Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Pathway Taken by Water
Pathway Taken by Water | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Pathway Taken by Water
- Osmosis drives water to move into the root hair cells, traverse through the root cortex, and enter the xylem vessels.
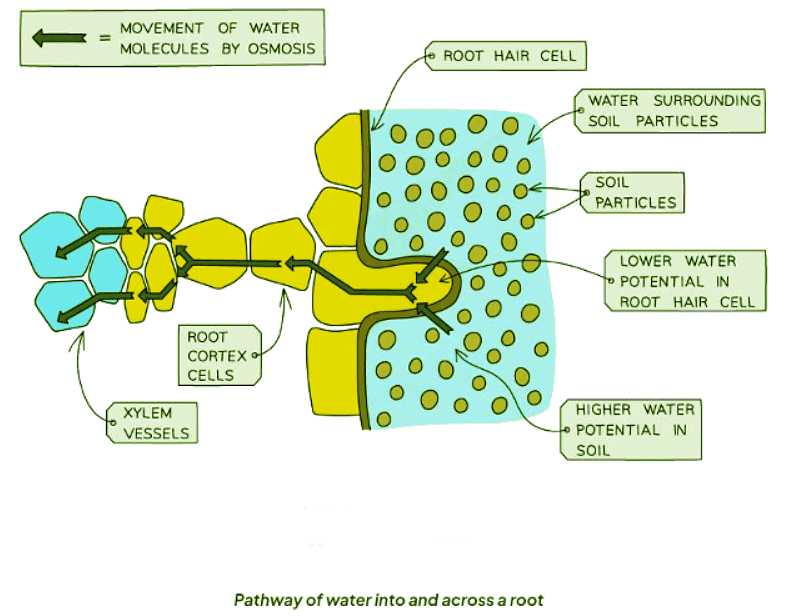
- Once water enters the xylem, it ascends to the leaves and permeates the mesophyll cells.
- Thus, the pathway is as follows: root hair cell → root cortex cells → xylem → leaf mesophyll cells.
Investigating Water Movement in Plants
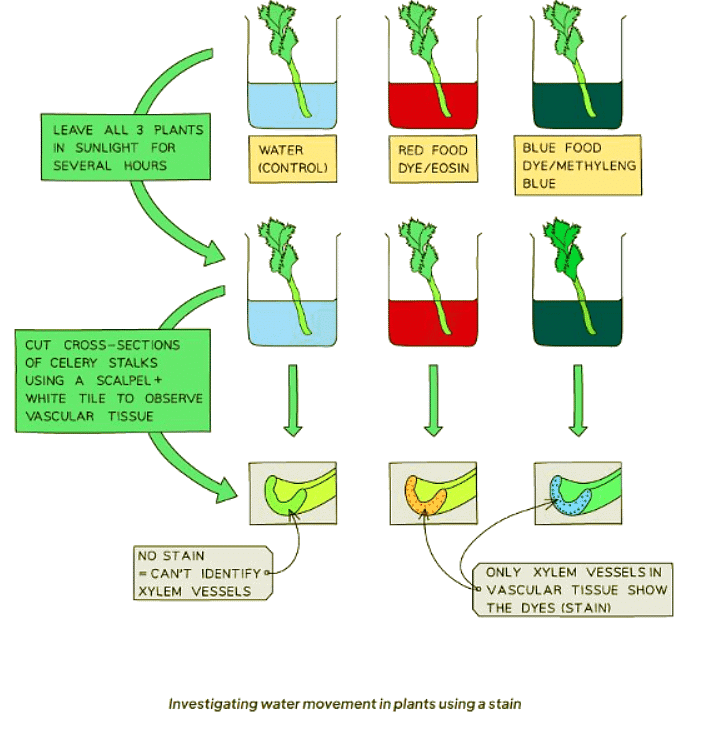
- The process of exploring how water moves in plants can be observed by immersing a plant, such as celery, in a beaker containing stained water. Food coloring serves as a suitable stain for this experiment.
- Over the course of a few hours, the leaves of the celery begin to adopt the color of the dyed water. This transformation serves as evidence that water is being absorbed by the celery.
- Upon cutting a cross-section of the celery, only specific regions of the stalk exhibit the color of the water stain. This phenomenon illustrates that water is being transported through distinct vessels within the stem, known as xylem vessels.
Question for Pathway Taken by WaterTry yourself: How does water move through a plant from the root to the leaves?View Solution
The document Pathway Taken by Water | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Pathway Taken by Water - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How does water move through plants? |  |
Ans. Water moves through plants primarily through a process called transpiration, where water is absorbed by the roots and then pulled up through the plant's vascular system to the leaves.
| 2. What role does the root system play in water movement in plants? |  |
Ans. The root system of a plant absorbs water and minerals from the soil, which is then transported through the plant to provide nutrients and support various physiological processes.
| 3. What environmental factors can affect water movement in plants? |  |
Ans. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind can impact water movement in plants by affecting the rate of transpiration and water uptake by the roots.
| 4. How do plants regulate water loss during transpiration? |  |
Ans. Plants can regulate water loss during transpiration by controlling the opening and closing of stomata, small pores on the surface of leaves, to adjust the rate of water vapor release.
| 5. What are some adaptations that plants have developed to cope with water scarcity? |  |
Ans. Plants have developed various adaptations such as deep root systems, succulent leaves, and waxy cuticles to help them conserve water and survive in arid environments.
Related Searches















