Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Translocation
Translocation | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Translocation: Extended
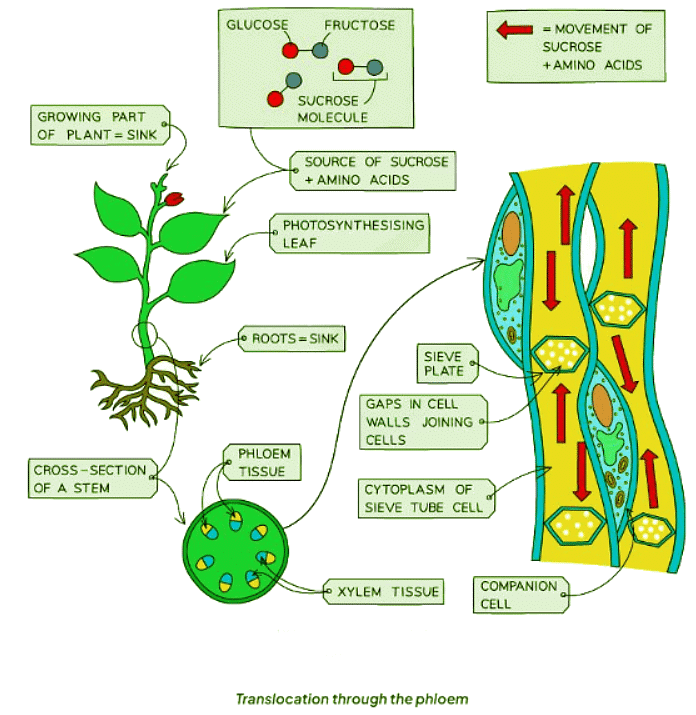
- The end products of photosynthesis include sugars, primarily sucrose, and amino acids.
- These essential nutrients are conveyed throughout the plant via phloem tubes, which consist of living cells in contrast to xylem vessels that are composed of deceased cells.
- Phloem cells are interconnected end to end, featuring sieve plates in their cell walls that facilitate the smooth movement of substances from one cell to another.
- The process of transferring sucrose and amino acids through the phloem, from sites of production to areas of storage or utilization, is termed translocation.
- Transport within the phloem can vary, depending on the plant's growth stage or the time of year, with nutrients consistently moving from sources (production sites) to sinks (storage or usage areas).
- For instance, during winter when many plants lack foliage, phloem tubes may transport dissolved sugars and amino acids from storage organs to sustain respiration.
- In periods of growth like spring, roots serve as sources while various plant parts act as sinks for nutrients.
- Subsequently, in peak growth periods like summer, leaves, being the primary sites of photosynthesis, transform into sources, transferring sugars to roots for storage as starch until required.
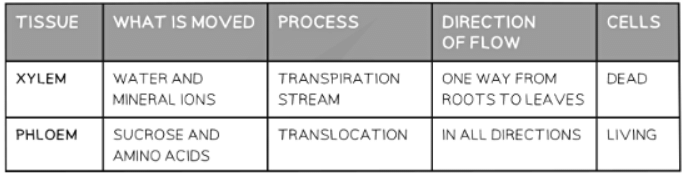
Comparison between Xylem and Phloem Tissue Table
- Translocation through the phloem: This process involves the movement of sugars and other nutrients through the phloem tissue in plants to different parts of the plant, such as leaves, roots, and fruits.
- Comparison between Xylem and Phloem Tissue: Xylem and phloem are two types of vascular tissues in plants. While xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, phloem carries sugars produced during photosynthesis to various plant parts.
Question for TranslocationTry yourself: What is the function of phloem tissue in plants?View Solution
The document Translocation | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Translocation - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is translocation in genetics? |  |
Ans. Translocation in genetics refers to a chromosomal abnormality where a portion of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another non-homologous chromosome.
| 2. How does translocation occur? |  |
Ans. Translocation can occur during cell division when chromosomes break and reattach to a different chromosome, leading to an alteration in the genetic material.
| 3. What are the different types of translocations? |  |
Ans. There are two types of translocations: reciprocal translocations, where two non-homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, and Robertsonian translocations, where two acrocentric chromosomes fuse at the centromere.
| 4. What are the consequences of translocation in genetics? |  |
Ans. Translocations can lead to various genetic disorders and health issues, depending on the specific chromosomes involved and the amount of genetic material that is exchanged.
| 5. How is translocation diagnosed and treated? |  |
Ans. Translocations can be diagnosed through genetic testing, such as karyotyping or FISH analysis. Treatment options depend on the specific genetic disorder associated with the translocation and may include genetic counseling, medication, or surgery.
Related Searches















