Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Covalent Bonds
Covalent Bonds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
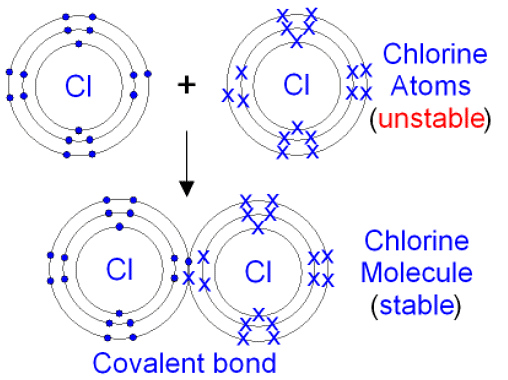
The Formation of Covalent Bonds
Covalent Compounds
- Covalent compounds are formed when pairs of electrons are shared between atoms
- Only non-metal elements participate in covalent bonding
- As in ionic bonding, each atom gains a full outer shell of electrons, giving them a noble gas electronic configuration
- When two or more atoms are covalently bonded together, we describe them as 'molecules'
- Dot-and-cross diagrams can be used to show the electron configurations in simple molecules
- Electrons from one atom are represented by a dot, and the electrons of the other atom are represented by a cross
- The electron shells of each atom in the molecule overlap, and the shared electrons are shown in the area of overlap
- The dot-and-cross diagram of the molecule clearly indicates the origin of each electron
Edurev Tip: When creating dot-and-cross diagrams for covalent compounds, ensure that each atom's electron shell is complete. Remember that the first shell can accommodate a maximum of two electrons.
Question for Covalent BondsTry yourself: Which types of elements participate in covalent bonding?View Solution
Single Covalent Bonds
Many simple molecules exist in which two adjacent atoms share one pair of electrons, forming a single covalent bond.
Common Examples of Simple Molecules

The document Covalent Bonds | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
72 videos|162 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Covalent Bonds - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do atoms form single covalent bonds? |  |
Ans. Atoms form single covalent bonds by sharing a pair of electrons between them. Each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair, creating a stable electron configuration.
| 2. What is the difference between a single covalent bond and other types of chemical bonds? |  |
Ans. In a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. In other types of chemical bonds, such as double or triple covalent bonds, atoms share two or three pairs of electrons, respectively.
| 3. Can single covalent bonds occur between different elements? |  |
Ans. Yes, single covalent bonds can occur between different elements. As long as the atoms involved have a similar electronegativity, they can share electrons to form a stable bond.
| 4. How does the number of valence electrons in an atom affect its ability to form single covalent bonds? |  |
Ans. Atoms with a few valence electrons are more likely to form single covalent bonds in order to achieve a full valence shell. These bonds help atoms reach a stable electron configuration.
| 5. What are some examples of compounds that contain single covalent bonds? |  |
Ans. Examples of compounds that contain single covalent bonds include hydrogen gas (H2), chlorine gas (Cl2), and water (H2O). These compounds form when atoms share electrons to create single covalent bonds.
Related Searches















