Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Codominance & Sex-Linked Characteristics
Codominance & Sex-Linked Characteristics | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
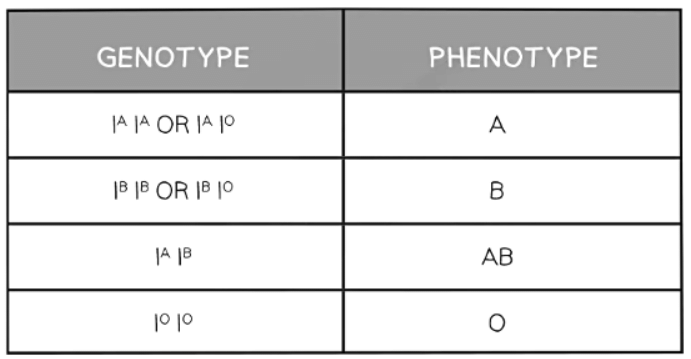
Codominance
- Codominance is observed when both alleles in heterozygous organisms jointly influence the physical traits displayed.
- An illustrative instance of codominance is the inheritance of blood groups, showcasing this genetic phenomenon.
- In the case of blood group inheritance, a departure from the usual genetic pattern occurs, involving three alleles governing the process instead of the typical two.
- Notably, alleles IA and IB exhibit codominance, exerting dominance over allele IO.
- The gene is represented by 'I', with 'A', 'B', and 'O' denoting the respective alleles.
- Allele IA prompts the production of antigen A within the blood system, while IB triggers the generation of antigen B. Conversely, IO results in the absence of any antigens.
- These distinct alleles offer various genotypic and phenotypic outcomes, showcasing the complexity and diversity of genetic inheritance.
- We can utilize genetic diagrams to forecast the results of crosses involving codominant alleles.
When a parent with blood group A and another with blood group B come together, they can have offspring with blood group O.
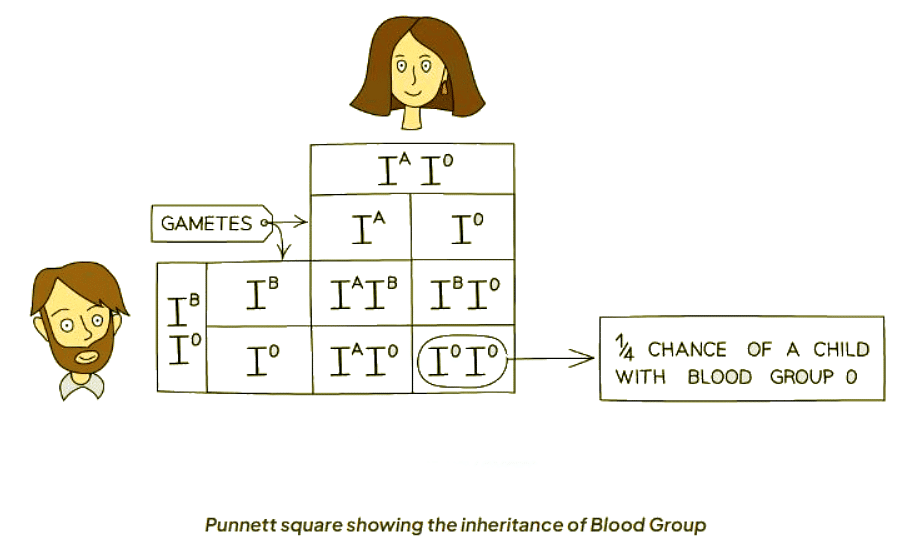
- The parent with blood group A possesses the genotype IAIO.
- The parent with blood group B has the genotype IBIO.
- These genotypes are confirmed, as they can produce a child with blood group O, indicating the child inherits an allele for group O from each parent.
- Parents with these blood types hold a 25% likelihood of having a child with blood type O.
Sex-Linked Characteristics
- Alleles on the same chromosome are said to be linked
- When alleles controlling a specific trait are located on the sex chromosomes, it leads to what we call 'sex-linked' inheritance. In most cases, these alleles are found on the X chromosome, as the Y chromosome is significantly smaller.
- Males, possessing only one X chromosome, are at a higher risk of displaying sex-linked recessive conditions like red-green color blindness and hemophilia.
- Females, with two X chromosomes, typically inherit at least one dominant allele that conceals the effects of the recessive allele.
- A female who carries one recessive allele in a masked state is termed a carrier. Although she does not exhibit the disease, there's a 50% chance of passing it on to her offspring.
- If the offspring is male, he will express the disease.
- When a normal male mates with a female carrier of color blindness, specific outcomes are observed:
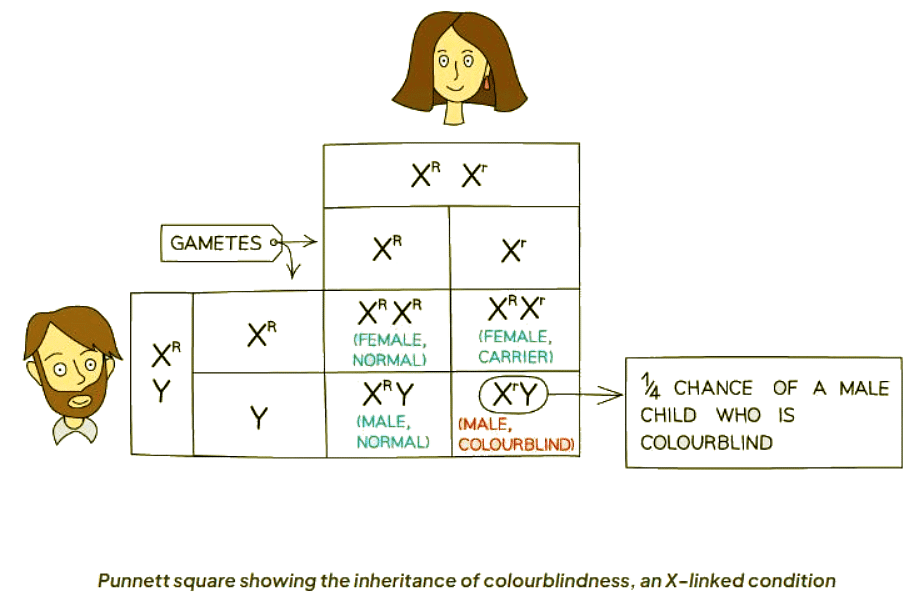
- When using a Punnett square for colorblindness, there is a 25% probability of producing a colorblind male.
- There is also a 25% chance of producing a female carrier, a 25% chance of a normal female, and a 25% chance of a normal male offspring.
Question for Codominance & Sex-Linked CharacteristicsTry yourself: What is codominance?View Solution
The document Codominance & Sex-Linked Characteristics | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Codominance & Sex-Linked Characteristics - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is codominance? |  |
Ans. Codominance is a genetic phenomenon where two different alleles for a trait are both expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual. This results in a unique phenotype where both alleles are visibly present.
| 2. Can you give an example of codominance in humans? |  |
Ans. A classic example of codominance in humans is the ABO blood group system. In this system, individuals can have blood type A, B, AB (codominant), or O (recessive).
| 3. What are sex-linked characteristics? |  |
Ans. Sex-linked characteristics are traits that are carried on the sex chromosomes, X and Y. These traits are often inherited differently between males and females due to the presence of these chromosomes.
| 4. How are sex-linked characteristics inherited differently in males and females? |  |
Ans. In males, who have one X and one Y chromosome, a sex-linked trait on the X chromosome will always be expressed since there is no corresponding allele on the Y chromosome to mask it. In females, who have two X chromosomes, the presence of two alleles can result in different expressions of the trait.
| 5. Can you provide an example of a sex-linked characteristic? |  |
Ans. A well-known example of a sex-linked characteristic is color blindness, which is more common in males since the gene for color blindness is located on the X chromosome. Females can be carriers of the gene but may not show symptoms of color blindness.
Related Searches















