Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Features of Organisms - 2
Features of Organisms - 2 | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Five Kingdoms: Extended
- The first division of living things in the classification system is to put them into one of five kingdoms
- They are:
- Animals
- Plants
- Fungi
- Protoctists
- Prokaryotes
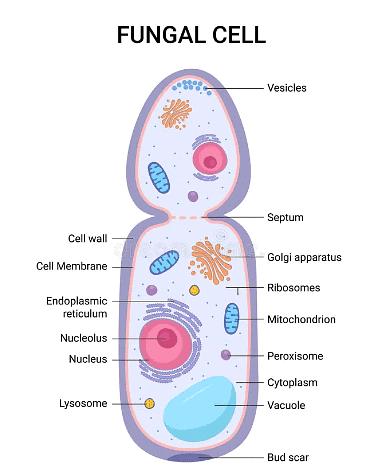
Main features of all fungi (e.g. moulds, mushrooms, yeast)
- Usually multicellular
- Cells have nuclei and cell walls not made of cellulose
- Do not photosynthesize but feed by saprophytic (on dead or decaying material) or parasitic (on live material) nutrition
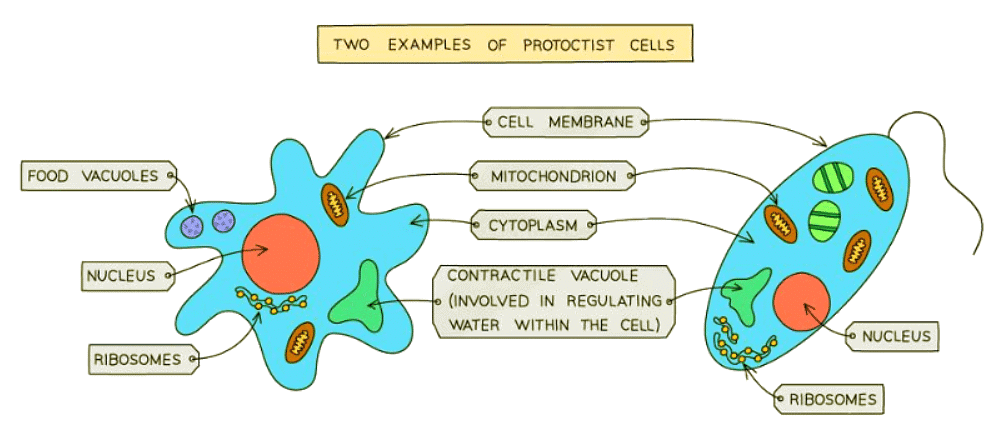
Main features of all Protoctists (e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium, Plasmodium)
- Most are unicellular, but some are multicellular
- All have a nucleus; some may have cell walls and chloroplasts
- This means some protoctists photosynthesize while others feed on organic substances made by other living things
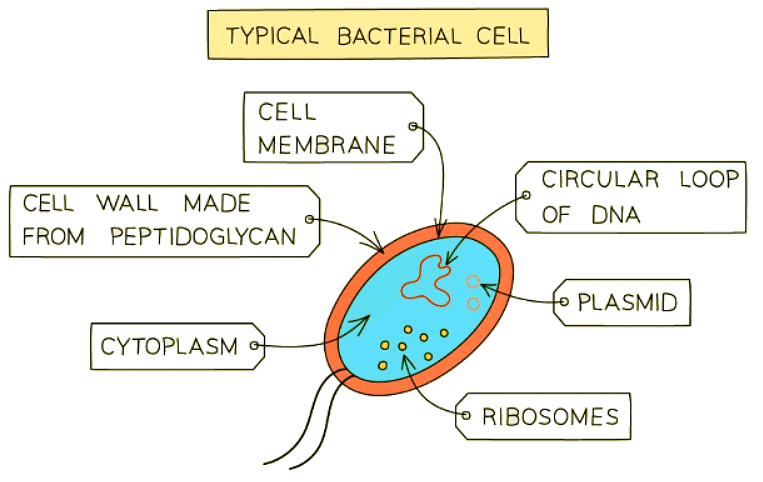
Main features of all Prokaryotes (bacteria, blue-green algae)
- Often unicellular
- Cells have cell walls (not made of cellulose) and cytoplasm but lack a nucleus or mitochondria
The Plant Kingdom: Extended
- Plants typically have green parts due to chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis.
- The plant kingdom encompasses various organisms like ferns and flowering plants.
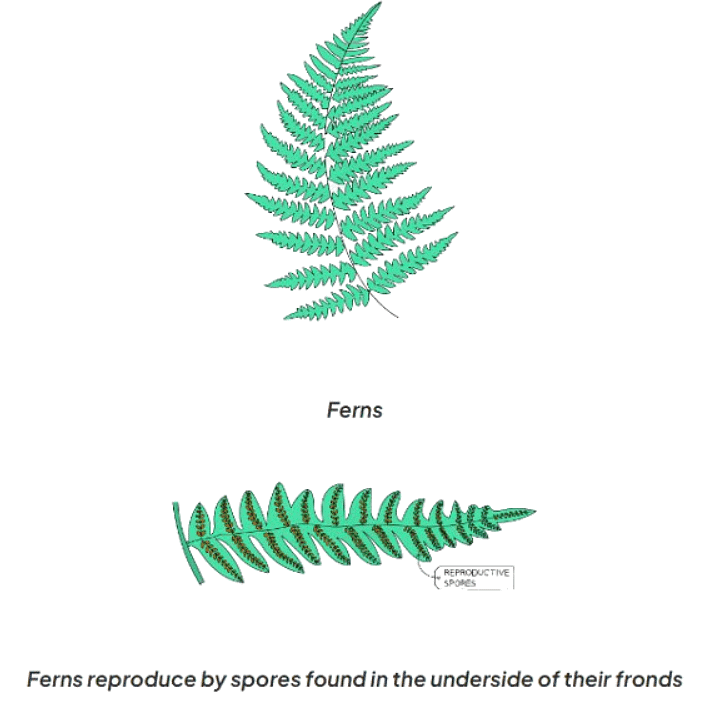
Ferns
- Ferns are characterized by fronds, which are leaf-like structures.
- Unlike flowering plants, ferns reproduce through spores located on the underside of their fronds.

Flowering plants
- Reproduce sexually through flowers and seeds
- Seeds are formed inside the ovary located at the base of the flower
- Can be classified into two groups: monocotyledons and dicotyledons
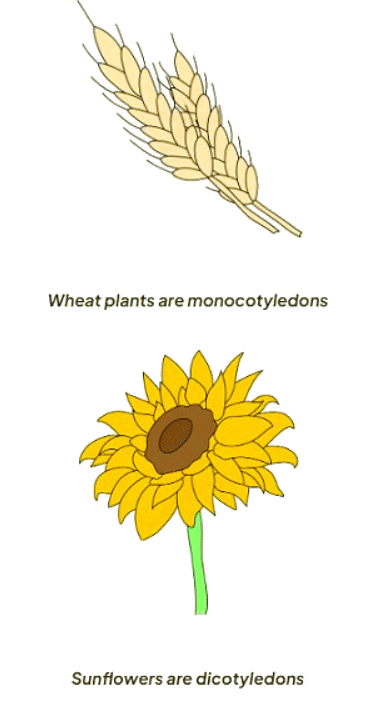
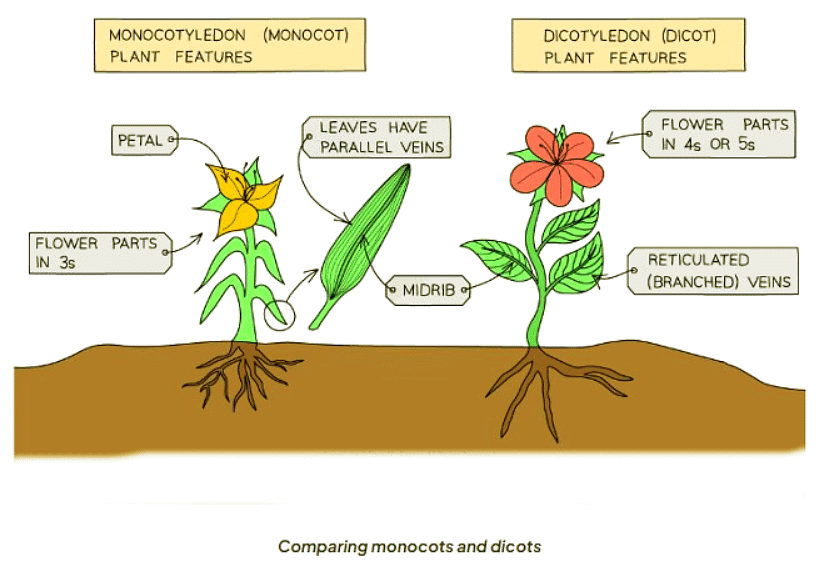
How do you distinguish between monocotyledons and dicotyledons?
Flowers
- Monocotyledons: Flowers from monocots have petals in multiples of 3.
- Dicotyledons: Flowers from dicots have petals in multiples of 4 or 5.
Leaves
- Monocotyledons: Leaves of monocots possess parallel leaf veins.
- Dicotyledons: Dicots exhibit reticulated leaf veins, forming an interconnected web-like network across the leaf.
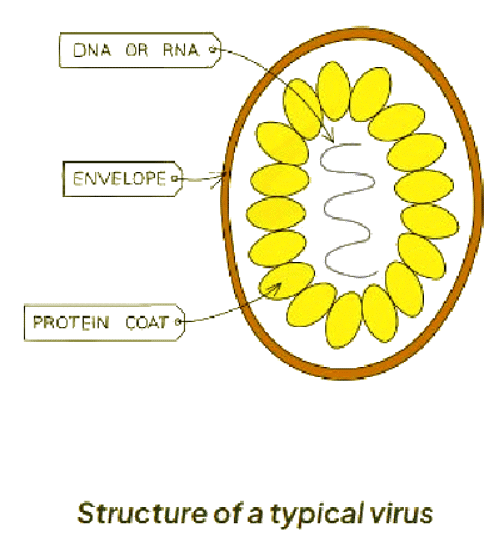
Viruses: Extended
- Viruses are not categorized within any classification system since they are not regarded as living organisms.
- They do not perform the essential life processes independently; instead, they hijack a host cell's metabolic pathways to replicate themselves.
- The structure of a virus essentially comprises genetic material (RNA or DNA) enclosed within a protein coat.
Question for Features of Organisms - 2Try yourself: Which kingdom includes organisms that reproduce through spores?View Solution
The document Features of Organisms - 2 | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Features of Organisms - 2 - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main features of all Prokaryotes? |  |
Ans. Prokaryotes, including bacteria and blue-green algae, are characterized by their lack of a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple cell structure with a single circular chromosome and lack membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.
| 2. Can you provide an example of a typical bacterial cell? |  |
Ans. A typical bacterial cell has a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a single circular chromosome. Some bacteria may also have flagella for movement or pili for attachment to surfaces.
| 3. What are some characteristics of fungi? |  |
Ans. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular (yeasts) or multicellular (molds and mushrooms). They obtain nutrients through absorption, have cell walls made of chitin, and reproduce through spores. Fungi play important roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
| 4. How do monocotyledons differ from dicotyledons in the Plant Kingdom? |  |
Ans. Monocotyledons are plants with seeds that have one cotyledon (seed leaf) and parallel venation in their leaves. Dicotyledons, on the other hand, have seeds with two cotyledons and reticulate venation in their leaves. Other differences include floral arrangement, root structure, and vascular bundle organization.
| 5. What are the Five Kingdoms of organisms? |  |
Ans. The Five Kingdoms of organisms are Monera (prokaryotes), Protista (single-celled eukaryotes), Fungi (multicellular decomposers), Plantae (photosynthetic plants), and Animalia (multicellular heterotrophs). These kingdoms classify organisms based on their cell structure, mode of nutrition, and other characteristics.
Related Searches




















