Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Meiosis
Meiosis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Meiosis
- Meiosis, a form of nuclear division, yields genetically diverse cells.
- Its primary function is to generate gametes, or sex cells.
- During gamete formation, the chromosome count must be reduced by half.
- Failure to halve the chromosome count would result in a doubling of chromosomes upon fertilization.
- Meiosis accomplishes this reduction, transitioning from diploid to haploid cells, ensuring genetic diversity.
- The process initiates with chromosome duplication, similar to mitosis, followed by two rounds of division.
- Through these divisions, each gamete receives only one set of chromosomes, rendering them haploid.
- Meiosis ultimately produces four haploid cells due to its double division.
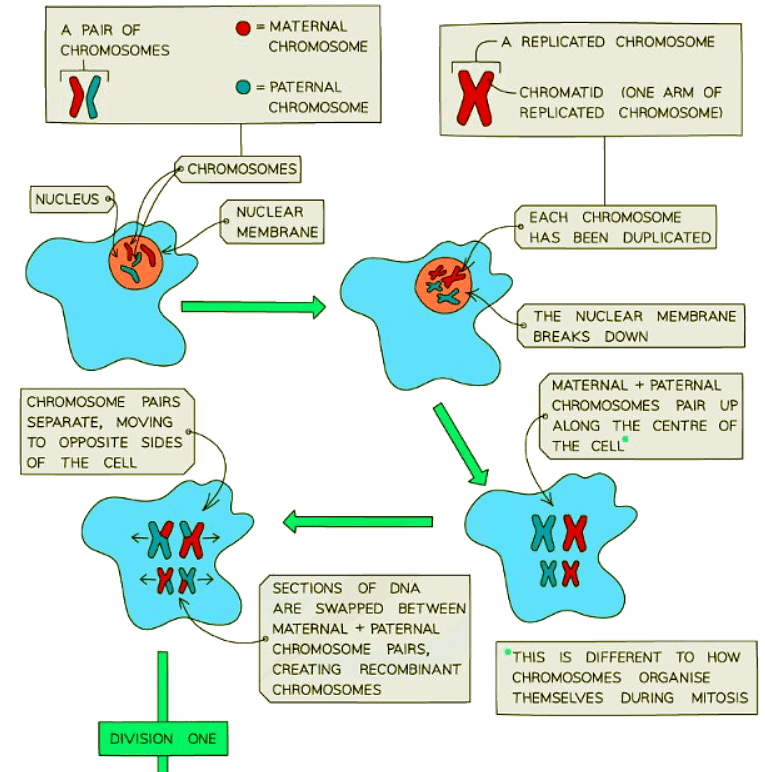
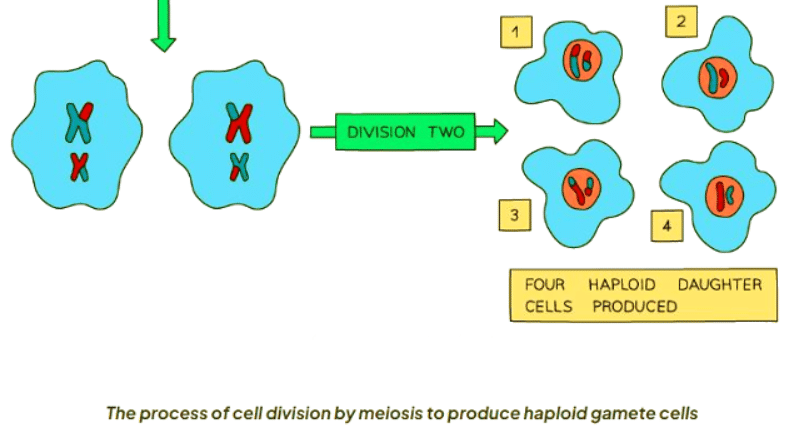
Process
- Each chromosome duplicates, forming X-shaped chromosomes.
- In the first division, chromosomes pair up in the cell's center, undergo recombination, and are separated by cell fibers, resulting in each new cell having one of each recombinant chromosome pair.
- The second division involves chromosomes lining up at the cell's center, with cell fibers separating them, similar to mitosis. This process yields four haploid daughter cells.
Importance of Meiosis
- Meiosis is crucial for the production of gametes like sperm cells, egg cells, pollen grains, and ovum.
- It enhances genetic variation among offspring, contributing to diversity.
Variation in Meiosis
- Meiosis generates diversity by creating new combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes with each gamete production.
- During fertilization, the random fusion of gametes results in each offspring being genetically distinct from others.
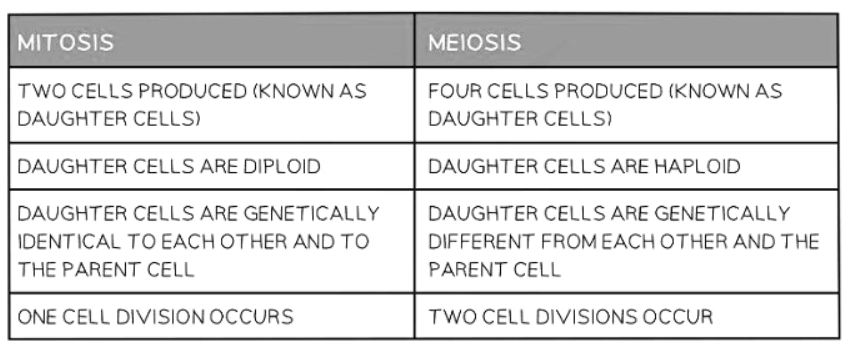
Differences between Mitosis & Meiosis
Question for MeiosisTry yourself: What is the primary function of meiosis?View Solution
The document Meiosis | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Meiosis - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is meiosis? |  |
Ans. Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, resulting in the formation of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
| 2. What is the purpose of meiosis? |  |
Ans. The purpose of meiosis is to produce genetically diverse gametes for sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic variation in offspring.
| 3. How many stages are there in meiosis? |  |
Ans. Meiosis consists of two main stages: meiosis I and meiosis II, each further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
| 4. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis? |  |
Ans. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four genetically unique daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
| 5. How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity? |  |
Ans. Meiosis contributes to genetic diversity through processes such as crossing over, independent assortment, and random fertilization, which shuffle and recombine genetic material to create unique combinations of genes in offspring.
Related Searches




















