Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Ionic Bonds & Lattice Structure
Ionic Bonds & Lattice Structure | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
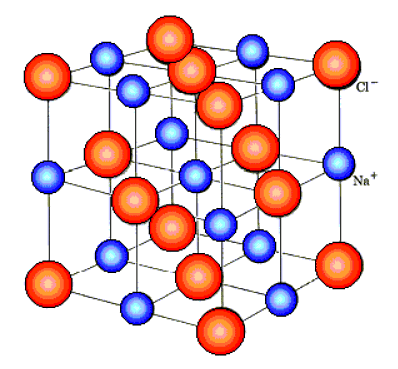
The Lattice Structure of Ionic Compounds
Lattice Structure
- Ionic compounds have a giant lattice structure
- Lattice structure refers to the arrangement of the atoms of a substance in 3D space
- In lattice structures, the atoms are arranged in an ordered and repeating fashion
- The lattices formed by ionic compounds consist of a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions
- Ionic compounds have a giant lattice structure
Question for Ionic Bonds & Lattice StructureTry yourself: What is the arrangement of atoms in a lattice structure of an ionic compound?View Solution
Ionic Bonds between Metallic & Non-Metallic Elements
Ionic compounds
- Ionic compounds are created through the reaction of metal and non-metal atoms, resulting in the formation of compounds with no net charge.
- For instance, Magnesium Oxide (MgO) exemplifies an ionic compound.
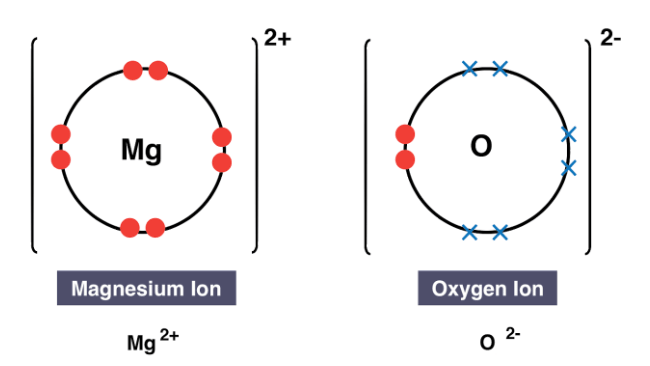
Explanation
- In the context of magnesium oxide, a Group II metal like Magnesium loses two outer electrons to attain a full outer electron shell.
- Consequently, a positively charged ion with a 2+ charge is produced.
- Oxygen, a Group VI non-metal, requires two electrons for a complete outer shell, leading to the transfer of two electrons from magnesium to oxygen.
- The oxygen atom acquires two electrons, resulting in a negatively charged ion with a 2- charge.
- Magnesium oxide remains electrically neutral overall.
Formula of ionic compound: Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Edurev Tip: In dot and cross diagrams, focus solely on depicting the electrons in the outer shell. Ensure to enclose the electron configuration within square brackets and denote the charge for each ion. It's crucial to balance the overall charge to zero, which might necessitate representing multiple positive or negative ions to nullify each other's charges.
Question for Ionic Bonds & Lattice StructureTry yourself: What is the charge on the magnesium ion in the ionic compound magnesium oxide (MgO)?View Solution
The document Ionic Bonds & Lattice Structure | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Ionic Bonds & Lattice Structure - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the relationship between ionic bonds and the lattice structure of compounds? |  |
Ans. Ionic bonds are the electrostatic forces of attraction between positively and negatively charged ions in a compound. These bonds create a strong lattice structure in ionic compounds, where the ions are arranged in a repeating pattern to maximize attraction and minimize repulsion.
| 2. How do metallic and non-metallic elements participate in the formation of ionic bonds? |  |
Ans. Metallic elements tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions, while non-metallic elements tend to gain electrons to form negatively charged ions. The attraction between these oppositely charged ions results in the formation of ionic bonds in compounds.
| 3. How does the lattice structure of ionic compounds contribute to their physical properties? |  |
Ans. The lattice structure of ionic compounds determines their melting and boiling points, as well as their hardness and brittleness. The strong electrostatic forces in the lattice require a significant amount of energy to break, leading to high melting and boiling points.
| 4. What factors affect the stability of the lattice structure in ionic compounds? |  |
Ans. The size and charge of the ions, as well as the arrangement of ions in the lattice, can affect the stability of the structure in ionic compounds. Smaller ions with higher charges tend to form more stable lattices.
| 5. How does the lattice energy of an ionic compound relate to its overall stability? |  |
Ans. The lattice energy of an ionic compound is the energy released when one mole of the compound is formed from its constituent ions in the gas phase. Higher lattice energy indicates a more stable lattice structure, as it reflects the strength of the ionic bonds holding the compound together.
Related Searches