonding usually possess lower enthalpies of vaporization and fusion.
- Due to the absence of free electrons, covalent compounds do not conduct electricity.
- Covalent compounds are generally insoluble in water.
What is the Octet Rule?
With the exception of noble gases, all atoms possess fewer than eight electrons in their valence shell, meaning their valence shells lack stable configurations. Consequently, these atoms engage in chemical bonding either with each other or with other atoms to achieve stable electronic configurations.
Hence,
"The drive of atoms from various elements to achieve a stable configuration with eight electrons in their valence shells underlies chemical combination."
and
"The principle dictating the attainment of a maximum of eight electrons in the valence shell of atoms is referred to as the octet rule."
Lewis introduced simplified symbols representing the electrons present in an atom's outer shell, termed valence electrons. These symbols are known as Electron Dot Symbols, and the arrangement of these symbols in compounds is referred to as the Lewis Dot Structure.
Conditions for Writing the Lewis Dot Structures
- Covalent bonds form through the sharing of an electron pair between atoms, where each bond entails two electrons contributed by each combining atom. Through this mutual sharing, each atom achieves an octet configuration in its valence shell.
- Electron dot structures of covalent molecules adhere to the octet rule, where all atoms, except hydrogen, strive to attain eight electrons in their valence shell to achieve stability akin to noble gases. Hydrogen, with only one electron, attains helium configuration by possessing just two electrons in its first shell.
- Elements from different groups exhibit varying degrees of electron sharing to attain stable octets: group 17 elements like chlorine share one electron, group 16 elements like oxygen and sulfur share two electrons, and group 15 elements share three electrons, and so forth.
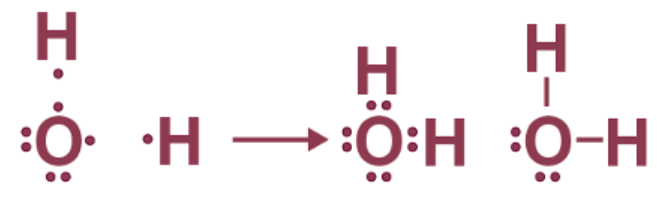
- For instance, oxygen, with six valence electrons, achieves an octet by sharing its two electrons with two hydrogen atoms, resulting in the formation of a water molecule.
Types of Covalent Bonds
Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be classified into:
1. Single Bonds
A single bond is formed when only one pair of electrons is shared between the two participating atoms. It is represented by one dash (-). Although this form of covalent bond has a smaller density and is weaker than a double and triple bond, it is the most stable.
For example, the HCL molecule has one hydrogen atom with one valence electron and one chlorine atom with seven valence electrons. In this case, a single bond is formed between hydrogen and chlorine by sharing one electron.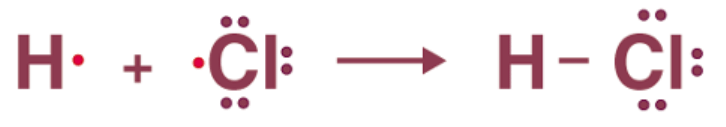
2. Double Bonds
A double bond is formed when two pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. It is represented by two dashes (=). Double covalent bonds are much stronger than single bonds, but they are less stable.
For example, a carbon dioxide molecule has one carbon atom with six valence electrons and two oxygen atoms with four valence electrons.
To complete its octet, carbon shares two of its valence electrons with one oxygen atom and two with another oxygen atom. Each oxygen atom shares its two electrons with carbon, and therefore there are two double bonds in CO2.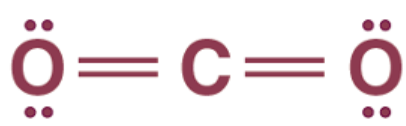
Oxygen Molecule: In the formation of the oxygen molecule, each oxygen atom has six electrons in its valence shell. Each atom requires two more electrons to complete its octet. Therefore, the atoms share two electrons each to form the oxygen molecule. Since two electron pairs are shared, there is a double bond between the two oxygen atoms.
Ethylene Molecule: In ethylene, each carbon atom shares two of its valence electrons with two hydrogen atoms and the remaining two electrons with the other carbon atom. So, there is a double bond between the carbon atoms.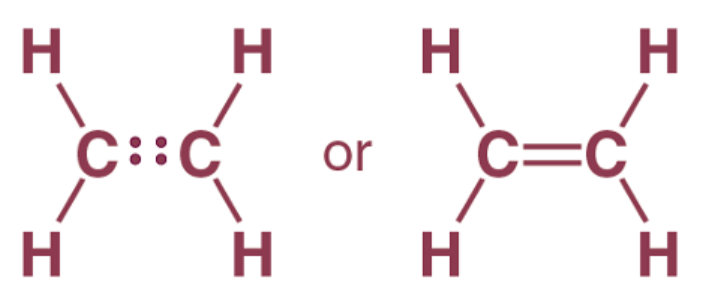
3. Triple Bond
A triple bond arises when two atoms share three pairs of electrons between them. Represented by three dashes (≡), triple covalent bonds are the least stable among covalent bonds.
For instance, in the creation of a nitrogen molecule, each nitrogen atom, possessing five valence electrons, contributes three electrons to form three electron pairs for sharing. Consequently, a triple bond forms between the two nitrogen atoms.
Polar Covalent Bond
This type of covalent bond exists where the unequal sharing of electrons occurs due to the difference in the electronegativity of combining atoms. More electronegative atoms will have a stronger pull for electrons. The electronegative difference between the atoms is greater than zero and less than 2.0. As a result, the shared pair of electrons will be closer to that atom.For example, molecules form hydrogen bonding as a result of an unbalanced electrostatic potential. In this case, the hydrogen atom interacts with electronegative fluorine, hydrogen, or oxygen.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
This type of covalent bond is formed whenever there is an equal share of electrons between atoms. The electronegativity difference between two atoms is zero. It occurs wherever the combining atoms have similar electron affinity (diatomic elements).
For example, Nonpolar Covalent Bond is found in gas molecules like hydrogen gas, nitrogen gas, etc.
Polarization of Covalent Bonds
It is noted that in sigma bonds between distinct atoms, the electron cloud consistently resides nearer to the more electronegative atom of the pair engaged in the sigma bond. As a result, a permanent dipole emerges within the bond, rendering the covalent bond polarized.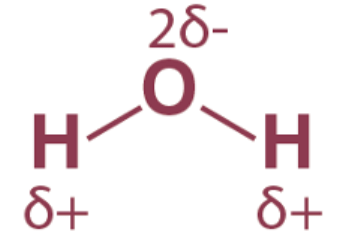
An illustration describing the polarity of the covalent bonds in a water molecule is provided above. The more electronegative atom is said to have a partial negative charge, and the less electronegative atom has a partial positive charge in the polar covalent bond.
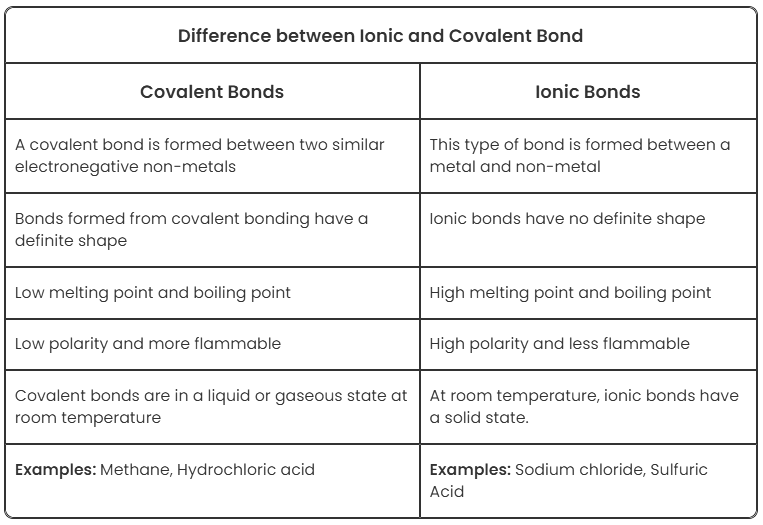
Difference between Covalent and Ionic Bonds
Covalent bonds and ionic bonds are types of atomic bonds. These bonds are different in their properties and structure. Covalent bonds include pairs of electrons by two atoms binding them in a fixed orientation, while a bond between two ions is called an ionic bond.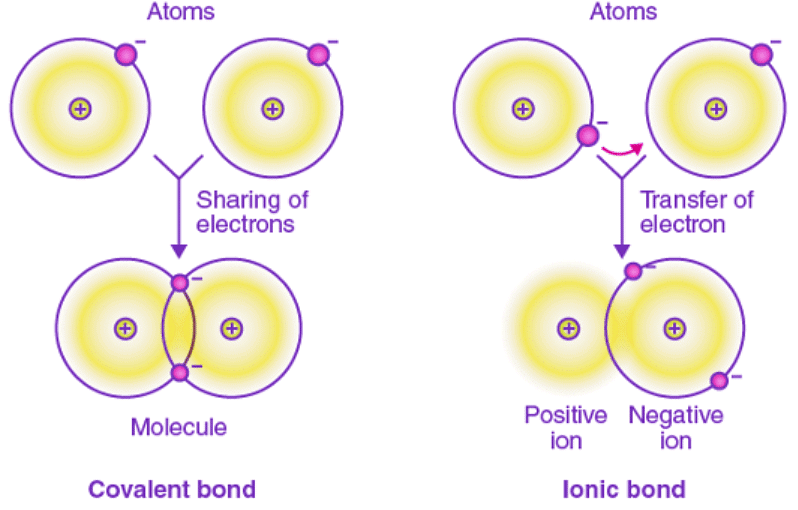
Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metallic atoms, characterised by the sharing of electron pairs between the atoms and other covalent bonds with an electronegativity difference greater than 2.0 (<2.0). In the case of covalent bond formation, polyatomic ions are formed, whereas the ionic bond is formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions.
Ionic Bond vs Covalent Bond
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Covalent Bonds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is a covalent bond and how does it form? |  |
| 2. What are some properties of covalent bonds? |  |
| 3. What is the Octet Rule and how does it relate to covalent bonds? |  |
| 4. How can one understand covalent bonds in terms of molecular geometry? |  |
| 5. How do the properties of covalent bonds differ from those of ionic bonds? |  |
















