Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Properties of Ionic Compounds
Properties of Ionic Compounds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds are typically solid at room temperature.
- They exhibit high melting and boiling points.
- Ionic compounds demonstrate conductivity in the molten state or when dissolved in a solution.
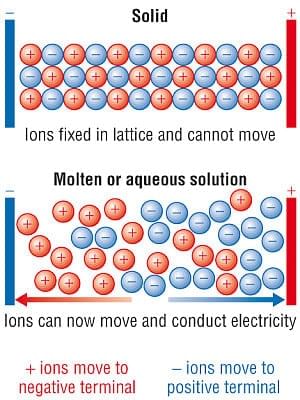
- However, they are poor conductors in their solid state.
Explaining the Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Ionic compounds exhibit high melting and boiling points because of the strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions.
- These electrostatic forces operate in all directions, necessitating a significant amount of energy to overcome them.
- The strength of the electrostatic forces and thus the melting point is directly proportional to the charge on the ions.
- For instance, magnesium oxide (MgO) comprising Mg^2+ and O^2- ions has a higher melting point compared to sodium chloride (NaCl) containing Na^+ and Cl^- ions.
- For electric current to flow, there must be freely moving charged particles like electrons or ions present.
- Ionic compounds act as good conductors of electricity in the molten state or in solution due to the presence of mobile ions that can carry a charge.
- In contrast, they are poor conductors in the solid state since the ions are fixed in positions within the lattice and cannot move.
Question for Properties of Ionic CompoundsTry yourself: Which state of matter do ionic compounds typically exist in at room temperature?View Solution
The document Properties of Ionic Compounds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Properties of Ionic Compounds - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the properties of ionic compounds? |  |
Ans. Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, and have a crystalline structure.
| 2. How do ionic compounds form? |  |
Ans. Ionic compounds form through the transfer of electrons between a metal and a non-metal, resulting in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions that are held together by electrostatic forces.
| 3. Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points? |  |
Ans. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because of the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positively and negatively charged ions, requiring a large amount of energy to break these bonds.
| 4. Do ionic compounds conduct electricity? |  |
Ans. Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in their solid state as the ions are held in a fixed position. However, they can conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, allowing the ions to move freely and carry an electric current.
| 5. How do the properties of ionic compounds differ from covalent compounds? |  |
Ans. Ionic compounds tend to have higher melting and boiling points, conduct electricity in a different manner, and have a crystalline structure compared to covalent compounds, which typically have lower melting points and do not conduct electricity as easily.
Related Searches















