Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Asexual Reproduction
- Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of sex cells or fertilization.
- In asexual reproduction, only one parent is needed, leading to offspring that are genetically identical to the parent and to each other, essentially creating clones.
- The offspring produced through asexual reproduction inherit the genetic information solely from the single parent.
Examples of Asexual Reproduction
Bacteria replicate themselves precisely through a form of asexual reproduction known as binary fission:
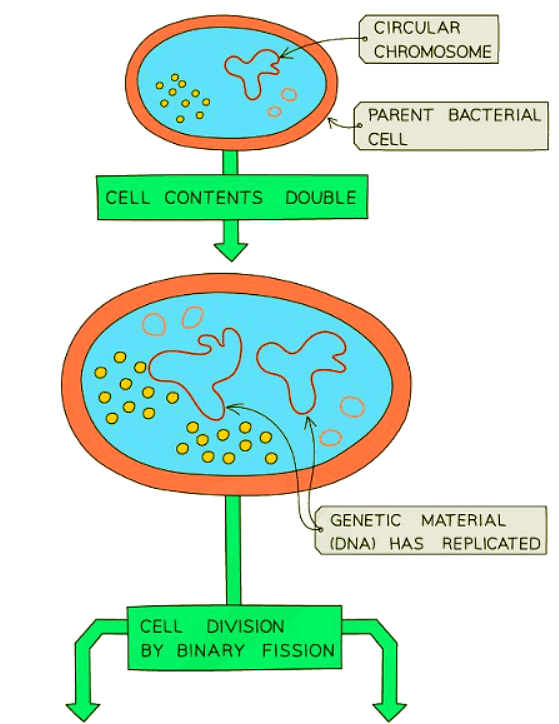
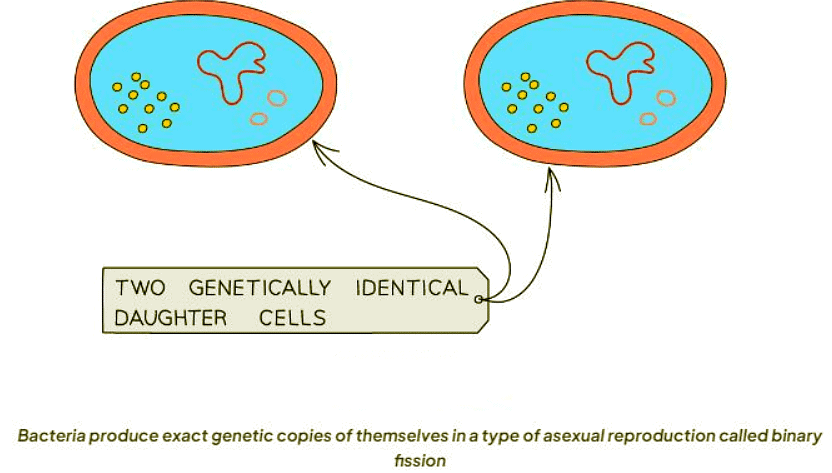
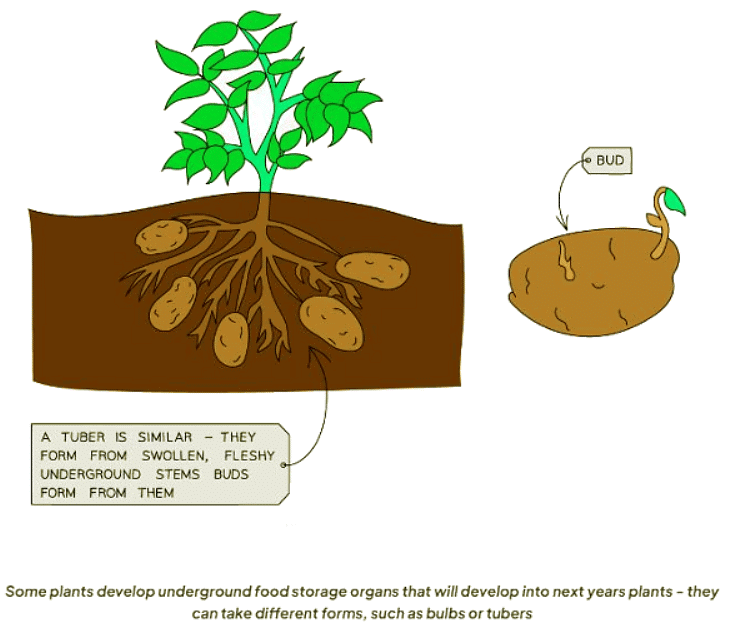
Plants also utilize asexual reproduction methods such as budding from bulbs and tubers. These storage organs give rise to new plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant.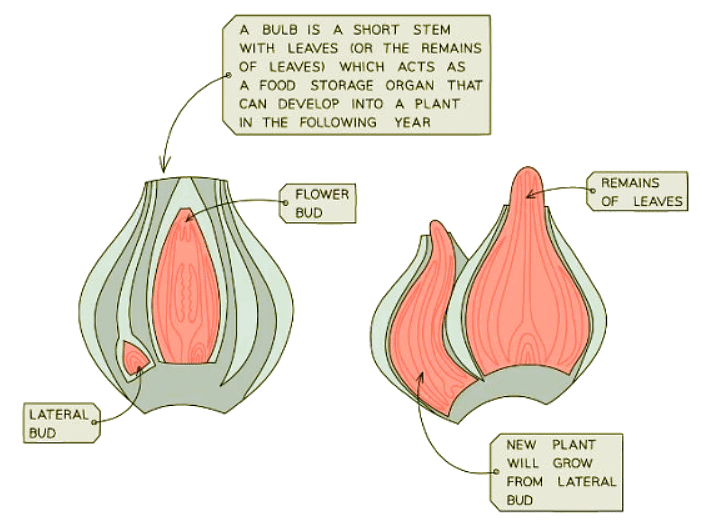
Some plants develop side shoots called runners, which bear tiny plantlets that can grow into new, genetically identical plants. These plantlets will eventually root themselves and establish as independent plants.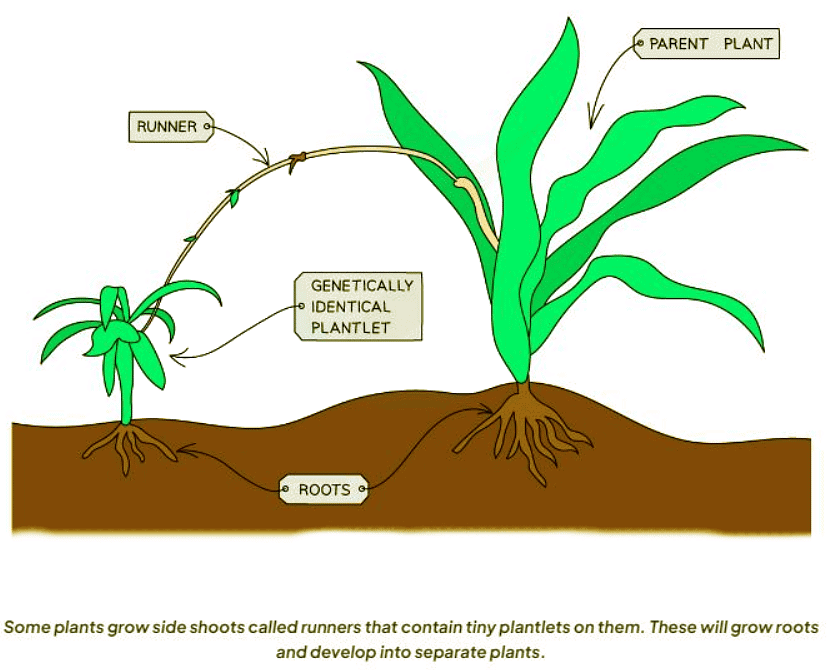
Advantages & Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
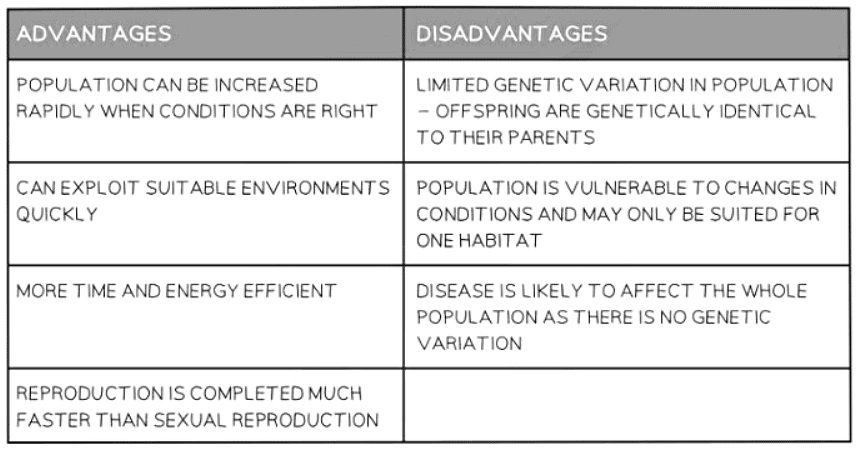
- In crop plants, asexual reproduction can be advantageous as it allows plants with desirable traits (such as high yield, disease resistance, and hardiness) to be reproduced asexually, ensuring that the entire crop inherits these beneficial characteristics.
- Asexual reproduction in crop plants results in uniformity throughout the entire crop, maintaining consistency in desirable traits across all plants.
Question for Asexual ReproductionTry yourself: What is asexual reproduction?View Solution
The document Asexual Reproduction | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Asexual Reproduction - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that only involves one parent organism. The offspring produced are genetically identical to the parent.
| 2. What are some examples of asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Examples of asexual reproduction include binary fission in bacteria, budding in yeast, fragmentation in starfish, and spore formation in fungi.
| 3. What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Some advantages of asexual reproduction include the ability to reproduce rapidly, the production of genetically identical offspring, and the lack of need for a mate.
| 4. What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Disadvantages of asexual reproduction include the lack of genetic diversity, which can make populations more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes, and the inability to adapt to new environments quickly.
| 5. How does asexual reproduction differ from sexual reproduction? |  |
Ans. Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces genetically varied offspring.
Related Searches















