Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & Humidity
Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & Humidity | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Explaining the Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & Humidity: Extended
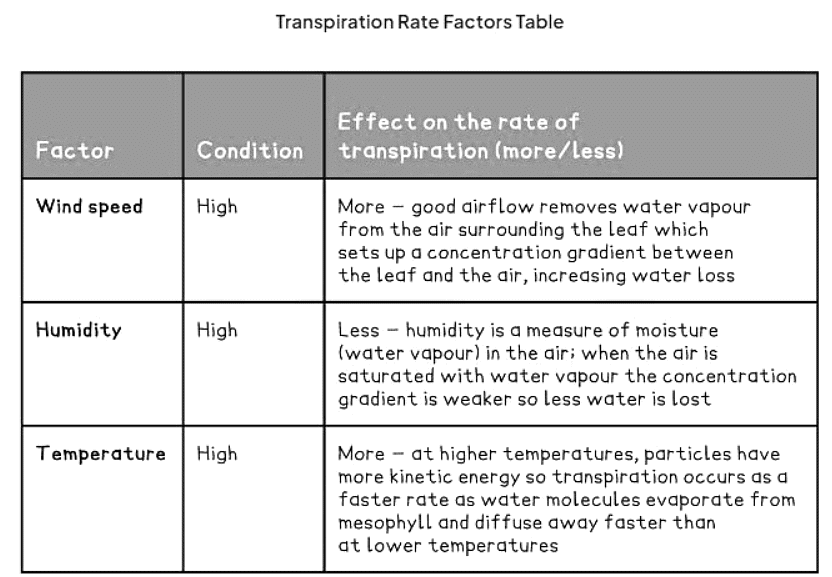
- Wind speed, humidity, and temperature exert influence on transpiration rates.
- The provided table delineates their impact on transpiration when they are all elevated; conversely, reduced levels of these factors would yield opposite effects.
- Utilizing a potometer allows for the examination of how environmental variables affect transpiration rates.
Wilting: Extended
- If a plant loses more water from its leaves than the soil can provide through osmosis, it results in wilting. This occurs when the plant cells lack sufficient water, causing the cell walls to lose strength and the plant to collapse.
- Wilting: This happens when the plant cells do not have enough water, leading to weakened cell walls and the plant's collapse.
 A wilted plant cannot support itself and starts to collapse
A wilted plant cannot support itself and starts to collapse
Question for Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & HumidityTry yourself: What is the result of a plant losing more water from its leaves than the soil can provide through osmosis?View Solution
The document Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & Humidity | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Effects of Temperature, Wind Speed & Humidity - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How does temperature affect wilting in plants? |  |
Ans. Temperature can affect plant wilting by increasing the rate of transpiration, causing the plant to lose water faster than it can absorb it, leading to wilting.
| 2. How does wind speed impact wilting in plants? |  |
Ans. High wind speeds can increase the rate of transpiration in plants, causing them to lose water quickly and potentially leading to wilting if the plant is unable to replace the lost water.
| 3. What role does humidity play in the wilting process of plants? |  |
Ans. Low humidity levels can increase the rate of transpiration in plants, leading to wilting as the plant loses water faster than it can absorb it. High humidity levels, on the other hand, can help reduce transpiration and prevent wilting.
| 4. Can plants recover from extended wilting caused by temperature, wind speed, and humidity? |  |
Ans. In some cases, plants can recover from extended wilting if they are provided with sufficient water and the environmental conditions are improved to reduce stress on the plant. However, prolonged wilting can cause irreversible damage to the plant.
| 5. How can gardeners mitigate the effects of temperature, wind speed, and humidity on plant wilting? |  |
Ans. Gardeners can protect plants from extreme temperatures by providing shade or shelter, reducing wind exposure by using windbreaks, and maintaining optimal soil moisture levels to counteract the effects of high temperatures and low humidity on plant wilting.
Related Searches















