Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > The Mole
The Mole | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Mole & the Avogadro Constant
- Chemical quantities are quantified using a unit called the mole.
- The mole, denoted as mol, is the standard unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI).
- A mole of any substance contains an equivalent number of particles, whether they are atoms, molecules, ions, or other entities.
- This quantity is defined as 6.02 x 1023 particles and is known as the Avogadro Constant.
- For instance:
- One mole of sodium (Na) comprises 6.02 x 1023 sodium atoms.
- One mole of hydrogen (H2) consists of 6.02 x 1023 hydrogen molecules.
- One mole of sodium chloride (NaCl) contains 6.02 x 1023 formula units of sodium chloride.
- The mass of one mole of a substance is referred to as the molar mass.
- For elements, the molar mass equals the relative atomic mass expressed in grams.
- For compounds, it is equivalent to the relative formula mass or relative molecular mass, also measured in grams.
The Mole & Volume of Gas
Avogadro's Law explains that under the same temperature and pressure conditions, equal quantities of gases will occupy identical volumes of space.
- Avogadro's Law: This principle asserts that at consistent temperature and pressure, gases will occupy the same volume.
- Room Temperature and Pressure: One mole of any gas occupies 24 dm3 or 24,000 cm3 of space under these conditions.
- Molar Gas Volume at RTP: This term refers to the volume one mole of gas occupies at room temperature and pressure.
- RTP: Stands for "room temperature and pressure," specifically at 20°C and 1 atmosphere (atm).
- Formula Triangle: This triangle elucidates the relationship between moles of gas, volume in dm3, and the molar volume.
- Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in dm3, and the molar volume:
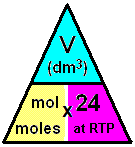
- If the volume is given in cm3 instead of dm3, then divide by 24,000 instead of 24.
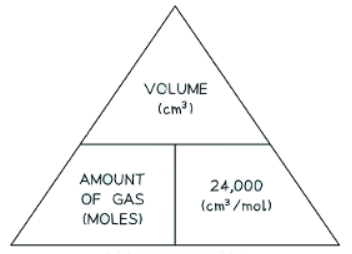
- Formula triangle showing the relationship between moles of gas, volume in cm3, and the molar volume.
Using the Formula Triangle
- The formula can be used to calculate the number of moles of gases from a given volume or vice versa.
- Simply cover the one you want, and the triangle tells you what to do.
Volume = Moles x Molar Volume
Examples of Converting Moles into Volumes Table
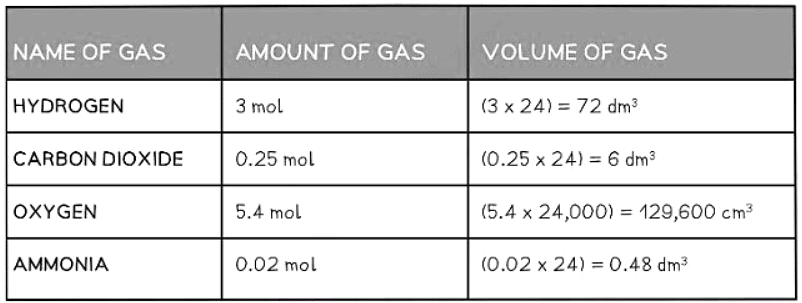
To find the moles of a gas
- Moles = Volume ÷ Molar Volume
Examples of Converting Volumes into Moles Table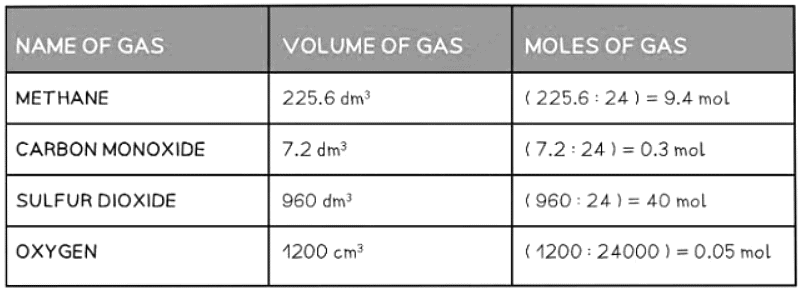
Question for The MoleTry yourself:What is the molar volume of a gas at room temperature and pressure (RTP)?
View Solution
The document The Mole | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on The Mole - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How is the Avogadro Constant related to the mole? |  |
Ans. The Avogadro Constant is a fundamental physical constant that represents the number of constituent particles (usually atoms or molecules) in one mole of a substance. It is defined as 6.02214076 x 10^23 particles per mole.
| 2. What is the significance of the Avogadro Constant in chemistry? |  |
Ans. The Avogadro Constant plays a crucial role in determining the relationship between the mass of a substance and the number of atoms or molecules it contains. It allows chemists to accurately measure and quantify chemical reactions and properties.
| 3. How is the volume of a gas related to the mole? |  |
Ans. The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas present, according to Avogadro's Law. This means that if the number of moles of gas is doubled, the volume of the gas will also double under constant temperature and pressure conditions.
| 4. Can you explain the concept of the mole in chemistry? |  |
Ans. The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express the amount of a substance. One mole of a substance contains Avogadro's number of particles, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23 particles.
| 5. How is the mole used in stoichiometry calculations? |  |
Ans. In stoichiometry, the mole is used to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of particles it contains. By using the molar mass of a substance, one can determine the number of moles present, which then allows for the calculation of other quantities in a chemical reaction.
Related Searches




















