Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Artificial Selection
Artificial Selection | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
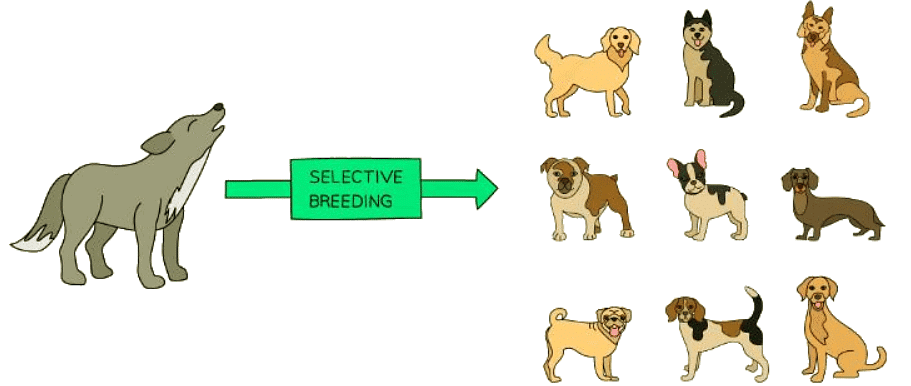
Selective Breeding
- Selective breeding involves choosing individuals with desired traits and breeding them together to enhance those characteristics.
- This process is iterative since not all offspring will exhibit the desired traits initially. Offspring displaying the desired traits are then selected for further breeding.
- Repeated over numerous generations, this selective breeding eventually leads to the development of a distinct "new breed" that consistently displays the chosen traits in all offspring.
- For instance, dog breeders selectively mate dogs to emphasize specific traits like coat color, resulting in the diverse dog breeds we see today, all originating from a common ancestor.
Question for Artificial SelectionTry yourself: What is the purpose of selective breeding?View Solution
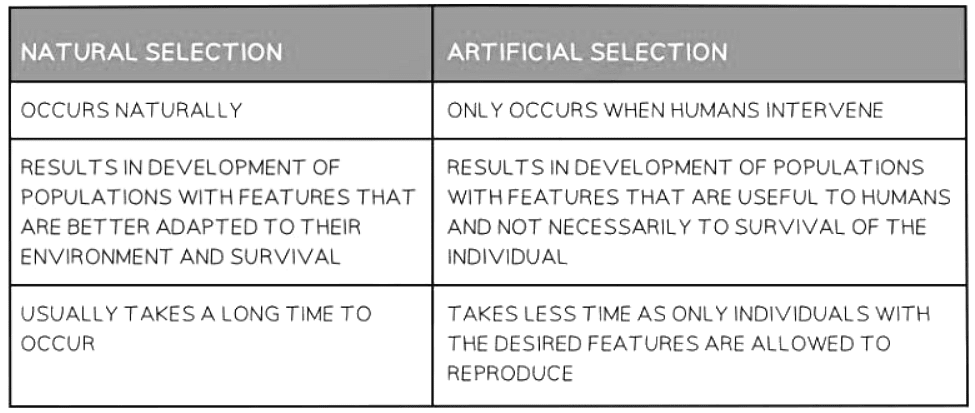
Natural vs Artificial Selection
The document Artificial Selection | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Artificial Selection - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How does selective breeding differ from natural selection? |  |
Ans. Selective breeding is a process in which humans intentionally choose which traits to pass on to the next generation of organisms, while natural selection is a process in which environmental factors determine which traits are passed on based on an organism's ability to survive and reproduce.
| 2. What are some examples of artificially selected traits in plants and animals? |  |
Ans. Some examples of artificially selected traits in plants include larger fruit size, higher crop yields, and resistance to pests. In animals, examples include increased milk production in dairy cows, faster growth rates in chickens, and specific coat colors in dogs.
| 3. How long has selective breeding been practiced by humans? |  |
Ans. Selective breeding has been practiced by humans for thousands of years, dating back to the domestication of plants and animals in ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Chinese.
| 4. What are some ethical considerations related to artificial selection? |  |
Ans. Ethical considerations related to artificial selection include concerns about genetic diversity, potential harm to the welfare of the organisms being bred, and the implications of manipulating genetic traits for human purposes.
| 5. How does selective breeding contribute to the development of new plant and animal varieties? |  |
Ans. Selective breeding allows for the accumulation of desired traits over generations, leading to the development of new plant and animal varieties that exhibit specific characteristics such as disease resistance, productivity, and aesthetic appeal.
Related Searches















