Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Drugs in Medicine
Drugs in Medicine | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What is a Drug?
- A drug is any substance taken into the body that alters or influences chemical reactions within the body.
- Certain drugs, like antibiotics, are classified as medicinal substances used to address symptoms or causes of diseases. For instance, antibiotics combat bacterial infections effectively.
- The liver plays a crucial role in drug metabolism, serving as the primary site where many drugs are processed and broken down.
- Specifically, the liver is responsible for the metabolism of drugs, ensuring that they can be effectively utilized or excreted by the body.
Antibiotics
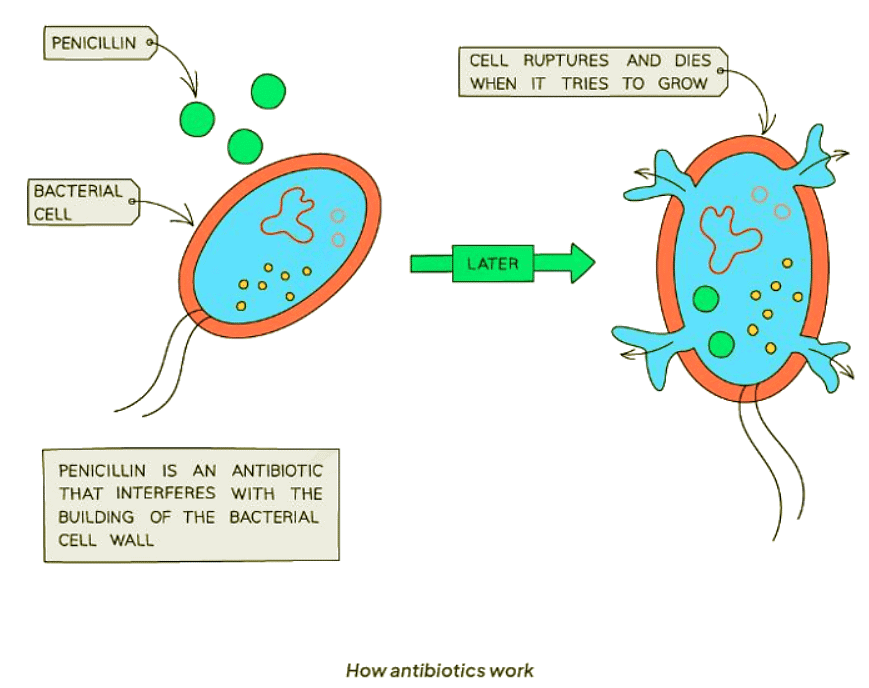
- Antibiotics are chemical substances produced by certain fungi or bacteria that impact the functioning of bacterial cells, either by disrupting their structure or function or by inhibiting their reproduction.
- These substances are specifically effective against bacteria and do not work against viruses.
- Antibiotics target processes and structures unique to bacterial (prokaryotic) cells, without causing harm to animal cells.
Antibiotic Resistance & Use
- Since the discovery of the first antibiotic in 1928, numerous antibiotics have been developed and widely used.
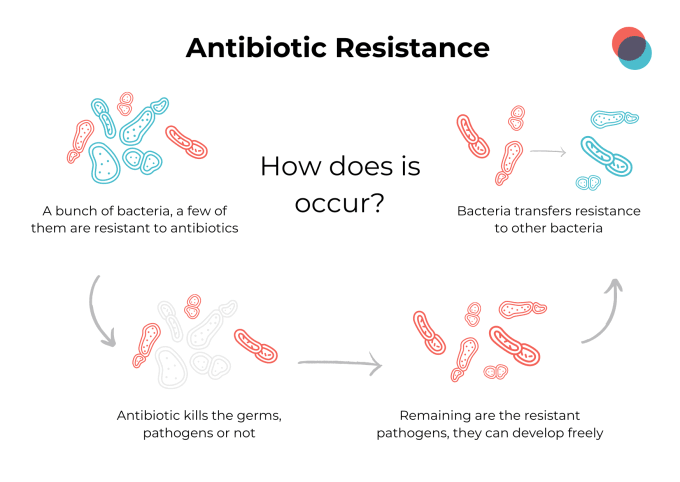
- Commonly prescribed antibiotics are losing effectiveness due to various reasons, such as overuse, unnecessary prescriptions, patients not completing full courses, and extensive agricultural use.
Reasons for Antibiotic Ineffectiveness
- Overuse of antibiotics in both medical and agricultural settings contributes to reduced effectiveness.
- Patients not finishing prescribed antibiotic courses can lead to antibiotic resistance.
- Agricultural practices involve mass antibiotic use to prevent diseases in livestock, even when animals are healthy, further decreasing antibiotic efficacy.
Impact of Antibiotic Resistance
- Antibiotic resistance is on the rise, making common bacterial infections harder to treat.
- Superbugs like MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) are becoming more prevalent.
Prevention of Antibiotic Resistance
- Use antibiotics only when necessary to avoid contributing to resistance.
- Complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve early.
Question for Drugs in MedicineTry yourself: What is the primary role of the liver in drug metabolism?View Solution
The document Drugs in Medicine | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Drugs in Medicine - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is a drug? |  |
Ans. A drug is a substance that is used to treat, cure, or prevent a disease or medical condition.
| 2. How do antibiotics work in the body? |  |
Ans. Antibiotics work by targeting and killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth, helping the body to fight off bacterial infections.
| 3. What is antibiotic resistance and why is it a concern? |  |
Ans. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria mutate and become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat. It is a concern because it can lead to ineffective treatment and the spread of resistant bacteria.
| 4. What are some factors contributing to antibiotic resistance? |  |
Ans. Factors contributing to antibiotic resistance include overprescription of antibiotics, improper use of antibiotics, not completing the full course of antibiotics, and the use of antibiotics in livestock for growth promotion.
| 5. How can antibiotic resistance be prevented? |  |
Ans. Antibiotic resistance can be prevented by using antibiotics only when necessary, following the prescribed dosage and schedule, not sharing antibiotics with others, and practicing good hygiene to prevent infections.
Related Searches




















