Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Transpiration
Transpiration | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Transpiration
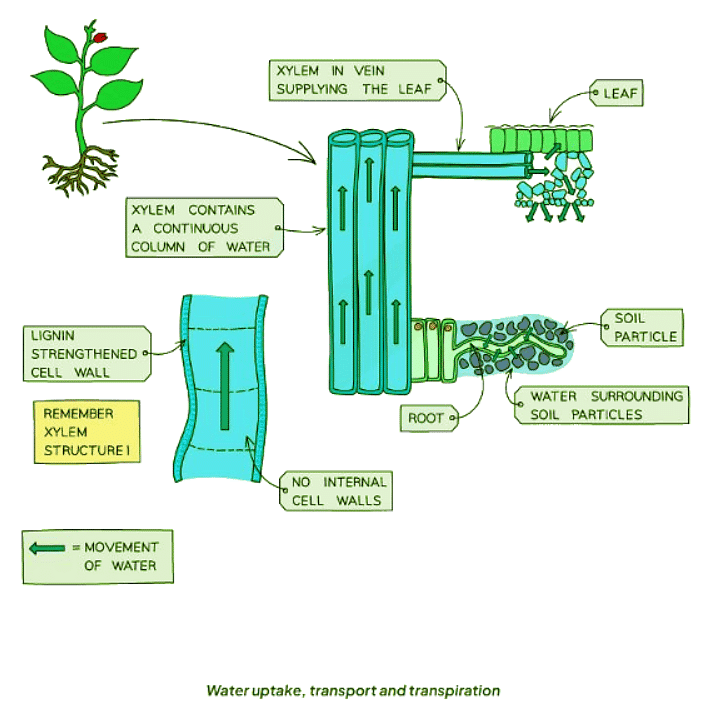
- Water ascends through the xylem from the roots to the leaves, replenishing lost water due to transpiration.
- Transpiration occurs when water vapor escapes from the surfaces of mesophyll cells in plant leaves, followed by diffusion through the stomata.
- The xylem exhibits several adaptations:
- Lignin deposition in cell walls leads to cell death, resulting in hollow, interconnected cells.
- These cells form a continuous tube, facilitating the movement of water and mineral ions.
- Lignin enhances plant strength, aiding in the resistance to water pressure.
- Xylem transport occurs unidirectionally, solely from roots to leaves, contrasting with the bidirectional movement in phloem.
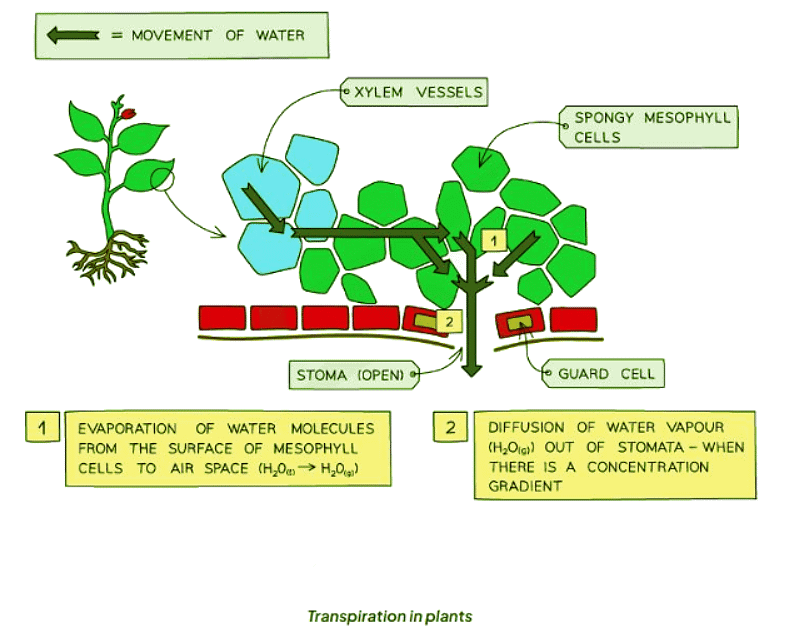
Functions of Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration serves various essential functions in plants:
- It aids in the transportation of mineral ions.
- It provides water to maintain cell turgidity, supporting the plant's structure.
- Water is supplied to leaf cells for photosynthesis.
- Maintaining leaf temperature (the transformation of liquid water into water vapor as it exits cells and enters the air spaces demands heat energy. The consumption of heat during water vaporization aids in cooling the plant).
The document Transpiration | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Transpiration - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is transpiration? |  |
Ans. Transpiration is the process through which plants absorb water from the soil and release it into the atmosphere through their leaves.
| 2. How does transpiration benefit plants? |  |
Ans. Transpiration helps plants regulate their temperature, transport nutrients from the soil to different parts of the plant, and maintain turgidity in their cells.
| 3. What factors can affect the rate of transpiration in plants? |  |
Ans. Factors such as humidity, temperature, wind speed, and the availability of water in the soil can affect the rate of transpiration in plants.
| 4. Can transpiration be harmful to plants? |  |
Ans. While transpiration is essential for plants, excessive transpiration can lead to water stress and dehydration, especially in dry or hot environments.
| 5. How can plants reduce water loss through transpiration? |  |
Ans. Plants can reduce water loss through transpiration by closing their stomata during hot or dry periods, developing thick cuticles on their leaves, and growing in shaded or humid environments.
Related Searches















