Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
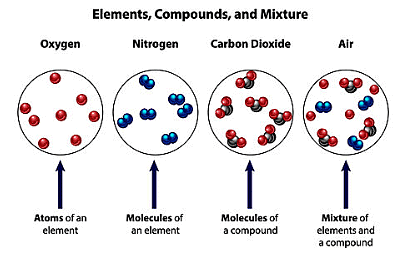
All substances can be classified into one of these three types
Element
- A fundamental substance consisting of atoms, each containing an identical number of protons and indivisible into simpler components. The Periodic Table comprises 118 distinct elements.
- Examples: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Iron
Compound
- A pure substance formed by the chemical bonding of two or more elements.
- Compounds are not separable into their constituent elements through physical methods.
Characteristics
- Compounds are chemically combined entities
- There exists an infinite variety of compounds
- Examples: Water (H2O), Sodium Chloride (NaCl), Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Question for Elements, Compounds and MixturesTry yourself: Which of the following is an example of an element?View Solution
Mixture
- A mixture refers to a blend of two or more substances, which can be elements or compounds, without any chemical bonding between them.
- Mixtures can be easily separated through physical methods like filtration or evaporation.
- For instance, separating sand and water, oil and water, or sulfur powder and iron filings.
The document Elements, Compounds and Mixtures | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Elements, Compounds and Mixtures - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the differences between an element, a compound, and a mixture? |  |
Ans. An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of atom, a compound is a substance made up of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together, and a mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded.
| 2. Can you provide examples of elements, compounds, and mixtures? |  |
Ans. Examples of elements include oxygen, gold, and iron. Examples of compounds include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and sodium chloride (NaCl). Examples of mixtures include air, saltwater, and soil.
| 3. How can you distinguish between an element, a compound, and a mixture? |  |
Ans. Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances, compounds can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical reactions, and mixtures can be separated into their individual components through physical means like filtration or distillation.
| 4. What are some properties that can help identify whether a substance is an element, a compound, or a mixture? |  |
Ans. Properties such as melting point, boiling point, density, and solubility can help determine whether a substance is an element, a compound, or a mixture. Elements have characteristic physical properties, compounds have fixed compositions, and mixtures can vary in composition.
| 5. How are elements, compounds, and mixtures used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Elements like oxygen and carbon are essential for life, compounds like water and salt are used in various industries, and mixtures like air and food are part of our daily routines. Understanding the differences between these substances helps in various scientific and industrial applications.
Related Searches
















