Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Sustainability
Sustainability | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Sustainable Use of Resources
- Sustainable use of resources refers to utilizing natural resources in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- It involves using resources efficiently and responsibly to ensure their availability for the long term.
- Examples of sustainable resource use include promoting recycling, reducing waste, and using renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- By practicing sustainable resource management, we can protect ecosystems, support biodiversity, and mitigate the negative impacts of human activities on the environment.
- We rely on various Earth resources, including sustainable ones like food, water, and wood.
- Sustainable resources are replenished at a rate equal to their consumption, ensuring they do not deplete.
- In contrast, fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are non-renewable since they are irreplaceable once used.
- To preserve non-renewable resources, it's crucial to limit their usage and seek sustainable alternatives.
- Fossil fuels serve as a primary energy source and essential raw materials for various products like plastics.
- Certain items like paper, plastic, glass, and metal can be reused and recycled, reducing environmental waste and conserving energy and raw materials.
- Resources like forests and fish stocks can be managed sustainably to ensure their long-term availability.
Sustainable Production Examples
Sustainable development involves meeting the needs of a growing human population while safeguarding the environment.
- When pursuing sustainable resource management, we must address conflicting interests. This includes ensuring that local communities can utilize resources in their vicinity while also catering to the profit motives of large corporations, such as those involved in forestry and fishing industries. Moreover, it entails striking a balance between human resource needs and the preservation of biodiversity, preventing habitat loss and species extinction.
- Sustainable development necessitates a careful equilibrium between satisfying current population requirements and safeguarding resources for future generations. For instance, overfishing to meet present demands can lead to depleted fish stocks, jeopardizing the availability of seafood for future populations.
- Local People vs. Large Companies: It is crucial to strike a balance between the ability of local communities to utilize resources within their immediate environment and the profit-driven motives of large corporations, especially concerning valuable resources like forests and fish.
- Human Needs vs. Ecosystem Conservation: Managing resources involves harmonizing the requirements of human populations with the preservation of the flora and fauna in those regions. This is essential for preventing habitat loss and species extinction.
- Present vs. Future Needs: Sustainable resource management necessitates considering not only the needs of current populations but also those of future generations. Overexploitation, such as excessive fishing today, can deplete stocks and compromise the ability of future populations to meet their needs.
Sustaining Forests
- Multi-level Cooperation: Sustainable development requires collaboration among individuals at local, national, and international levels in the planning and governance of resources. This collective effort is vital for ensuring resource sustainability and long-term well-being.
- Forests play a crucial role in the production of paper goods and the supply of timber, addressing both industrial and construction needs.
- The global paper industry predominantly sources its raw materials from forests, with a focus on sustainable practices like replanting trees to ensure a continuous supply for the future.
- Tropical hardwoods, including sought-after varieties like teak and mahogany, have lengthy regrowth periods but are highly valued for furniture making.
- Efforts to promote sustainability in the use of these woods have been bolstered by initiatives such as the Forestry Stewardship Council, which monitor logging activities and wood sourcing.
- Education plays a pivotal role in advocating for sustainable practices within logging companies and raising consumer awareness about the significance of supporting products derived from sustainable sources.
Question for SustainabilityTry yourself: Which of the following is an example of sustainable resource use?View Solution
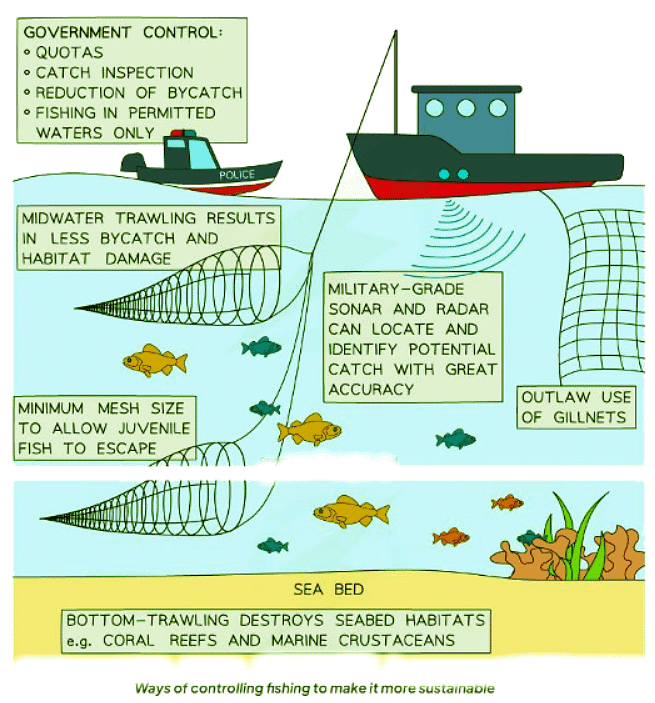
Sustaining Fish Stocks
- Controlling the Number of Fish Caught Each Year (Quotas) Sustainable fish stock management involves setting limits on the amount of fish that can be caught annually. By implementing quotas, we can prevent overfishing and ensure the fish population remains stable.
- Controlling the Size of Fish Caught It is crucial to regulate the size of fish that can be caught to ensure that there are enough mature fish for breeding. By protecting fish of suitable breeding age, we support the sustainability of fish stocks.
- Controlling the Time of Year for Fishing Managing the timing of fishing activities is essential to prevent the large-scale depletion of fish stocks. By restricting fishing during critical breeding periods, we can safeguard the future of fish populations.
- Restocking Initiatives Restocking involves breeding fish and nurturing their offspring until they reach a size where they can thrive in their natural habitat. Releasing these fish back into the wild helps replenish depleted populations.
- Educating Fishermen and Consumers It is vital to educate fishermen about local and international fishing laws to ensure compliance. Additionally, informing consumers about sustainable fishing practices empowers them to make responsible seafood choices, contributing to conservation efforts.
The document Sustainability | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
110 videos|210 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Sustainability - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the concept of sustainability in relation to ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Sustainability in ecosystems refers to the responsible and balanced use of resources to ensure that they can be maintained for future generations without causing harm to the environment.
| 2. Can you provide examples of sustainable production practices in ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Examples of sustainable production practices in ecosystems include organic farming, reforestation projects, and the use of renewable energy sources.
| 3. Why is resource management important for maintaining the health of ecosystems? |  |
Ans. Resource management is important for maintaining the health of ecosystems because it helps prevent overexploitation of resources, promotes biodiversity, and ensures the long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
| 4. How can fish stocks be managed sustainably to prevent depletion? |  |
Ans. Fish stocks can be managed sustainably through measures such as implementing catch limits, establishing marine protected areas, and promoting responsible fishing practices.
| 5. What are some ways to control fishing for sustainability? |  |
Ans. Some ways to control fishing for sustainability include implementing quotas, enforcing fishing regulations, and promoting sustainable fishing methods such as selective fishing gear.
Related Searches















