Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE > Emprical and Molecular Formula
Emprical and Molecular Formula | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
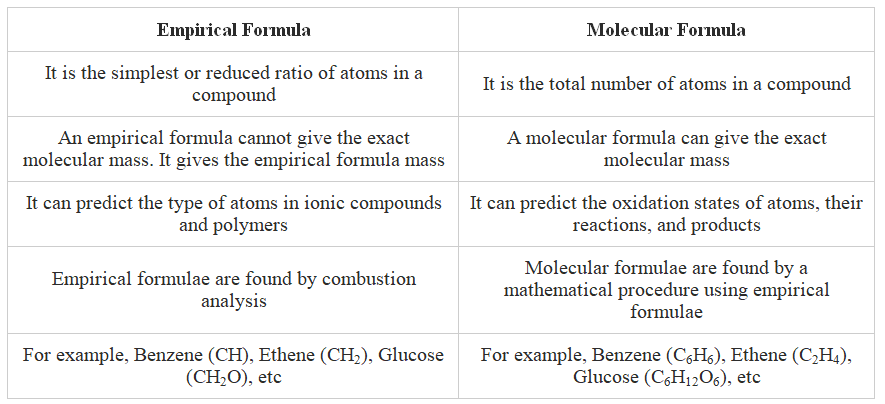
Calculating Empirical Formula
- The empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of atoms for each element in one molecule or formula unit of a compound. For instance, the empirical formula of ethanoic acid is CH2O.
- Organic molecules may exhibit varying empirical and molecular formulae, illustrating different structural compositions.
- Notably, the formula of an ionic compound consistently aligns with an empirical formula.
Calculating Molecular Formula
- The molecular formula provides the precise numbers of atoms of each element found in the compound's formula.
- To calculate the molecular formula, follow these steps:
- Determine the relative formula mass of the empirical formula.
- Utilize the given equation:
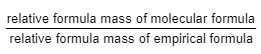
- Multiply the count of each element in the empirical formula by the derived value from step 2 to ascertain the molecular formula.
Table showing the Relationship between Empirical and Molecular Formula
Question for Emprical and Molecular FormulaTry yourself: What is the purpose of calculating the empirical formula?View Solution
Deducing formulae of hydrated salts
- The formula of hydrated salts can be established through experimental procedures.
- Initially, a sample of the hydrated salt is weighed, followed by heating it until all water of crystallization is removed.
- After this process, the anhydrous salt is reweighed, allowing the determination of both the mass of anhydrous salt and the mass of water of crystallization.
- Similar to deducing empirical formulas, these results enable the calculation of the hydrated salt's formula.
The document Emprical and Molecular Formula | Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|147 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Emprical and Molecular Formula - Chemistry for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How do you calculate the empirical formula of a compound? |  |
Ans. To calculate the empirical formula of a compound, you need to determine the mass of each element present in the compound, convert the mass of each element to moles, divide each mole value by the smallest mole value obtained, and then round the resulting ratios to the nearest whole number to obtain the subscripts in the empirical formula.
| 2. How is the molecular formula different from the empirical formula? |  |
Ans. The molecular formula represents the actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule, while the empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
| 3. How can you deduce the formula of a hydrated salt? |  |
Ans. To deduce the formula of a hydrated salt, you need to determine the mass of the anhydrous salt and the mass of water lost upon heating. Then, calculate the moles of each component and divide by the smallest number of moles to obtain the ratio of anhydrous salt to water molecules.
| 4. What is the significance of determining the empirical formula of a compound? |  |
Ans. Determining the empirical formula of a compound is significant as it provides information about the simplest ratio of elements present in the compound, which can help in identifying the compound and understanding its chemical properties.
| 5. Can the molecular formula of a compound be the same as its empirical formula? |  |
Ans. Yes, the molecular formula of a compound can be the same as its empirical formula if the compound is in its simplest form, where the ratio of elements is already in its simplest whole-number form.
Related Searches




















