Batch Costing | Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What Is Batch Costing? |

|
| Batch Costing Overview |

|
| Formula |

|
| Advantages and Disadvantages |

|
| Batch Costing vs Job Costing |

|
| Difference between Batch Costing And Process Costing |

|
What Is Batch Costing?
Batch costing is a method of cost accounting utilized by companies engaged in batch production of goods. This approach involves dividing the production process into batches, with separate recording of costs associated with each batch. The primary objective is to enhance operational efficiency by providing detailed cost data to support informed decision-making.
Importance of Batch Costing
Batch costing plays a crucial role in enabling companies to allocate budgets accurately to individual production lots. By offering insights into material, labor, and overhead expenses for each batch, businesses can effectively manage costs and optimize resource utilization.
Benefits of Batch Costing
- Efficiency Enhancement: Batch costing helps in identifying inefficiencies within the production process. For example, it can pinpoint areas where material wastage or excessive labor costs occur, enabling managers to take corrective actions.
- Cost Management: Through batch costing, companies can minimize waste, defects, and rework costs. This method aids in setting appropriate prices for goods, maintaining quality standards, and optimizing production processes based on available resources.
Key Takeaways
- Batch costing is a costing method used when a group of identical units are produced in a single batch.
- Batch costing helps in calculating the cost per unit more accurately by spreading batch-level costs across all units produced.
- Formula for batch costing involves dividing total costs by the number of units in the batch.
- For example, if a batch of 100 units costs $1000 to produce, the cost per unit would be $10.
- Advantages of batch costing include better cost control and efficiency in production planning.
- Disadvantages may include higher setup costs for each batch and the challenge of accurately allocating batch-level costs.
- Batch costing differs from job costing in that job costing is used for unique, custom-made products, while batch costing is for groups of identical units.
- The main difference between batch costing and process costing lies in the production flow and how costs are assigned.
- Frequently asked questions about batch costing may include inquiries about cost allocation methods and cost monitoring techniques.
- For more in-depth understanding, refer to recommended articles on batch costing practices and case studies.
- Batch costing is a method utilized by industries that manufacture large quantities of products in a single production cycle.
- It enables businesses to compute the cost per unit and make necessary adjustments to pricing or production volumes.
- Batch costing plays a crucial role in quickly identifying quality control issues within businesses.
- It distinguishes itself from other costing approaches such as job costing and process costing, with the selection of the method being contingent upon the business's nature and production procedures.
Batch Costing Overview
The batch costing system in cost accounting determines the cost per batch of a particular product. This system enables manufacturers to allocate a budget to a specific lot and ascertain the production costs incurred. Additionally, it aids managers in analyzing production costs and deciding on the pricing of the produced lot using the batch costing formula.
Process of Batch Costing
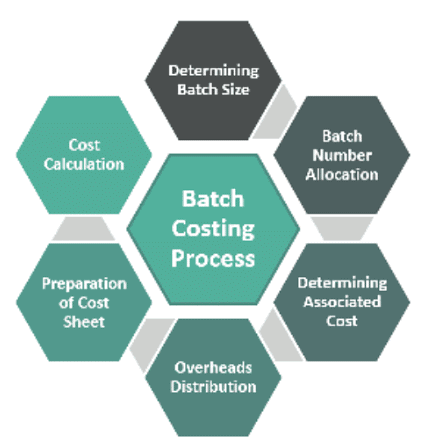
The format of batch costing encompasses materials, labor, and overhead costs. Materials cost represents the expenditure on raw materials utilized in batch production. Labor cost encompasses the expenses related to workers engaged in the production process, including salaries, wages, and direct benefits. Lastly, overhead cost, comprising indirect expenses like rent, utilities, and other operational costs, plays a vital role in business cost management.
The batch costing approach is advantageous for companies engaged in batch production. It aids in allocating production costs to specific batches, facilitating quick identification of expenses associated with any particular batch. This capability is particularly useful in addressing issues that may arise within a batch. Moreover, it enables businesses to accurately compute the cost per production unit, empowering them to make well-informed pricing decisions.
Companies can leverage various software tools to automate batch costing processes, which can otherwise be time-consuming. This system enables effective data analysis, providing prompt and precise per-unit cost information. Furthermore, it equips managers with valuable insights into financial performance, trends, and resource utilization for each batch, facilitating informed decision-making.
Formula
The batch costing formula calculates the cost per lot using the above format. The formula is as follows:
Batch Cost Per Unit = (Material Cost + Labor Cost + Overhead Cost) / Number of Units Produced in the Batch
For example, if the total cost of goods produced is $100,000 and the number of units produced is 10,000, the batch cost is $10 per unit. If the lot size is 500 units, the total cost will be $5,000.
Example 1:
Suppose a bakery produces cookies in a batch of 1000 units. To determine the cost per cookie, businesses calculate the production budget for the entire lot, which includes materials, labor, and overhead costs, and then divide it by 1000 units.
Calculating the cost per cookie as $1, based on the total cost of producing the lot of $1000 and 1000 cookies produced, enables the bakery to determine the profitability of each cookie sold. This enables them to adjust pricing or production quantities accordingly for better profitability. Additionally, since the cookies are identical, it is easy to catch any quality control issues and take corrective actions quickly.
Example 2:
Automobile manufacturers produce cars in lots, commonly known as production runs, and calculate the total production budget for the entire lot, including materials, labor, and overhead costs. They then divide the total cost by the number of units produced to determine the cost per car.
If the total cost of producing a lot of 1000 cars is $10 million, then the cost per car would be $10,000. It allows the automobile manufacturer to determine the profitability of each car sold and adjust the pricing or production quantities accordingly.
Advantages and Disadvantages
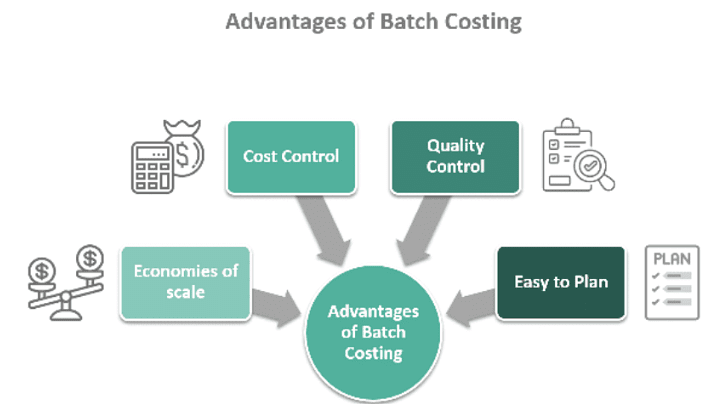
Advantages
- Economies of Scale: Batch costing facilitates cost savings on materials, labor, and overhead costs by leveraging economies of scale.
- Cost Management: The uniformity of items within a batch simplifies the determination of production costs, enabling effective cost control and accurate profitability forecasting.
- Efficient Planning: Batch costing supports improved planning and control by enabling the scheduling of production orders and advance material procurement. This leads to optimal resource utilization and reduced lead times.
- Quality Assurance: Producing numerous identical products concurrently enhances the ability to detect defects or quality issues promptly and take appropriate corrective measures.
Disadvantages
- High Initial Investment: Batch costing necessitates significant initial investments, including setting up production lines, acquiring equipment and materials, and hiring additional labor, which can be financially burdensome for small businesses.
- Limited Flexibility: It lacks flexibility and is restricted to producing a narrow range of products, posing a challenge if customer demand shifts or market conditions change.
- Inventory Management Challenges: Batch production may result in excess inventory accumulation, requiring storage until sold. This can strain cash flow and incur additional costs for businesses.
- Delayed Feedback Loop: The simultaneous production of all items within a batch can delay feedback on the finished product's quality, potentially causing issues and leading to delays in addressing quality concerns.
Batch Costing vs Job Costing
Job Costing and Batch Costing serve as prevalent methods of cost accounting that aid businesses in budgeting for their products.
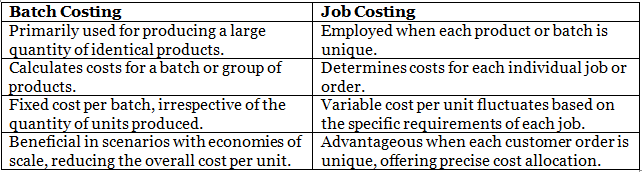
Each method is tailored to track and analyze costs differently, enabling businesses to accurately ascertain product costs and make informed decisions regarding pricing and production processes.
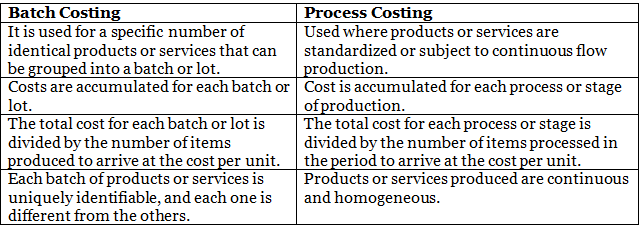
Difference between Batch Costing And Process Costing
In batch costing, businesses group specified numbers of identical products or services into lots and accumulated costs accordingly. In contrast, businesses use process costing for continuous-flow production, where they accumulate costs for each process or stage, and the resulting products or services are homogeneous.
|
24 videos|60 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Batch Costing - Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate
| 1. What is batch costing? |  |
| 2. What is the formula for batch costing? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of batch costing? |  |
| 4. How does batch costing differ from job costing? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between batch costing and process costing? |  |















