Service Costing | Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Definition |

|
| Features of Service Costing |

|
| Cost Unit in Service Costing |

|
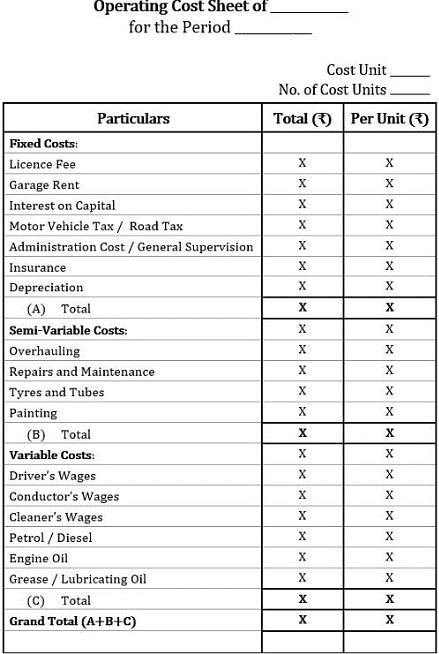
| Format of Service Costing |

|
| Types of Service Costing |

|
Definition
Service costing, also known as operating costing, involves calculating the total operational expenses associated with each unit of an intangible product. These intangible products or services can take the form of internal services that industries perform as support activities for manufacturing goods, or external services provided as primary products by service sector companies.
Service costing is crucial for every service organization to determine its business overheads accurately. This process ensures fair pricing of services and helps in managing both fixed and variable costs effectively.
Features of Service Costing
Characteristics of Service Costing:
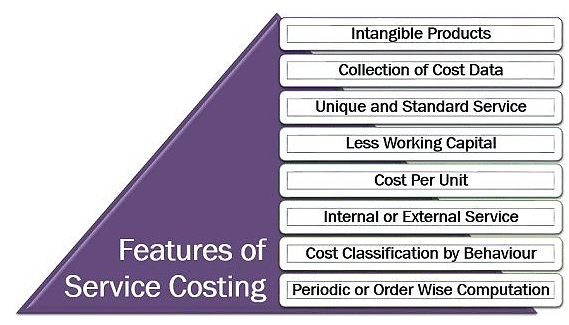
Intangible Products
- Service costing involves determining the operating costs of products that lack physical form but meet consumer needs and wants.
Collection of Cost Data
- Documents used for service costing include cost sheets, bills payable, daily log sheets, and other relevant records.
Unique and Standard Service
- The services provided by such organizations are often specialized and exclusive.
Less Working Capital
- Service costing typically requires less working capital, as the direct costs of raw materials and other direct expenses are relatively low.
Cost Per Unit
- In service costing, the cost per unit is calculated based on the specific service industry. This varies between industries; for example, in goods transport, it is measured in "tonne-miles," while in the boiler industry, it is measured in "per cubic centimetre-litre."
Internal or External Service
- Service costing can be conducted internally to determine the operating costs of support activities in manufacturing industries, or externally by companies specializing in providing these services.
Cost Classification by Behaviour
- In the operating cost sheet format, all business costs are classified based on their behaviour: fixed costs, semi-variable costs, and variable costs.
Periodic or Order-Wise Computation
- Service costing records overheads at regular intervals, such as monthly or yearly. However, for operating costs of vehicles like tractors and JCB machines, computation is done on an order-wise basis.
Cost Unit in Service Costing
- Measuring the cost of business operations in the service industry is a complex task that requires considering all cost parameters to determine an appropriate unit for costing.
The two types of cost units used in service costing are:
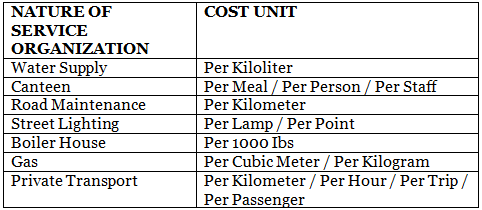
Simple Cost Unit
- A simple cost unit uses only one parameter to measure the service cost.
The following are examples of different service organizations and their corresponding simple cost units:
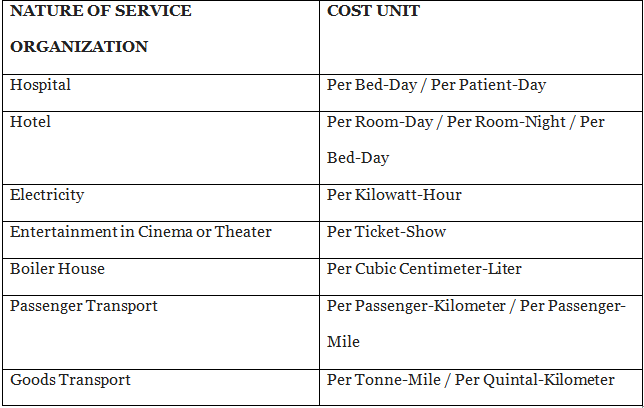
Composite Cost Unit
- The most commonly used cost unit in service costing is the composite cost unit. Here, the measurement of two parameters is combined to form a single cost unit.
Following are the different types of service organizations and their composite cost units:
Calculation of Cost Per Unit: The formula for computing the cost of each service unit (i.e., cost per unit) is given below:
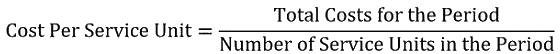
Format of Service Costing
Next, we will discuss transport costing as an example of service costing. In this section, we will examine the computation of transport costing.
Transport is a major service industry today, and it is crucial to understand the format for determining the operating costs of such organizations.
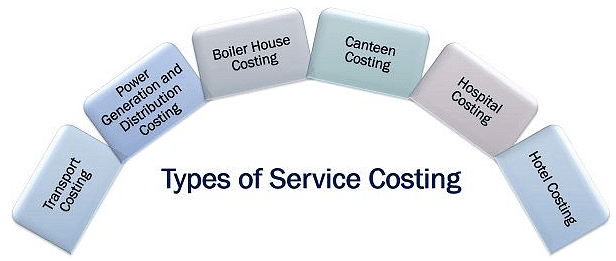
Types of Service Costing
When we think of services, we often recall the various intangible products we use daily. However, did you know that each of these services has different cost units and elements in their computation?
This variation arises because each service is unique and involves different types of overheads. Therefore, service costing for each type of service organization differs and can be classified as follows:
Transport Costing
Costing in the transport industry serves multiple objectives, which vary based on the type of transport service an organization provides:
- Private Transport: Service costing determines the hiring charges when a vehicle is hired individually for private tours.
- Passenger Transport: For public or passenger transport companies, it ascertains the cost of conveyance per passenger for a certain distance.
- Goods Transport: In goods transport services, service costing determines the cost of transporting a defined quantity of goods over a specific distance.
Common objectives of transport costing include comparing costs between different vehicles or groups of vehicles and deciding whether to use an alternative source of transport or an owned vehicle based on the costs involved.
For a practical overview of transport costing, refer to the example in this article focused on goods transport services.
Power Generation and Distribution Costing
Powerhouses produce energy in the form of electricity using water, gas, or sunlight. The cost of power generation services primarily includes fixed costs (such as interest on capital, depreciation, repairs and maintenance, and administration expenses) and variable costs (such as steam consumption, labor wages, lubricants, and coal).
Boiler House Costing
The boiler house provides supporting services to power and electricity generation units by producing steam used in air conditioning, power generation, and air compression.
The total cost of boiler services includes overheads like fuel (coal, oil), direct and indirect labor, water and its processing, indirect materials (tools, service materials), maintenance, and fixed costs (rent, taxes, depreciation, administration expenses, etc.).
Canteen Costing
Government organizations, factories, companies, offices, colleges, schools, and hospitals often have canteens to provide affordable food such as meals, refreshments, and snacks to staff, students, and patients.
The canteen manager or supervisor controls costs and performs service costing to ascertain the revenue of these business organizations.
The costs involved in canteen services include the cost of material, labour, services, consumable stores and miscellaneous overheads.
Hospital Costing
Medical organizations such as hospitals, health centers, nursing homes, medical camps, and clinics require cost analysis, which is facilitated through service costing.
Hospital costs include fixed charges like labor salaries, maintenance charges, rent, administration expenses, and other overheads, as well as variable charges such as medicines, bed charges, and doctors' fees.
Hotel Costing
Hotels provide accommodation to guests, involving high maintenance costs alongside fixed costs. Fixed costs include depreciation, staff salaries, interest on capital, and taxes, while variable costs cover expenses like electricity charges and temporary staff salaries.
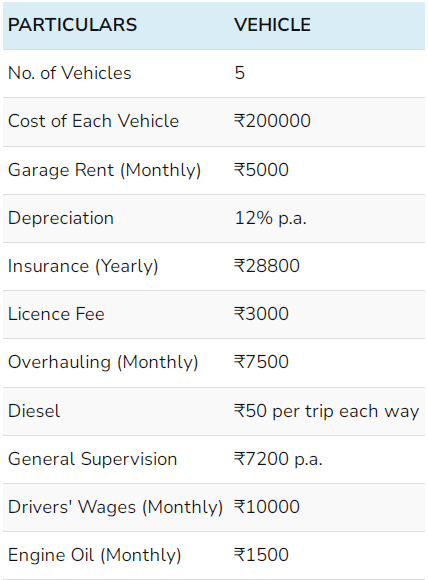
Example: XYZ Transport Co. provides the following data for the month ending on January 31, 2019:
Note that:
We have assumed that the licence fee was calculated every month. Also, each vehicle has the capacity of 2-tonne of goods.
If,
- each vehicle covers a distance of 100 miles each way daily to and from the city;
- each vehicle runs on an average of 20 days a month; and
- while going to the city, the capacity was full and while returning the capacity is 25% occupied;
find out the following:
- Operating cost per tonne-mile; and
- Rate per trip to be charged, if the company plans to make 40% profit on freightage.
Computation:
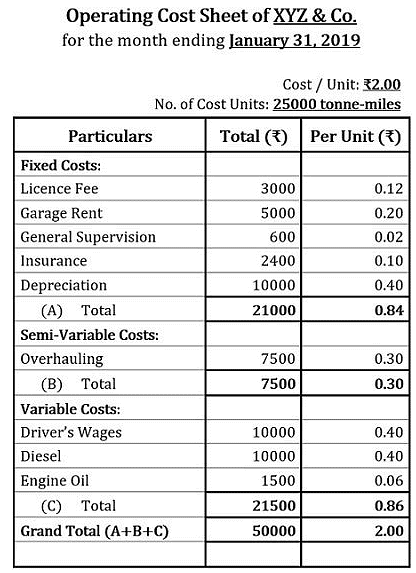
No. of Cost Units:
On the first way of the trip: 100% capacity was occupied, i.e., 2-tonnes
No. of Cost Units=Distance×Capacity Occupied×Working Days×No. of Vehicles
No. of Cost Units=100×2×20×5=20000 tonne-miles
On the second way of the trip: 25% capacity was occupied, i.e., 0.5-tonnes; Similarly,
No. of Cost Units=100×0.5×20×5=5000 tonne-miles
Hence,
Total No. of Cost Units=20000+5000=25000 tonne-miles
General Supervision:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly expense on general supervision=7200/12=₹600
Insurance:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly expense on insurance=28800/12=₹2400
Depreciation:
It is given annually, therefore;
Monthly depreciation=(Total Cost of 5 Vehicles×Rate of Depreciation)/(100×12)
Monthly depreciation=(1000000×12)/(100×12)=₹10000
Diesel:
Monthly expense on diesel=Cost per Trip×No. of Ways per Trip×No. of Working Days×No. of Vehicles
Monthly expense on diesel=50×2×20×5=₹10000
Service costing has given a new dimension to the intangible products in the accounting world. This is also important in the sense that the service industry has rapidly evolved in recent years, introducing a variety of service products for consumers.
|
24 videos|60 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Service Costing - Cost and Management Accounting for CA Intermediate
| 1. What are the main features of Service Costing? |  |
| 2. What is the cost unit in Service Costing? |  |
| 3. What is the format of Service Costing? |  |
| 4. What are the types of Service Costing? |  |
| 5. How can Service Costing be useful for businesses? |  |















