Capital Structure – Definition, Theories and Approach | Financial Management & Strategic Management for CA Intermediate PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Capital Structure |

|
| Capital Structure Theories |

|
| Arbitrage Process |

|
| Proforma Statement Showing EBIT, EPS & MPS |

|
| Indifference Point |

|
What is Capital Structure
Capital structure refers to the mix of funding sources a company uses to finance its operations.
Capital Structure Theories
Various theories exist to explain how companies should determine their capital structures.
Net Income Approach (NI)
The use of debt can lead to a decrease in the weighted average cost of capital (WACC), resulting in an increase in the firm's value and the market price of its shares.
Key points from the NI Approach include:- Kd and Ke will remain constant.
- Ko will decrease with the help of use of Debt.
- MV of Equity and Firm will increase with the help of use of Debt.

Formulae:

Note: The cost of equity and overall capital of an unlevered firm are equal.
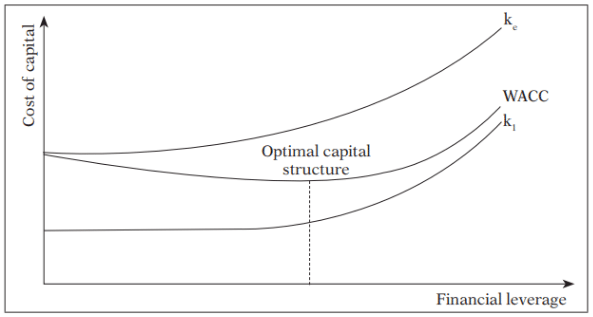
Traditional Approach
The traditional approach suggests that, initially, due to financial leverage, the cost of capital decreases, leading to an increase in the firm's value. However, beyond a certain point, this trend reverses.
According to the Traditional Approach:
- Kd, Ke, Ko and MV of Equity and MV of Firm are variable
- Company has to select capital structure with lowest Ko or highest MV of Firm
Net Operating Income Approach (NOI)
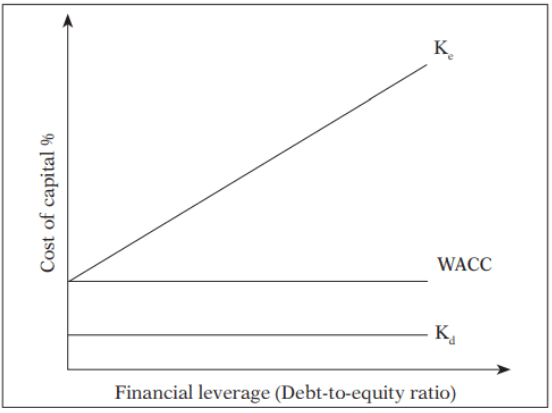
Net Operating Income Approach (NOI) suggests that the firm's capital structure decisions are inconsequential. Changes in leverage do not impact the total value of the firm or the market price of shares because the overall cost of capital remains unaffected by the level of leverage.
Key Points of NOI Approach:
- Kd, Ko and MV of Firm will remain constant in case of without tax structure.
- Kd will remain constant in case of with tax structure, with the increase in Debt, MV of firm will increase and Ko will decrease
Value of Firms according to NOI Approach:
Step 1: Determining the Value of Unlevered Firm:
Value of Unlevered Firm
Step 2: Calculating the Value of Levered Firm:
Value of Levered Firm (VL) = VU - DT
Modiglani-Miller Approach (MM)
The Net Operating Income (NOI) approach is primarily definitional and lacks behavioral significance. In contrast, the Modigliani-Miller approach offers a behavioral rationale for the consistent overall cost of capital and, consequently, the total value of the firm.
Assumptions of Modigliani-Miller (MM) Approach
- Capital markets are assumed to be perfect, characterized by efficient trading and information dissemination.
- All relevant information is assumed to be freely available to all market participants.
- There are no transaction costs incurred during trading activities.
- Rationality is a key assumption, with all investors making decisions based on maximizing their utility.
- Firms are categorized into 'Equivalent risk classes' based on their risk profiles.
- The assumption of the non-existence of corporate taxes simplifies the analysis.
It's important to note that the solutions to practical problems remain consistent between the Net Operating Income (NOI) and Modigliani-Miller (MM) Approaches.
The Trade Off Theory
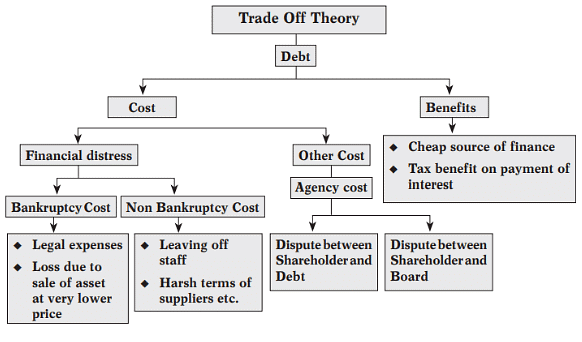
Pecking Order Theory
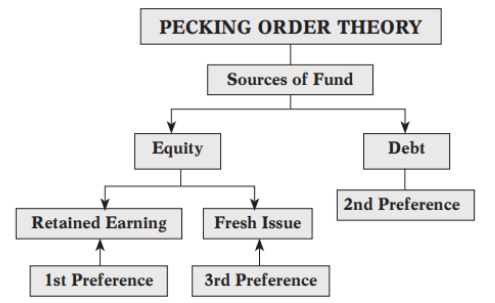
Arbitrage Process
Capital structure arbitrage involves a tactic employed by both companies and individuals to exploit market mispricing across various securities for profit. This strategy entails purchasing shares of undervalued firms while selling shares of overvalued firms. The primary goal is to capitalize on pricing inefficiencies and generate profits. It is anticipated that the pricing disparities will eventually converge or reach equilibrium.
Proforma Statement Showing EBIT, EPS & MPS
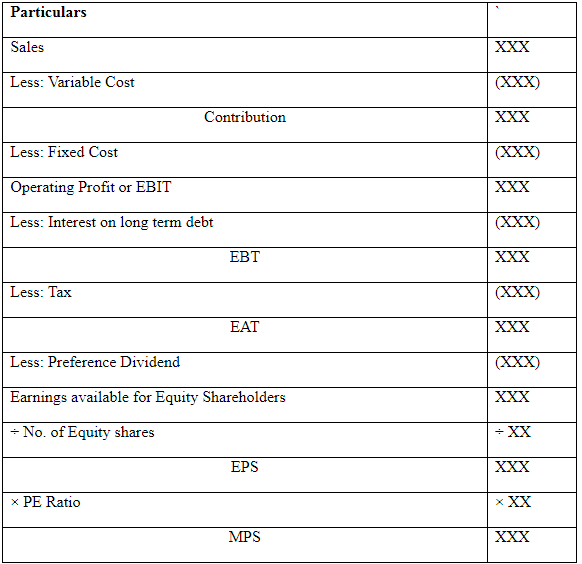
Note:
- MPS = EPS × PE Ratio
- Number of Equity Shares = Existing Shares + New Shares
- New Equity Shares

- Net Proceeds from Share = Issue Price – Issue Expenses
If nothing is specified in the question, MPS is assumed to be Issue Price.
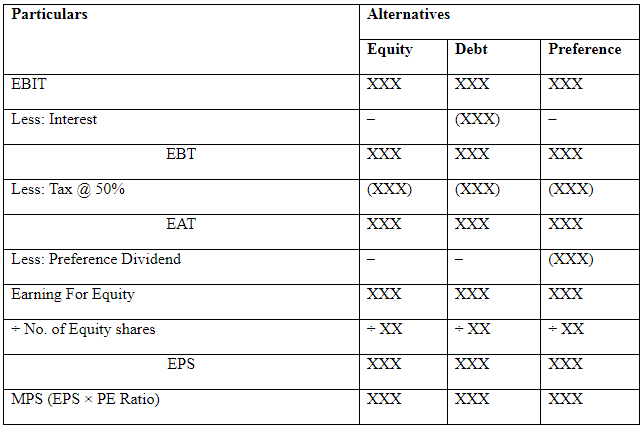
Selection of plan on the basis of EPS or MPS (New company)
Statement of EPS & MPS
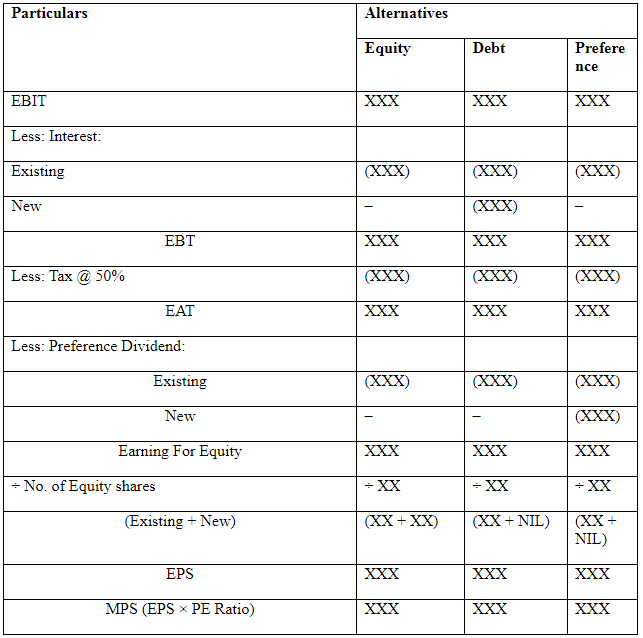
Selection of plan on the basis of EPS or MPS (Existing company)
Statement of EPS & MPS
Indifference Point
Indifference point is the EBIT level where the Earnings Per Share (EPS) under two different options are equal.
EPS under option 1 = EPS under option 2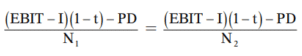
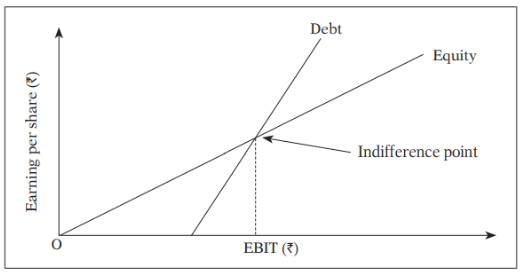
Course of Action:
Financial Break Even Point
Financial Break Even Point refers to the EBIT level at which the Earnings Per Share (EPS) will be zero.
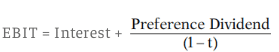
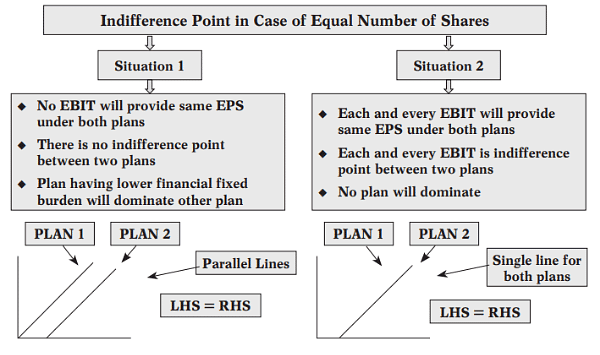
Indifference Point in case of Equal Number of Share
FAQs on Capital Structure – Definition, Theories and Approach - Financial Management & Strategic Management for CA Intermediate
| 1. What is the definition of capital structure in finance? |  |
| 2. What are the main theories of capital structure? |  |
| 3. What is the indifference point in capital structure? |  |
| 4. How can a company determine its optimal capital structure? |  |
| 5. What approach should companies take when determining their capital structure? |  |




















