Introduction To Code Combat Important Notes | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
What is Program
- A computer program consists of a set of instructions that a computer follows to perform a specific task.
- Programs are designed to operate faster , safer , and more efficiently .
- They are responsible for reading and writing data, managing memory, and carrying out calculations.
- Programs are the fundamental components of the operating system , which oversees essential functions and the programs we create.
- The operating system is a crucial program that handles basic tasks like memory and file management.
- Programming languages such as C++, Java, Python, and Ruby are used to construct programmes. These are human-readable and writable high-level programming languages.
Why Python for AI?
At the core of every modern artificial intelligence system is Python. It’s the programming language of choice for data scientists and engineers building the critical infrastructure that powers today’s most advanced AI systems. For this reason, many organizations are turning to Python to build their next generation of AI systems. This guide will help you get started using Python for AI.
Lisp, Prolog, C++, Java, and Python are some of the programming languages that can be used to create AI applications.
Python is the most popular of these because of the following reasons:
- Simplicity: Python is easy to understand, read, and maintain, thanks to its clear syntax and straightforward keywords.
- Extensive Libraries: Python boasts a vast library of built-in functions that are useful for tackling a wide range of problems.
- Testing and Debugging: Python offers a mode for testing and debugging code snippets, making it easier to catch errors.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python works on various operating systems and hardware platforms, providing a consistent user experience.
- Customization: With the Python interpreter, programmers can incorporate low-level models to enhance the efficiency of their tools through customization.
- Database Connectivity: Python supports connections to all major open-source and commercial databases and offers a more structured framework for large-scale systems compared to shell scripting.
Applications of Python
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. It is different from other languages such as C and Java that are designed to be compiled to machine code. Python is easy to learn and can be used to write virtually anything that can be described in code.There are different type of Python Application:
- Web and Internet Development
- Desktop GUI Application
- Software Development
- Database Access
- Business Application
- Games and 3D Graphics
Installation of Python
- Python is a cross-platform programming language, which means it runs on a variety of platforms including Windows, MacOS or Linux operating system.
- A Python interpreter must be installed on our computer in order to write and run Python programmes.
Downloading and Setting up Python
- Step 1: Download Python from python.org using link python.org/downloads
- Step 2: Select appropriate download link as per Operating System [Windows 32 Bit/64 Bit, Apple iOS]
- Step 3: Click on Executable Installer
- Step 4: Install
Python IDLE installation
After installing Python, you’ll need an IDE to write Python programmes. IDLE is a Python editor with a graphical user interface. IDLE stands for Integrated Development Environment. This IDLE is also known as the Python shell, and it has two modes of operation: interactive mode and script mode. Interactive Mode allows us to communicate with the operating system, whereas Script Mode allows us to generate and edit Python source files.
Interactive Mode
Python IDLE Shell provides a Python prompt, You can write single line python commands and execute them easily.
Script Mode
In Python, the Script Mode allows you to add numerous lines of code. In script mode, we type a Python programme into a file and then use the interpreter to run the code. Working in interactive mode is useful for beginners and for testing little parts of code because it allows us to test them right away. However, while writing code with more than a few lines, we should always save it so that we may alter and reuse it.
Python Statement and Comments
Python Statement
A statement is a piece of code that can be executed by a Python interpreter. So, in simple words, anything written in Python is a statement. In The Python programming language, there are various types of statements, such as assignment statements, conditional statements, looping statements and so on. These assist the user in obtaining the desired result.
Multiline Statement
The token NEWLINE character is used at the end of a Python statement. However, we can use the line continuation character to extend the statement across many lines (\).
We can utilize these characters when we need to execute long calculations and can’t fit all of the assertions on a single line.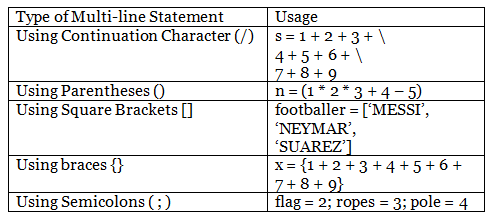
Python Comments
In Python, comments are lines of code that are skipped by the interpreter while the programme is being run. Comments improve the readability of the code and assist programmers in completely comprehending it. In Python there are two types of comment.
a. Single Line comment
A single-line comment in Python begins with the hash symbol (#) and continues until the end of the line.
Example
# Single line comment
b. Multiple Line comment
There are a variety of methods for writing multiline comments.
Example
c. Using Multiple hash (#)
# Multiple line comment 1
# Multiple line comment 2
d. Multiline comment using String literals
“ “ “ Multiline comment in
Python statement “ “ “
Or
‘ ‘ ‘ Multiline comment in
Python statement ‘ ‘ ‘
Python Keywords and Identifiers
Keywords: Keywords are reserved words in Python that the Python interpreter uses to recognise the program’s structure. In Python, keywords are predefined words with specific meanings. The keyword can’t be used as a variable name, function name, or identifier. Except for True and False, all keywords in Python are written in lower case.
Example of Keywords:
False, class, finally, is, return, None, continue, for lambda, try, True, def, from, nonlocal, while, and, del, global, not, with, as, elif, if, or, yield, assert, else, import, pass, break, except, in, raise etc.
Identifiers: An identifier is a name given to a variable, function, class, module, or other object. The identification is made up of a series of digits and underscores. The identification should begin with a letter or an Underscore and then be followed by a digit. A-Z or a-z, an UnderScore (_), and a numeral are the characters (0-9). Special characters (#, @, $, percent,!) should not be used in identifiers.
- Identifiers can be a combination of letters in lowercase (a to z) or uppercase (A to Z) or digits (0 to 9) or an underscore _.
- An identifier cannot start with a digit
- Keywords cannot be used as identifiers
- We cannot use special symbols like !, @, #, $, % etc. in our identifier
- Identifier can be of any length
- Python is a case-sensitive language.
Example of Identifier
var1
_var1
_1_var
var_1
Variables, Constants and Data Types
Variables
A variable is a memory location where you store a value in a programming language. In Python, a variable is formed when a value is assigned to it. Declaring a variable in Python does not require any further commands.
There are a certain rules and regulations we have to follow while writing a variable
- A number cannot be used as the first character in the variable name. Only a character or an underscore can be used as the first character.
- Python variables are case sensitive.
- Only alpha-numeric characters and underscores are allowed.
- There are no special characters permitted.
Constants
A constant is a kind of variable that has a fixed value. Constants are like containers that carry information that cannot be modified later.
Declaring and assigning value to a constant
NAME = “Rajesh Kumar”
AGE = 20
Datatype
In Python, each value has a datatype. Data types are basically classes, and variables are instances (objects) of these classes, because everything in Python programming is an object.
Python has a number of different data types. The following are some of the important datatypes.
- Numbers
- Sequences
- Sets
- Maps
a. Number Datatype
Numerical Values are stored in the Number data type.
There are four categories of number datatype:
- Int: Int datatype is used to store the whole number values.
Example: x=500 - Float: Float datatype is used to store decimal number values.
Example: x=50.5 - Complex: Complex numbers are used to store imaginary values. Imaginary values are denoted with ‘j’ at the end of the number.
Example: x=10 + 4j - Boolean: Boolean is used to check whether the condition is True or False.
Example: x = 15 > 6 type(x)
b. Sequence Datatype
A sequence is a collection of elements that are ordered and indexed by positive integers. It’s made up of both mutable and immutable data types. In Python, there are three types of sequence data types:
- String: Unicode character values are represented by strings in Python. Because Python does not have a character data type, a single character is also treated as a string. Single quotes (‘ ‘) or double quotes (” “) are used to enclose strings. These single quotes and double quotes merely inform the computer that the beginning of the string and end of the string. They can contain any character or symbol, including space.
Example: name = ”Rakesh kumar” - List: A list is a sequence of any form of value. The term “element” or “item” refers to a group of values. These elements are indexed in the same way as an array is. List is enclosed in square brackets.
Example: dob = [19,”January”,1995] - Tuples: A tuple is an immutable or unchanging collection. It is arranged in a logical manner, and the values can be accessed by utilizing the index values. A tuple can also have duplicate values. Tuples are enclosed in ().
Example: newtuple = (15,20,20,40,60,70)
c. Sets Datatype
A set is a collection of unordered data and does not have any indexes. In Python, we use curly brackets to declare a set. Set does not have any duplicate values. To declare a set in python we use the curly brackets.
Example: newset = {10, 20, 30}
d. Mapping
This is an unordered data type. Mappings include dictionaries.
Dictionaries
In Python, Dictionaries are used generally when we have a huge amount of data. A dictionary is just like any other collection array. A dictionary is a list of strings or numbers that are not in any particular sequence and can be changed. The keys are used to access objects in a dictionary. Curly brackets are used to declare a dictionary.
Example: d = {1:’Ajay’,’key’:2}
Operators
Operators are symbolic representations of computation. They are used with operands, which can be either values or variables. On different data types, the same operators can act differently. When operators are used on operands, they generate an expression.
Operators are categorized as:
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Identity operators
- Membership operators
- Bitwise operators
Arithmetic Operators:
Mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are performed using arithmetic operators.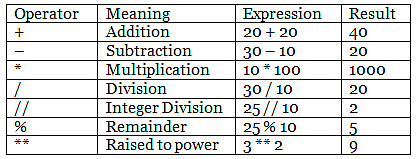
Assignment Operator
When assigning values to variables, assignment operators are used.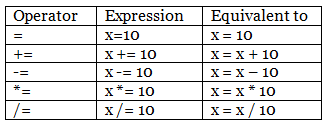
Comparison Operator
The values are compared using comparison operators or relational operators. Depending on the criteria, it returns True or False.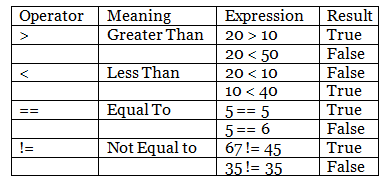
Logical Operator
Logical operators are used to combine the two or more then two conditional statements: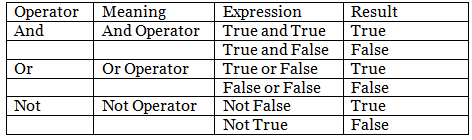
Type Conversion
Type conversion is the process of converting the value of one data type (integer, text, float, etc.) to another data type. There are two types of type conversion in Python.
- Implicit Type Conversion
- Explicit Type Conversion
Implicit Type Conversion
Python automatically changes one data type to another via implicit type conversion. There is no need for users to participate in this process.
Example:
x = 5
y=2.5
z = x / z
In the above example, x is containing integer value, y is containing float value and in the variable z will automatically contain float value after execution.
Explicit Type Conversion
Users transform the data type of an object to the required data type using Explicit Type Conversion.
To do explicit type conversion, we employ predefined functions such as int(), float(), str(), and so on.
Because the user casts (changes) the data type of the objects, this form of conversion is also known as typecasting.
Example: Birth_day = str(Birth_day)
Python Input and Output
Python Output Using print() function
To output data to the standard output device, we use the print() method (screen).
Data can also be saved to a file. The following is an example.
Example:
a = “Hello World!”
print(a)
Output: Hello World!
Python User input
In python, input() function is used to take input from the users.
|
31 videos|79 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction To Code Combat Important Notes - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. Why is Python considered a popular choice for AI development? |  |
| 2. How can I install Python on my computer? |  |
| 3. What are Python keywords and why are they important? |  |
| 4. What are the basic data types available in Python? |  |
| 5. How do I take user input in Python? |  |





















