Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces
Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces
- The locations where organisms perform gas exchange vary significantly, and different species have developed diverse methods to reach these surfaces based on factors like size and habitat.
- All structures involved in gas exchange share common characteristics.
- These shared traits facilitate the efficient exchange of gases across the surface area within a short duration.
- Essential features include:
- Large Surface Area: This feature allows for the faster diffusion of gases across the surface, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
- Thin Walls: Thin walls are essential to ensure that diffusion distances remain short, thus speeding up the process of gas exchange.
- Good Ventilation with Air: Adequate ventilation is necessary to maintain diffusion gradients, enabling the movement of gases in and out effectively.
- Good Blood Supply: A rich blood supply helps maintain a high concentration gradient, leading to faster diffusion of gases.
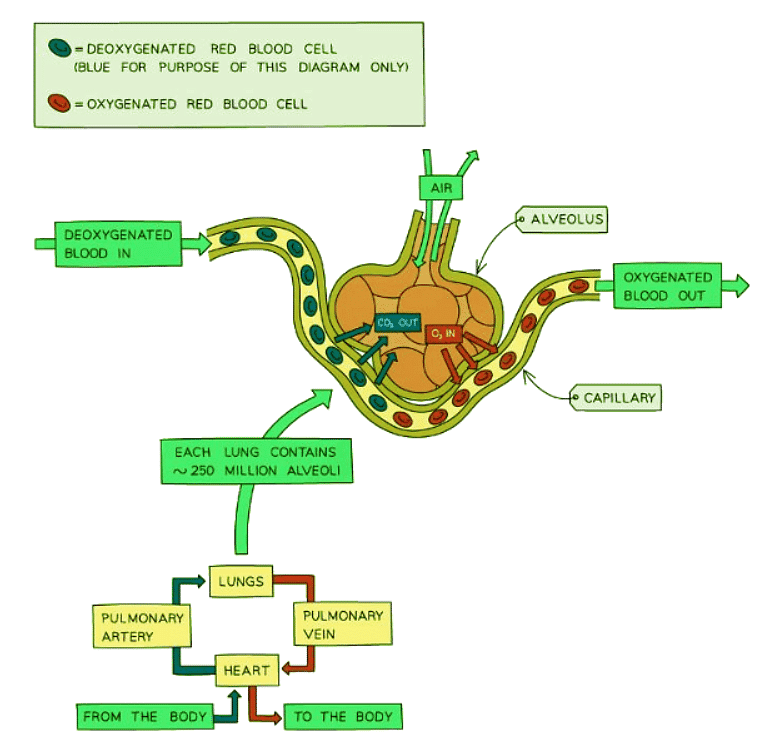 The alveolus is the gas exchange surface in humans
The alveolus is the gas exchange surface in humans
Question for Features of Gas Exchange SurfacesTry yourself: What are the essential features of gas exchange surfaces?View Solution
The document Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the key features of gas exchange surfaces? |  |
Ans. Gas exchange surfaces are characterized by being thin, moist, and having a large surface area to facilitate the exchange of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.
| 2. How do gas exchange surfaces work in the human respiratory system? |  |
Ans. In the human respiratory system, gas exchange surfaces in the lungs, specifically the alveoli, allow for the diffusion of oxygen from the air into the bloodstream and the removal of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the air.
| 3. Why is it important for gas exchange surfaces to be thin? |  |
Ans. Gas exchange surfaces need to be thin to allow for a short diffusion distance, enabling gases to move quickly and efficiently between the external environment and the internal tissues.
| 4. How does the surface area of gas exchange surfaces affect their function? |  |
Ans. A larger surface area of gas exchange surfaces allows for more efficient exchange of gases, as there is more area available for molecules to diffuse across, increasing the rate of gas exchange.
| 5. What role does moisture play in gas exchange surfaces? |  |
Ans. Moisture on gas exchange surfaces helps to dissolve gases, making it easier for them to diffuse across the surface. It also helps to keep the surface thin and flexible, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
Related Searches




















