Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Osmosis
Osmosis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Osmosis
- Every cell is enveloped by a cell membrane, which exhibits partial permeability.
- Water can traverse into and out of cells via a process known as osmosis.
- Osmosis refers to the movement of water molecules from a solution of lower solute concentration (thus higher water concentration) to one of higher solute concentration (and lower water concentration) across a partially permeable membrane.
- This movement entails water flowing down its concentration gradient.
- The partial permeability of the cell membrane implies that it permits the passage of small molecules, such as water, while impeding the movement of larger molecules, such as solute molecules.
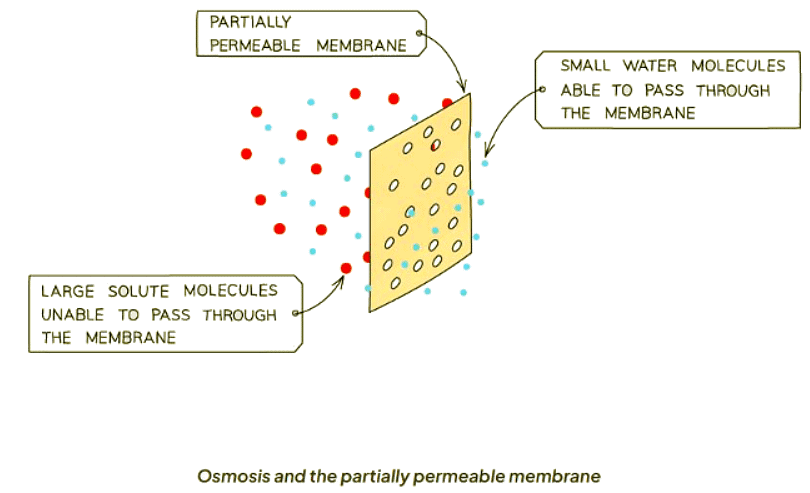
Osmosis and the Partially Permeable Membrane
Osmosis is the process of water moving from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a partially permeable membrane. This movement occurs without the input of energy.
- Definition: Osmosis is the spontaneous movement of water molecules through a partially permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration.
- Importance: Osmosis is crucial for the balance of water in cells and organisms. It helps in maintaining cell turgidity and plays a role in processes like nutrient uptake in plants.
- Mechanism: Osmosis occurs due to the random movement of water molecules. The net flow of water happens from the side with lower solute concentration to the side with higher solute concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- Example: In plant cells, osmosis is responsible for the entry of water into the cell, creating turgor pressure that keeps the cell rigid and helps support the plant structure.
Question for OsmosisTry yourself: What is osmosis?View Solution
The document Osmosis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Osmosis - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is osmosis? |  |
Ans. Osmosis is the process by which water molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a partially permeable membrane.
| 2. How does osmosis work with a partially permeable membrane? |  |
Ans. A partially permeable membrane allows only certain molecules, such as water, to pass through while restricting the movement of larger molecules. In osmosis, water molecules move through this membrane to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides.
| 3. What factors can affect the rate of osmosis? |  |
Ans. Factors that can affect the rate of osmosis include the concentration gradient, temperature, surface area of the membrane, and thickness of the membrane. A steeper concentration gradient or higher temperature can increase the rate of osmosis.
| 4. How is osmosis different from diffusion? |  |
Ans. Osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion is the movement of any type of molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Both processes involve passive transport.
| 5. Can osmosis be harmful to cells? |  |
Ans. Yes, osmosis can be harmful to cells if there is an imbalance of water concentration inside and outside the cell. If a cell takes in too much water through osmosis, it may swell and burst (lyse). Conversely, if a cell loses too much water, it may shrink and become dehydrated.
Related Searches















