Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Cell Structure
Cell Structure | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
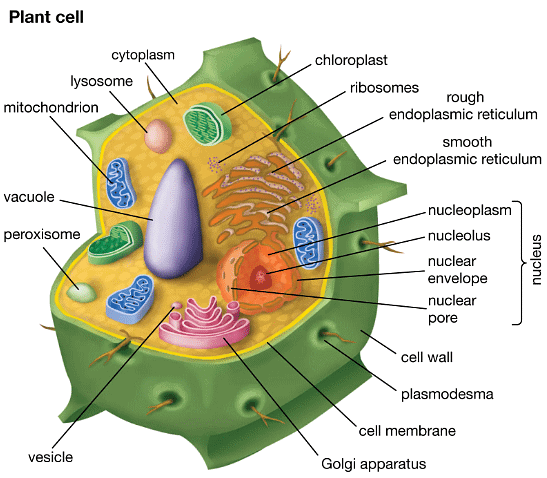
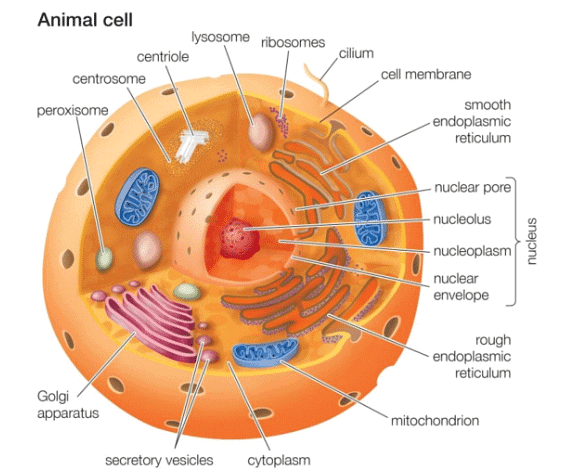
Animal & Plant Cells
Animals
The main features of animals:
- Animals are multicellular organisms.
- Their cells contain a nucleus with a distinct membrane.
- They lack cellulose cell walls in their cells.
- Animals do not contain chloroplasts, hence cannot carry out photosynthesis.
- They rely on organic substances produced by other living organisms for food.
- Carbohydrates are often stored as glycogen in animal cells.
- Animals typically exhibit nervous coordination.
- They have the ability to move from one place to another.
Plants
The main features of plants:
- Plants are multicellular organisms.
- The cells of plants contain a nucleus with a distinct membrane.
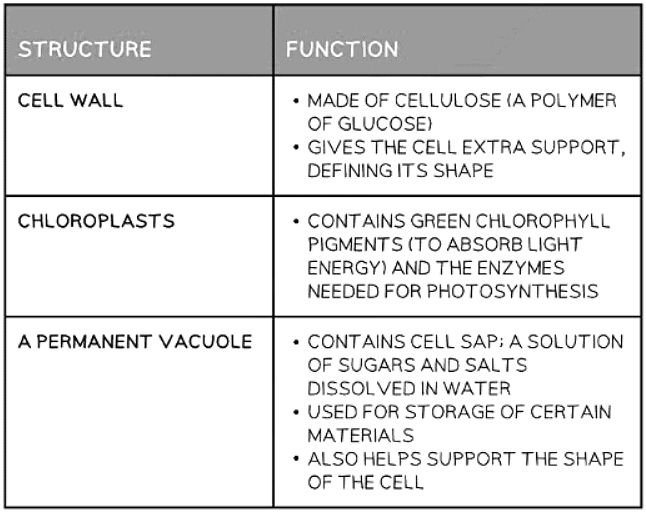
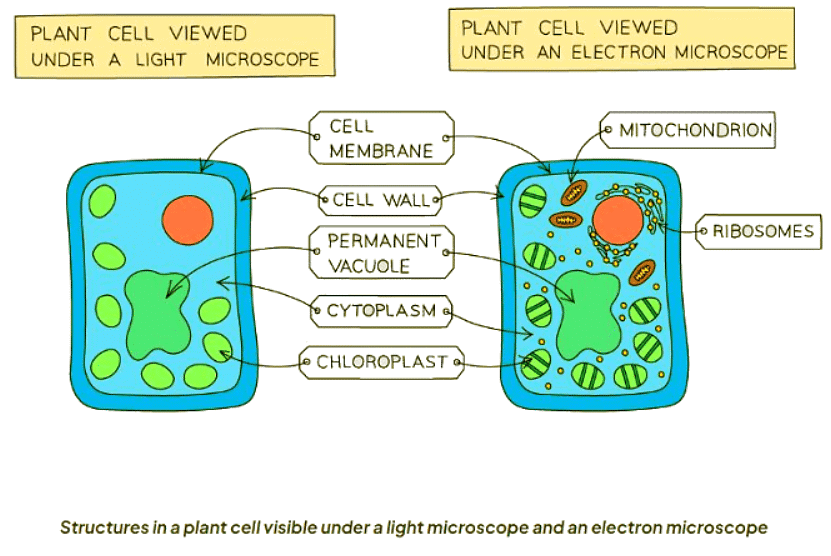
- Plant cells are surrounded by cell walls composed of cellulose.
- Chloroplasts are present in plant cells, allowing them to carry out photosynthesis.
- Plants obtain their energy through the process of photosynthesis.
- Carbohydrates in plants are stored as starch or sucrose.
- Plants lack nervous coordination as seen in animals.
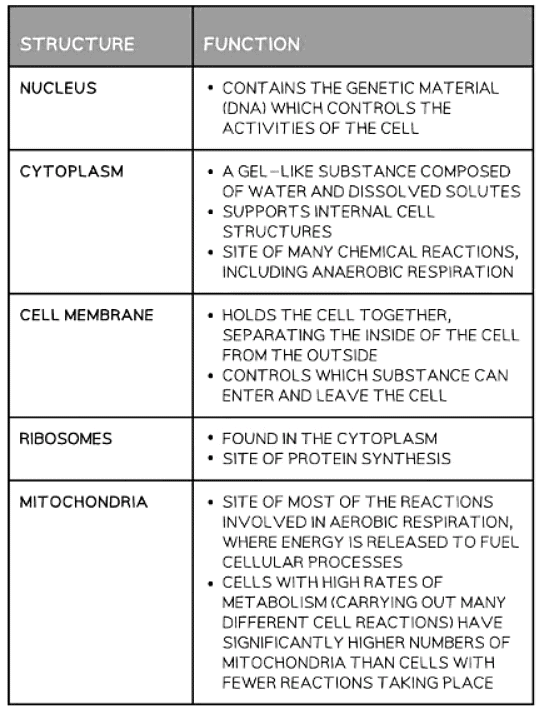
Cell Structures Found in Both Animal and Plant Cells Table
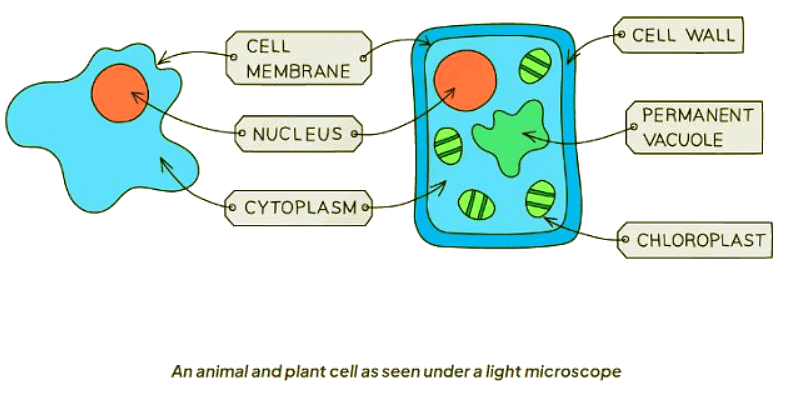
Cell Structures Found Only in Plant Cells Table
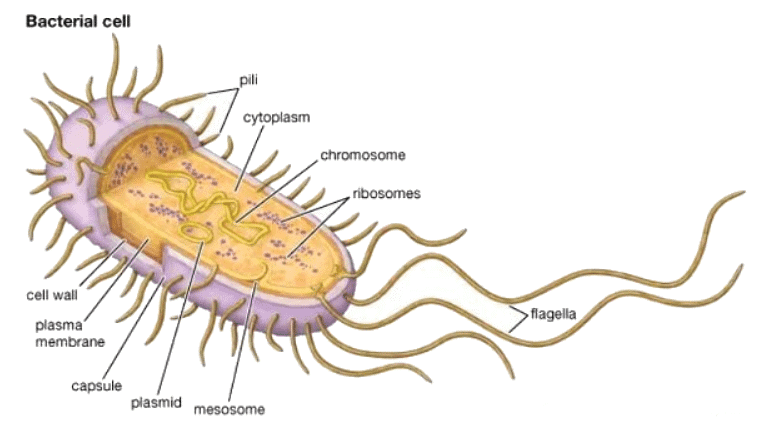
Bacteria Cells
- Bacteria exhibit a diverse range of shapes and sizes, but they all share certain key biological characteristics:
- Bacteria are tiny single-celled organisms that can only be seen under a microscope.
- They have a unique cell structure comprising a cell wall made of peptidoglycan (not cellulose), a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.
- Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacteria lack a nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is in the form of a circular chromosome of DNA that floats freely in the cytoplasm.
- Some bacteria may also contain plasmids, which are small circular DNA molecules that carry additional genes not found in the main chromosome.
- Bacteria do not possess mitochondria, chloroplasts, or other membrane-bound organelles commonly found in plant and animal cells.
- Certain types of bacteria may have flagella, which are whip-like structures that enable them to move around.
- Examples of bacteria include:
- Lactobacillus: A rod-shaped bacterium utilized in the production of yogurt from milk.
- Pneumococcus: A spherical bacterium known for causing pneumonia as a pathogen.
Question for Cell StructureTry yourself: Which of the following is a feature unique to animal cells?View Solution
Identifying Cell Structures & Function
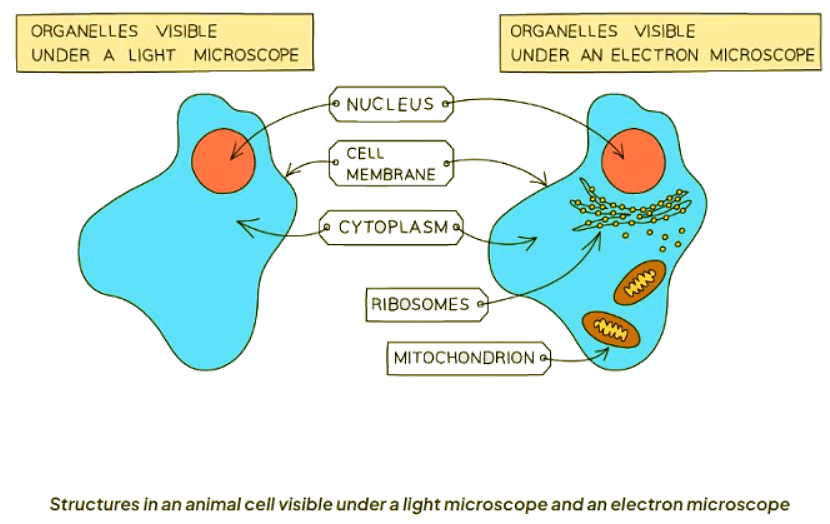
When observing cells under higher magnification, various organelles can be seen within the cytoplasm, except in prokaryotic cells.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) are organelles found throughout the cytoplasm. They are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell since they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are tiny structures that can be free within the cytoplasm or attached to a system of membranes within the cell known as the Endoplasmic Reticulum. These structures are responsible for protein synthesis in the cell, translating genetic information into proteins.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Endoplasmic Reticulum, particularly the rough ER studded with ribosomes, looks rough under the microscope, hence its name. This organelle plays a crucial role in the synthesis and processing of proteins within the cell.
- Vesicles: Vesicles are small circular structures that can be observed moving throughout the cytoplasm. These membrane-bound sacs are involved in various cellular processes, including transport of materials within the cell and between different cells.
The document Cell Structure | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Cell Structure - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main differences between animal and plant cells? |  |
Ans. Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts, while plant cells do. Animal cells also have lysosomes, while plant cells do not.
| 2. How do bacteria cells differ from animal and plant cells? |  |
Ans. Bacteria cells do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles like animal and plant cells. They have a cell wall and a single circular chromosome.
| 3. What are some common structures found in both animal and plant cells? |  |
Ans. Both animal and plant cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and a nucleus.
| 4. What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells? |  |
Ans. The cell wall in plant cells provides structural support and protection, helping the cell maintain its shape.
| 5. How do organelles in cells contribute to their overall function? |  |
Ans. Organelles like the mitochondria produce energy for the cell, while the nucleus contains the cell's genetic material. Each organelle plays a specific role in the cell's overall function and survival.
Related Searches